Chemistry 2011-2012
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matt ...
... SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matt ...
AP CHEMISTRY Chang -Chemistry 9
... Types of solutions and factors affecting solubility Methods of expressing concentration (The use of normalities is not tested.) Raoult's law and colligative properties (nonvolatile solutes); osmosis Non-ideal behavior (qualitative aspects) ...
... Types of solutions and factors affecting solubility Methods of expressing concentration (The use of normalities is not tested.) Raoult's law and colligative properties (nonvolatile solutes); osmosis Non-ideal behavior (qualitative aspects) ...
Physical Behavior of Matter Review
... • The boiling point (distillation) is used to separate crude oil (a mixture of hydrocarbons) into fractions based on molecular size. • Unequal distribution of charge is a euphemism for a polar molecule. These molecules have dipoles [partial (+) and (–) parts of the molecule]. • For similar molecule ...
... • The boiling point (distillation) is used to separate crude oil (a mixture of hydrocarbons) into fractions based on molecular size. • Unequal distribution of charge is a euphemism for a polar molecule. These molecules have dipoles [partial (+) and (–) parts of the molecule]. • For similar molecule ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
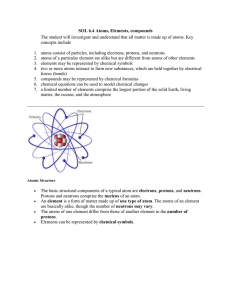
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Chemical Reactions - Mr. Brown`s Science Town
... An Intro. To Chemical Reactions What is a chemical reaction? How do we represent chemical reactions? ...
... An Intro. To Chemical Reactions What is a chemical reaction? How do we represent chemical reactions? ...
Chem vocab quiz definitons
... Gas is the state of matter that is described as having no definite shape, or volume. Solid is the state of matter that is described as having a definite shape and volume. Viscosity is a property of liquids that describe their resistance or ability to flow. Crystal is a solids in which the particles ...
... Gas is the state of matter that is described as having no definite shape, or volume. Solid is the state of matter that is described as having a definite shape and volume. Viscosity is a property of liquids that describe their resistance or ability to flow. Crystal is a solids in which the particles ...
The retrospect of the science and the thermodynamics
... Calculating the work requirement and heat transfer to a series of chemical engineering process, a plants. Prediction or estimation the composition in each phase at equilibria states. Phase equilibrium problems ...
... Calculating the work requirement and heat transfer to a series of chemical engineering process, a plants. Prediction or estimation the composition in each phase at equilibria states. Phase equilibrium problems ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute acid) Add a catalyst – a catalyst is a chemical that speeds up a reaction but does not get used up by the reaction ...
... Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute acid) Add a catalyst – a catalyst is a chemical that speeds up a reaction but does not get used up by the reaction ...
Physical Science Semester 2 Final Exam 2013 –STUDY GUIDE
... 17. Increasing the speed of an object ____ its potential energy. 18. The SI (metric) unit for energy is the ____. 19. You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____. 20. You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation ____. 21. According to the law of conservatio ...
... 17. Increasing the speed of an object ____ its potential energy. 18. The SI (metric) unit for energy is the ____. 19. You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____. 20. You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation ____. 21. According to the law of conservatio ...
Electric potential
... viewed as analogous to height: just as a released object will fall through a difference in heights caused by a gravitational field, so a charge will 'fall' across the voltage caused by an electric field.[43] As relief maps show contour lines marking points of equal height, a set of lines marking poi ...
... viewed as analogous to height: just as a released object will fall through a difference in heights caused by a gravitational field, so a charge will 'fall' across the voltage caused by an electric field.[43] As relief maps show contour lines marking points of equal height, a set of lines marking poi ...
potential difference
... it moves a the same amount the same but distance of energy in aΔX the energy shorter The distance. steepness gained is less This means the of the slope so the field has field to be must represents the stronger be less strong field strength ...
... it moves a the same amount the same but distance of energy in aΔX the energy shorter The distance. steepness gained is less This means the of the slope so the field has field to be must represents the stronger be less strong field strength ...