HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Define and predict products for combustion reactions Product testing - Know the tests for some common products such as oxygen, water, hydrogen and carbon dioxide: burning splint for oxygen, hydrogen or carbon dioxide, and lime water for carbon dioxide. Investigate mass of reactants and products in a ...
... Define and predict products for combustion reactions Product testing - Know the tests for some common products such as oxygen, water, hydrogen and carbon dioxide: burning splint for oxygen, hydrogen or carbon dioxide, and lime water for carbon dioxide. Investigate mass of reactants and products in a ...
Physics 7701: Problem Set #9
... density λ is located perpendicular to the x–y plane in the first quadrant at (x0 , y0 ). The intersecting planes x = 0, y ≥ 0 and y = 0, x ≥ 0 are conducting boundary surfaces held at zero potential. Consider the potential, fields, and surface charges in the first quadrant. (a) The well-known potent ...
... density λ is located perpendicular to the x–y plane in the first quadrant at (x0 , y0 ). The intersecting planes x = 0, y ≥ 0 and y = 0, x ≥ 0 are conducting boundary surfaces held at zero potential. Consider the potential, fields, and surface charges in the first quadrant. (a) The well-known potent ...
7.2 Writing Chemical Equations
... In chemical reactions, one or more substances, the reactants, change into one or more new substances, the products. When writing chemical reactions, the reactants are separated from the products with an arrow. ...
... In chemical reactions, one or more substances, the reactants, change into one or more new substances, the products. When writing chemical reactions, the reactants are separated from the products with an arrow. ...
Chemical Reactions and The Mole Review
... • As you watch the video, jot down your thoughts on the focus question under your catalyst. Then, be ready to share. ...
... • As you watch the video, jot down your thoughts on the focus question under your catalyst. Then, be ready to share. ...
ChemThink Particulate Nature of Matter
... 15. Describe the typical movement of molecules in a gas? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 16. How do you indicate in a chemical formula that a substance is a gas? ___________________________ ...
... 15. Describe the typical movement of molecules in a gas? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 16. How do you indicate in a chemical formula that a substance is a gas? ___________________________ ...
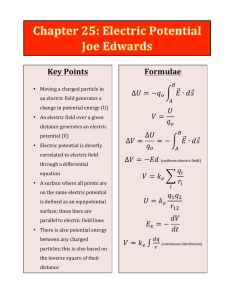
Electric Potential Energy
... (a) The change in electric potential energy of the electron. (b) The speed of the electron (m = 9.1 × 10-31 kg) as a result of this acceleration. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... (a) The change in electric potential energy of the electron. (b) The speed of the electron (m = 9.1 × 10-31 kg) as a result of this acceleration. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 1 Sect 1.3: Properties of matter Vocabularies: Physical
... A large sample of carbon would take up a bigger area than a small sample of carbon, so volume is an extensive property. Some of the most common types of extensive properties are; length, volume, mass and weight. Intensive properties: properties, which do not depend on the size of the sample involved ...
... A large sample of carbon would take up a bigger area than a small sample of carbon, so volume is an extensive property. Some of the most common types of extensive properties are; length, volume, mass and weight. Intensive properties: properties, which do not depend on the size of the sample involved ...
Remember Question words
... Law of Conservation of Mass = no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. However, the state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction. For example, substances in a chemical reaction can change from solid states to gaseous states but the total mass will not change. Or mor ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass = no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. However, the state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction. For example, substances in a chemical reaction can change from solid states to gaseous states but the total mass will not change. Or mor ...
Section 15
... and the phase of each substance is sometimes represented by an s, g, or l for solid, gas or liquid; materials that are dissolved in water are designated as aq for aqueous. Coefficients are also placed in front of each substance to indicate relative quantity used in the reaction (no coefficient means ...
... and the phase of each substance is sometimes represented by an s, g, or l for solid, gas or liquid; materials that are dissolved in water are designated as aq for aqueous. Coefficients are also placed in front of each substance to indicate relative quantity used in the reaction (no coefficient means ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Element – A substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means. Compound – A substance made of 2 or elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. Chemical bond – the force that holds 2 atoms together. Mixture – Two or more substances that are mixed together ...
... Element – A substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means. Compound – A substance made of 2 or elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. Chemical bond – the force that holds 2 atoms together. Mixture – Two or more substances that are mixed together ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, SYMBOLS, FORULAS 7
... kind of atom on the right side of the arrow for the equation to be balanced. ...
... kind of atom on the right side of the arrow for the equation to be balanced. ...
Heriot-Watt University
... The Second Law: To appreciate that The Second Law of Thermodynamics dictates the course of all spontaneous physical and chemical changes The Third Law: To appreciate that the Third Law of Thermodynamics allows the determination of absolute entropies The Free Energy: To appreciate that the Free ...
... The Second Law: To appreciate that The Second Law of Thermodynamics dictates the course of all spontaneous physical and chemical changes The Third Law: To appreciate that the Third Law of Thermodynamics allows the determination of absolute entropies The Free Energy: To appreciate that the Free ...