phase diagrams and IMF
... 4.) Use the phase diagram for water (above). It is not drawn to scale. The triple point occurs at 0.0060 atm and 0.01oC. Using this knowledge, answer the following questions: a. Label the triple point – use this as a reference point for the following questions (put a dot ...
... 4.) Use the phase diagram for water (above). It is not drawn to scale. The triple point occurs at 0.0060 atm and 0.01oC. Using this knowledge, answer the following questions: a. Label the triple point – use this as a reference point for the following questions (put a dot ...
Chem Unit 3 Vocabulary
... 16 dynamic condition in which 2 opposing changes occur at equal rates in a closed system 17 pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its corresponding liquid at a given temperature 18 process by which particles escape from the surface of a non-boiling liquid & enter the gas state 19 substance ...
... 16 dynamic condition in which 2 opposing changes occur at equal rates in a closed system 17 pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its corresponding liquid at a given temperature 18 process by which particles escape from the surface of a non-boiling liquid & enter the gas state 19 substance ...
Scope and Sequence for Classifying Matter
... -has mass and takes up space -made up of atoms -name something you can see that isn’t made of matter – a shadow ...
... -has mass and takes up space -made up of atoms -name something you can see that isn’t made of matter – a shadow ...
Week 3 - Help-A-Bull
... • Links the “macroscopic” properties of gases and solids to the kinetic energy of atoms/molecules; • Explains the pressure of gases … heat capacity of metals … average speed of electrons in semiconductors etc. • Assumes that atoms/molecules of gases, liquids, solids are in constant motion when above ...
... • Links the “macroscopic” properties of gases and solids to the kinetic energy of atoms/molecules; • Explains the pressure of gases … heat capacity of metals … average speed of electrons in semiconductors etc. • Assumes that atoms/molecules of gases, liquids, solids are in constant motion when above ...
Science Starter Tuesday Week 2
... If we can’t see air, how do we know it exists? List at least 3 examples of EVIDENCE or things you could do that helps us know that air exists. ...
... If we can’t see air, how do we know it exists? List at least 3 examples of EVIDENCE or things you could do that helps us know that air exists. ...
Study Sheet
... Convert one concentration into another Realize when density is needed for these calculations Define unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated. Compare these terms with dilute and concentrated. (AgNO3 970 g/100g & AgCl .00127 g/100g) Solids and gases are called soluble and insoluble. Liquids are cal ...
... Convert one concentration into another Realize when density is needed for these calculations Define unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated. Compare these terms with dilute and concentrated. (AgNO3 970 g/100g & AgCl .00127 g/100g) Solids and gases are called soluble and insoluble. Liquids are cal ...
Unit 3: Properties and States of Matter
... you can observe directly or measure with a tool without changing the composition of the substance. (It does not change chemically) • Examples: boiling point, freezing/melting point, density, solubility, viscosity, electrical conductivity. ...
... you can observe directly or measure with a tool without changing the composition of the substance. (It does not change chemically) • Examples: boiling point, freezing/melting point, density, solubility, viscosity, electrical conductivity. ...
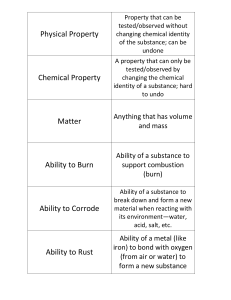
Physical Property
... Ability of a metal (like iron) to bond with oxygen (from air or water) to form a new substance ...
... Ability of a metal (like iron) to bond with oxygen (from air or water) to form a new substance ...
Unit 8-10 Review Answers
... (a) Molecules in a liquid are much more closely packed than molecules in a gas. (b) Molecules in a liquid can vibrate and rotate, but they cannot move about freely as molecules in a gas. (c) Liquids are much more difficult to compress into a smaller volume than are gases. (d) Liquids diffuse more sl ...
... (a) Molecules in a liquid are much more closely packed than molecules in a gas. (b) Molecules in a liquid can vibrate and rotate, but they cannot move about freely as molecules in a gas. (c) Liquids are much more difficult to compress into a smaller volume than are gases. (d) Liquids diffuse more sl ...
11-16 States of Matter
... 3. Evaporation is the change of state from a liquid to gas. Evaporation occurs at the surface of a liquid that is below its boiling point. Boiling is the change of a liquid to a gas throughout the liquid. The temperature a liquid boils is its boiling point. Boiling Point is 212F or 100C. ...
... 3. Evaporation is the change of state from a liquid to gas. Evaporation occurs at the surface of a liquid that is below its boiling point. Boiling is the change of a liquid to a gas throughout the liquid. The temperature a liquid boils is its boiling point. Boiling Point is 212F or 100C. ...
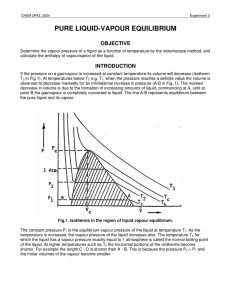
pure liquid-vapour equilibrium - Theoretical and Computational
... where for a one-component system ...
... where for a one-component system ...
EXPERIMENT NO: 2
... 5. Switch off the stirrer and allow the liquid to come to rest. 6. Let liquid slowly allowed to runoff through the immersion tube from the dish on the magnetic stirrer into the dish located adjacent to the stirrer. To achieve this, open the one-way stopcock, which is connected to the immersion tube ...
... 5. Switch off the stirrer and allow the liquid to come to rest. 6. Let liquid slowly allowed to runoff through the immersion tube from the dish on the magnetic stirrer into the dish located adjacent to the stirrer. To achieve this, open the one-way stopcock, which is connected to the immersion tube ...
Physical Properties
... • Molecules at the surface break away and become gas. • Only those with enough Kinetic energy (KE) escape. • Breaking IM forces requires energy. The process of evaporation is endothermic. • Evaporation is a cooling process. • It requires heat. ...
... • Molecules at the surface break away and become gas. • Only those with enough Kinetic energy (KE) escape. • Breaking IM forces requires energy. The process of evaporation is endothermic. • Evaporation is a cooling process. • It requires heat. ...
states of matter - Haiku for Ignatius
... Heat leaves the gas Gas to liquid Condensation as it condenses. Heat goes into the Solid to gas Sublimation solid as it sublimates. ...
... Heat leaves the gas Gas to liquid Condensation as it condenses. Heat goes into the Solid to gas Sublimation solid as it sublimates. ...
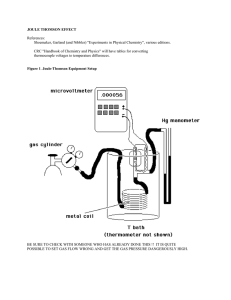
joule thomson effect
... Recommended gases are carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Hook up the carbon dioxide first (it shows the largest effect and is therefore easiest to work with at the star.) Make about 10 measurements between 50 and 200 kPa. For each pressure, set the pressure changes slowly, make sure that the magnetic stir ...
... Recommended gases are carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Hook up the carbon dioxide first (it shows the largest effect and is therefore easiest to work with at the star.) Make about 10 measurements between 50 and 200 kPa. For each pressure, set the pressure changes slowly, make sure that the magnetic stir ...
Energy and Changes of State - SCIENCE
... outside the plasma atoms, are removed to form a gas again. Electrodes to which voltage is applied change the charges of ions ...
... outside the plasma atoms, are removed to form a gas again. Electrodes to which voltage is applied change the charges of ions ...
Chemical Changes in Matter Worksheet
... For each of the following reactions, replace words with formulas and symbols. Be sure to include coefficients and physical states. 1. Two atoms of solid lithium react with two molecules of liquid water to produce two units of aqueous lithium hydroxide and one molecule of hydrogen gas. ...
... For each of the following reactions, replace words with formulas and symbols. Be sure to include coefficients and physical states. 1. Two atoms of solid lithium react with two molecules of liquid water to produce two units of aqueous lithium hydroxide and one molecule of hydrogen gas. ...
Kinetic Molecular Theory
... -Heat energy is transferred through the COLLISION OF MOLECULES. Examples: Metals are good conductors. Glass is an insulator. -Convection -Heat is transferred through convection currents. This occurs when FLUIDS RISE AND FALL THROUGH EXPANSION AND CONTRACTION. Examples: In the earth (continents move, ...
... -Heat energy is transferred through the COLLISION OF MOLECULES. Examples: Metals are good conductors. Glass is an insulator. -Convection -Heat is transferred through convection currents. This occurs when FLUIDS RISE AND FALL THROUGH EXPANSION AND CONTRACTION. Examples: In the earth (continents move, ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Which states or types of matter would be characterized by each of the following statements? a. High individual molecular speeds. b. A melting point spread over a wide temperature range. c. A regular repeating array of structural units. d. Molecules move with respect to one another but are held toget ...
... Which states or types of matter would be characterized by each of the following statements? a. High individual molecular speeds. b. A melting point spread over a wide temperature range. c. A regular repeating array of structural units. d. Molecules move with respect to one another but are held toget ...
Changes TO - Spring Branch ISD
... THIS STUDY GUIDE! Elements and symbols vocabulary below make flashcards for +5 ...
... THIS STUDY GUIDE! Elements and symbols vocabulary below make flashcards for +5 ...
Matter and Energy Notes
... Signs of a Chemical Change change in color or odor formation of a gas (bubbles) formation of a precipitate (solid) change in light or heat ...
... Signs of a Chemical Change change in color or odor formation of a gas (bubbles) formation of a precipitate (solid) change in light or heat ...
States of Matter
... More dense than gases, less than solids (except water) Incompressible Particles are in contact but able to move past each other Liquids (and gases) are fluids – able to flow Viscosity – resistance to flow ...
... More dense than gases, less than solids (except water) Incompressible Particles are in contact but able to move past each other Liquids (and gases) are fluids – able to flow Viscosity – resistance to flow ...
Find your NEW seats Bellringer: Please complete Ms - Parkway C-2
... Vapor Pressure • Definition: is the amount of gas/vapor pressure above a liquid in a closed system. • Over time, the number of particles entering the vapor phase (liquid to gas) increases and some of the particles condense (gas to liquid) and return to the liquid state. • Eventually, the number of ...
... Vapor Pressure • Definition: is the amount of gas/vapor pressure above a liquid in a closed system. • Over time, the number of particles entering the vapor phase (liquid to gas) increases and some of the particles condense (gas to liquid) and return to the liquid state. • Eventually, the number of ...
Key - Sardis Secondary
... 15. What is the relationship between the kinetic energy of molecules and their physical state? ...
... 15. What is the relationship between the kinetic energy of molecules and their physical state? ...
Regents Chemistry
... Be able to describe the effect of polarity, temperature & pressure on the solubility of solids in liquids, liquids in liquids or gas in liquids o remember: pressure only effects solubility of gases in liquids o as temperature increases the solubility of solids tends to increase but the solubility of ...
... Be able to describe the effect of polarity, temperature & pressure on the solubility of solids in liquids, liquids in liquids or gas in liquids o remember: pressure only effects solubility of gases in liquids o as temperature increases the solubility of solids tends to increase but the solubility of ...
Liquid

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Water is, by far, the most common liquid on Earth. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena.The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than in a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matter. On the other hand, as liquids and gases share the ability to flow, they are both called fluids. Although liquid water is abundant on Earth, this state of matter is actually the least common in the known universe, because liquids require a relatively narrow temperature/pressure range to exist. Most known matter in the universe is in gaseous form (with traces of detectable solid matter) as interstellar clouds or in plasma form within stars.