Matter - Wsfcs
... Physical Properties Physical properties can be described as being intensive or extensive. ...
... Physical Properties Physical properties can be described as being intensive or extensive. ...
Chemical Principles – by Steven Zumdahl (5 ) Chapter 1
... States of Matter: We classify matter into several states because it helps us classify information in a systematic way. Solid State: Solids are rigid. They have definite shapes. The dimensions of solids change slightly with temperature and pressure. Liquid State: Liquids flow and assume the shape of ...
... States of Matter: We classify matter into several states because it helps us classify information in a systematic way. Solid State: Solids are rigid. They have definite shapes. The dimensions of solids change slightly with temperature and pressure. Liquid State: Liquids flow and assume the shape of ...
Chemistry Review: Unit2 - Menno Simons Christian School
... new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical change and how you know. Observation Sugar dissolves in water. ...
... new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical change and how you know. Observation Sugar dissolves in water. ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound ...
... elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Product – what is made during the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
... • Product – what is made during the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
Physics 12 Electric Potential Notes.
... First let’s examine electric potential energy. If a charged object is in an electric field it has electric potential energy - that is it has the potential to move in that field. Note that the potential energy it has could be used to… A non-uniform field, such as that provided by a point, is one whic ...
... First let’s examine electric potential energy. If a charged object is in an electric field it has electric potential energy - that is it has the potential to move in that field. Note that the potential energy it has could be used to… A non-uniform field, such as that provided by a point, is one whic ...
CLASS NOTES- Balancing Chemical Equations.pptx
... • The Law of Conservation of Mass as it relates to chemical changes of substances • The parts of a chemical reaction Learners will be able to… • Write and balance chemical equations • Perform stoichiometry calculations ...
... • The Law of Conservation of Mass as it relates to chemical changes of substances • The parts of a chemical reaction Learners will be able to… • Write and balance chemical equations • Perform stoichiometry calculations ...
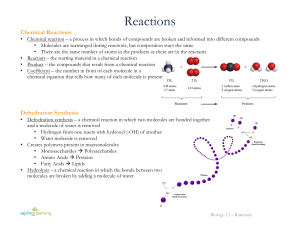
Reactions
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
Key Points on “electric potential”
... result of the situation that is at hand. For example, a book on top of the side cabinet has higher potential energy than a book laying on the ground due to the “situation or position” it is in. ...
... result of the situation that is at hand. For example, a book on top of the side cabinet has higher potential energy than a book laying on the ground due to the “situation or position” it is in. ...
Chemical Reactions
... substance by using symbols to represent solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g) and aqueous (aq) ...
... substance by using symbols to represent solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g) and aqueous (aq) ...
Matter and Energy
... -atoms found on the reactants side will also be found on the products side. They will be broken apart and rearranged to create new substances. -creates a “Balanced” equation CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O ...
... -atoms found on the reactants side will also be found on the products side. They will be broken apart and rearranged to create new substances. -creates a “Balanced” equation CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O ...
Predictions of binary mixtures of noble gases and n
... * Presenting author a Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, College of Engineering, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI 48201, USA b Department of Computer Science, College of Engineering, Wayne State University DESCRIPTION: Transferrable force fields, based on the n-6 Lennard Jo ...
... * Presenting author a Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, College of Engineering, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI 48201, USA b Department of Computer Science, College of Engineering, Wayne State University DESCRIPTION: Transferrable force fields, based on the n-6 Lennard Jo ...