Fractional Distillation
... fractionating column. It is important to keep the column from flooding. If the column begins to flood, reduce the heat. (The packing should be moistened by condensing vapors but should not contain any flowing liquid.) As soon as the vapor ring begins moving up the column, wrap the column in glass wo ...
... fractionating column. It is important to keep the column from flooding. If the column begins to flood, reduce the heat. (The packing should be moistened by condensing vapors but should not contain any flowing liquid.) As soon as the vapor ring begins moving up the column, wrap the column in glass wo ...
2.26 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... (network or pattern) that is repeated throughout. Three dimensional pattern Large attractive forces between atoms or molecules Molecule at relatively fixed position in solid. ...
... (network or pattern) that is repeated throughout. Three dimensional pattern Large attractive forces between atoms or molecules Molecule at relatively fixed position in solid. ...
INERT GASES -
... dissolved in liquid xenon, corresponded almost exactly in position mith the spectral line recorded for mercurj in solid xenon. Similar results have observed for a number of other simple solvents. This indicates that there is a tendency for "clusters" to form in these liquids, with intermolecular dis ...
... dissolved in liquid xenon, corresponded almost exactly in position mith the spectral line recorded for mercurj in solid xenon. Similar results have observed for a number of other simple solvents. This indicates that there is a tendency for "clusters" to form in these liquids, with intermolecular dis ...
CHEMISTRY 313 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I Additional Problems for
... with its vapor in a closed vessel. (a) How many phases and components are present. (b) What is the variance of the system? Identify the independent variables. III.10. Suppose that the solution referred to in Problem III.9 is not saturated. (a) How many phases and components are present. (b) What is ...
... with its vapor in a closed vessel. (a) How many phases and components are present. (b) What is the variance of the system? Identify the independent variables. III.10. Suppose that the solution referred to in Problem III.9 is not saturated. (a) How many phases and components are present. (b) What is ...
Chemistry 101 2007
... 1.1 The Atomic and molecular Perspectives of Chemistry. Chemistry is the study of the properties and behavior of matter. A property is a characteristic that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter. All the matter in the world is comprised of about 116 elements. ...
... 1.1 The Atomic and molecular Perspectives of Chemistry. Chemistry is the study of the properties and behavior of matter. A property is a characteristic that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter. All the matter in the world is comprised of about 116 elements. ...
Properties of Pure Substance
... either elements or compounds. Ø Elements Substances which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means. Ø Compounds Can be decomposed into two or more elements. ...
... either elements or compounds. Ø Elements Substances which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means. Ø Compounds Can be decomposed into two or more elements. ...
Lecture 19 - University of Windsor
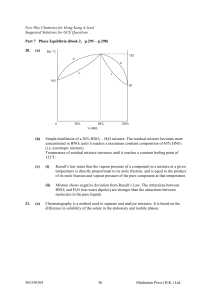
... minima indicate partially miscible phases, and as the temperature rises, single minimum occurs at the upper critical temperature ...
... minima indicate partially miscible phases, and as the temperature rises, single minimum occurs at the upper critical temperature ...
Basic Concepts for Simple and Complex Liquids
... depending on a limited number of thermodynamic parameters. The most common states are either solid or fluid in character, and are characterized by qualitatively different responses to an applied stress. At ambient temperatures, the solid states of matter are generally associated with the mineral wor ...
... depending on a limited number of thermodynamic parameters. The most common states are either solid or fluid in character, and are characterized by qualitatively different responses to an applied stress. At ambient temperatures, the solid states of matter are generally associated with the mineral wor ...
Unit 2 - Classifying Matter
... b. Answer the following guide questions: i. How many phases do you see in each set-up? ii. Which systems are homogeneous? Heterogeneous? iii. How would you define a homogeneous system? a heterogeneous system? Answer: A homogeneous system is a one-phase system where all parts show the same properties ...
... b. Answer the following guide questions: i. How many phases do you see in each set-up? ii. Which systems are homogeneous? Heterogeneous? iii. How would you define a homogeneous system? a heterogeneous system? Answer: A homogeneous system is a one-phase system where all parts show the same properties ...
New Liquid Crystalline Tolanes from (-)
... Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate was alkylated with ndecylbromide by a traditional method. After hydrolysis the resultant acid was esteri cated with 4ethynylphenol [7] furnishing the alkyne 5. Palladium catalysed cross-coupling between 5 and 4a or 4b led to the desired compounds 6a and 6b. Selected data for ...
... Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate was alkylated with ndecylbromide by a traditional method. After hydrolysis the resultant acid was esteri cated with 4ethynylphenol [7] furnishing the alkyne 5. Palladium catalysed cross-coupling between 5 and 4a or 4b led to the desired compounds 6a and 6b. Selected data for ...
Examples of Colligative properties are
... To see this in graphical form, see the phase diagram for pure water, below. Three lines are present indicating the phase transition (read equilibrium) between solid, liquid and gas. Where all three lines meet is the triple point where all three phases are in equilibrium. We see that at an external p ...
... To see this in graphical form, see the phase diagram for pure water, below. Three lines are present indicating the phase transition (read equilibrium) between solid, liquid and gas. Where all three lines meet is the triple point where all three phases are in equilibrium. We see that at an external p ...
Solutions
... dissolved in something else. Insoluble means something cannot be dissolved in something else. ...
... dissolved in something else. Insoluble means something cannot be dissolved in something else. ...
Lectures 1-6 - TCD Chemistry
... For elements, cubic – and hexagonal- close packing; body-centred and facecentred cubic structures: For ionic compounds NaCl and CsCl structures. Octahedral and tetrahedral holes. Examples of network and molecular solids ...
... For elements, cubic – and hexagonal- close packing; body-centred and facecentred cubic structures: For ionic compounds NaCl and CsCl structures. Octahedral and tetrahedral holes. Examples of network and molecular solids ...
Unit 2 Assignments Answers
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
Problems and Solutions
... formula given in the text of the problem should not be applied to the mixture of the saturated vapors in the bubbles formed on the surface separating the liquids. However, the numerical data have been chosen in such a way that even such incorrect solution of the problem gives the correct value of th ...
... formula given in the text of the problem should not be applied to the mixture of the saturated vapors in the bubbles formed on the surface separating the liquids. However, the numerical data have been chosen in such a way that even such incorrect solution of the problem gives the correct value of th ...
Intermolecular forces liquids and Solids
... • Graph of pressure-temperature relationship; describes when 1,2,3 or more phases are present and/or in equilibrium with each other. • Lines indicate equilibrium state two phases. • Triple point- Temp. and press. where all three phases co-exist in equilibrium. • Critical temp.- Temp. where substance ...
... • Graph of pressure-temperature relationship; describes when 1,2,3 or more phases are present and/or in equilibrium with each other. • Lines indicate equilibrium state two phases. • Triple point- Temp. and press. where all three phases co-exist in equilibrium. • Critical temp.- Temp. where substance ...
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
... physical state at room temperature Odor, electrical conductivity, solubility (ability to dissolve in a liquid) and crystalline form ...
... physical state at room temperature Odor, electrical conductivity, solubility (ability to dissolve in a liquid) and crystalline form ...
Phase-separation in ion-containing mixtures in electric fields
... tions. The dissociated ions in the solution are impor- the homogeneous viscosity ηm , and the two surfaces tant because they bring about large field gradients will slide with a certain velocity vm with respect to even in a flat electrode geometry. Field gradients each other. In the presence of elect ...
... tions. The dissociated ions in the solution are impor- the homogeneous viscosity ηm , and the two surfaces tant because they bring about large field gradients will slide with a certain velocity vm with respect to even in a flat electrode geometry. Field gradients each other. In the presence of elect ...
10 Vapor Pressure - Blue Valley Schools
... Turning by clamping the nylon Luer-Lok between extended index finger and thumb will limit the amount of force you can apply. b. Plug the Gas Pressure Sensor into CH1 and the Temperature Probe into CH2 of the computer interface. The Gas Pressure Sensor should be hung such that it is well above the fl ...
... Turning by clamping the nylon Luer-Lok between extended index finger and thumb will limit the amount of force you can apply. b. Plug the Gas Pressure Sensor into CH1 and the Temperature Probe into CH2 of the computer interface. The Gas Pressure Sensor should be hung such that it is well above the fl ...
Molar Mass by Freezing Point Depression
... rule of thumb is that the freezing point should be lower with a 12% (w/w) solution than with a 10% solution. Otherwise the solute is precipitating at a concentration which is probably too low for an accurate molecular weight determination by this method. This test should also be applied to the known ...
... rule of thumb is that the freezing point should be lower with a 12% (w/w) solution than with a 10% solution. Otherwise the solute is precipitating at a concentration which is probably too low for an accurate molecular weight determination by this method. This test should also be applied to the known ...
Gas Chromatography
... amount (moles) of compound eluted. – See Pavia for method of triangulation to calculate peak areas. Do your calculations exactly as shown there. – The mole percent composition of a mixture can be approximated by comparing the relative areas of the peaks in the chromatogram. • This method assumes tha ...
... amount (moles) of compound eluted. – See Pavia for method of triangulation to calculate peak areas. Do your calculations exactly as shown there. – The mole percent composition of a mixture can be approximated by comparing the relative areas of the peaks in the chromatogram. • This method assumes tha ...
Diapositivo 1
... substance present as a dilute vapor must be equal to the chemical potential of the liquid, at equilibrium. Remember also that it is usual, in order to characterize a given solution, to distingue between the solvent (usually the substance in bigger quantity or in the same physical state of solution) ...
... substance present as a dilute vapor must be equal to the chemical potential of the liquid, at equilibrium. Remember also that it is usual, in order to characterize a given solution, to distingue between the solvent (usually the substance in bigger quantity or in the same physical state of solution) ...
a) octane, a chain of 8 C atoms: C8H18 b) benzene, a ring of 6 C
... Water has the strongest intermolecular forces: the others are all non‐polar compounds. The cohesive forces within water droplets (hydrogen bonding) are stronger than the adhesive forces between water and wax, so water doesn’t form a film. ...
... Water has the strongest intermolecular forces: the others are all non‐polar compounds. The cohesive forces within water droplets (hydrogen bonding) are stronger than the adhesive forces between water and wax, so water doesn’t form a film. ...
The Effect of Water and light Alcohols on the Viscosity of Ionic Liquids
... It can therefore be hypothesized that this same behavior will be observed when other ionic liquids are exposed to water. Since water is a simple alcohol it is expected that a decrease in viscosity of ionic liquids exposed to different alcohols will also be observed. It has also been found that diffe ...
... It can therefore be hypothesized that this same behavior will be observed when other ionic liquids are exposed to water. Since water is a simple alcohol it is expected that a decrease in viscosity of ionic liquids exposed to different alcohols will also be observed. It has also been found that diffe ...
Book 2,Part 7 - GEOCITIES.ws
... The liquid mixture is said to be ideal if the intermolecular attraction between the molecules in the mixture is approximately equal to that in pure A and that in pure B. The liquid mixtures which approximate to ideal behaviour can be separated into their pure components by fractional distillation. T ...
... The liquid mixture is said to be ideal if the intermolecular attraction between the molecules in the mixture is approximately equal to that in pure A and that in pure B. The liquid mixtures which approximate to ideal behaviour can be separated into their pure components by fractional distillation. T ...
Liquid

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Water is, by far, the most common liquid on Earth. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena.The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than in a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matter. On the other hand, as liquids and gases share the ability to flow, they are both called fluids. Although liquid water is abundant on Earth, this state of matter is actually the least common in the known universe, because liquids require a relatively narrow temperature/pressure range to exist. Most known matter in the universe is in gaseous form (with traces of detectable solid matter) as interstellar clouds or in plasma form within stars.