Matter Key
... 1.) Physical properties can be __used to identify a substance____ and __be used to separate it from other substances_____. ...
... 1.) Physical properties can be __used to identify a substance____ and __be used to separate it from other substances_____. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Table of elements arranged by their atomic number – the number of protons. An elements position on the table will show many of its general properties Periods- The table is arranged in horizontal rows called periods. The period tells you how many electron energy levels the atom has. Groups- Verti ...
... Table of elements arranged by their atomic number – the number of protons. An elements position on the table will show many of its general properties Periods- The table is arranged in horizontal rows called periods. The period tells you how many electron energy levels the atom has. Groups- Verti ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Table of elements arranged by their atomic number – the number of protons. An elements position on the table will show many of its general properties Periods- The table is arranged in horizontal rows called periods. The period tells you how many electron energy levels the atom has. Groups- Verti ...
... Table of elements arranged by their atomic number – the number of protons. An elements position on the table will show many of its general properties Periods- The table is arranged in horizontal rows called periods. The period tells you how many electron energy levels the atom has. Groups- Verti ...
SOL Essential Knowledge
... 3. Forces of attraction between molecules determine the physical changes of state. 4. Pressure, temperature and volume changes can cause a change in physical state. 5. Solid, liquid and gas phases of a substance have different energy content. B. Recognize the following properties of gases: 1. Gases ...
... 3. Forces of attraction between molecules determine the physical changes of state. 4. Pressure, temperature and volume changes can cause a change in physical state. 5. Solid, liquid and gas phases of a substance have different energy content. B. Recognize the following properties of gases: 1. Gases ...
Chemistry Standard Outline
... affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a catalyst. SC5a. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical proc ...
... affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a catalyst. SC5a. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical proc ...
Chemical Reactions are…
... oxygen (O2) react to make a single molecule, Na2O The reactant in this equation are Na + O2 The product in this equation is Na2O ...
... oxygen (O2) react to make a single molecule, Na2O The reactant in this equation are Na + O2 The product in this equation is Na2O ...
1.2 PowerPoint
... Distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Contrast chemical and physical changes. Apply the law of conservation of matter to chemical changes. ...
... Distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Contrast chemical and physical changes. Apply the law of conservation of matter to chemical changes. ...
Word - The University of British Columbia
... Chemical and Phase Equilibria, and Physical Chemistry ...
... Chemical and Phase Equilibria, and Physical Chemistry ...
Document
... 18. What type of reaction is shown in the following chemical equation: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2? 19. Each substance to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation is a ________________. 20. An atom that has a +2 oxidation number has ______________________ 21. The __________ _____________ tells you how many ...
... 18. What type of reaction is shown in the following chemical equation: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2? 19. Each substance to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation is a ________________. 20. An atom that has a +2 oxidation number has ______________________ 21. The __________ _____________ tells you how many ...
Whole version
... characterize the material surroundings in which the substance is situated: state of aggregation, solvent A, temperature T, pressure p, mole fractions xB, xC … . − The term reaction also includes, in a wider sense, phase transition and exchange of substances between adjacent regions. − We say that a ...
... characterize the material surroundings in which the substance is situated: state of aggregation, solvent A, temperature T, pressure p, mole fractions xB, xC … . − The term reaction also includes, in a wider sense, phase transition and exchange of substances between adjacent regions. − We say that a ...
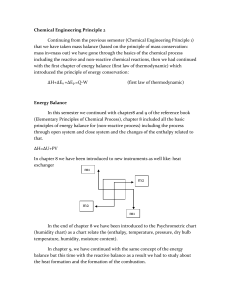
Chemical Engineering Principle 2 Continuing from the previous
... In the second part of this course we moved to a new topic which is new and different topic than the previous one even though it is talking about heat which is one form of energy. The second part of the chapter was divided into three chapters: ...
... In the second part of this course we moved to a new topic which is new and different topic than the previous one even though it is talking about heat which is one form of energy. The second part of the chapter was divided into three chapters: ...