Chemistry 341
... cycle, Calculations of entropy changes, third law of thermodynamics, Thermodynamic relationships, Gibbs-Helmholtz equation, Rfrigeration and heat pumps. 5. Chapter 4: Chemical equilibrium, Chemical equilibrium involving ideal gases, Chemical equilibrium in solution, Coupling of reactions, Temperatur ...
... cycle, Calculations of entropy changes, third law of thermodynamics, Thermodynamic relationships, Gibbs-Helmholtz equation, Rfrigeration and heat pumps. 5. Chapter 4: Chemical equilibrium, Chemical equilibrium involving ideal gases, Chemical equilibrium in solution, Coupling of reactions, Temperatur ...
CH17 notes
... Consider a proton in an electric field. The above statements correspond to: ~ ∆V decreasing, K increasing. 1. Proton moving in direction of E: ~ ∆V increasing, K decreasing. 2. Proton moving opposite E: ~ ∆V = ∆K = 0. 3. Proton moving ⊥ E: ...
... Consider a proton in an electric field. The above statements correspond to: ~ ∆V decreasing, K increasing. 1. Proton moving in direction of E: ~ ∆V increasing, K decreasing. 2. Proton moving opposite E: ~ ∆V = ∆K = 0. 3. Proton moving ⊥ E: ...
PPt3 - WordPress.com
... produce a potential which can be maintained and accurately determined, while allowing small currents to be drawn into the system without changing the voltage. ...
... produce a potential which can be maintained and accurately determined, while allowing small currents to be drawn into the system without changing the voltage. ...
Contact and Non-Contact Forces Study Guide
... Know how to find x when given an equilibrium position and a stretched position. 5. Be able to calculate potential energy given a variety of data for gravitational potential energy. GPE = m g h Understand how changing the mass and height affect GPE. 6. Be able to look at a picture and identify high a ...
... Know how to find x when given an equilibrium position and a stretched position. 5. Be able to calculate potential energy given a variety of data for gravitational potential energy. GPE = m g h Understand how changing the mass and height affect GPE. 6. Be able to look at a picture and identify high a ...
Thermochemistry is the study of the change in thermal energy
... energy. Some examples would be thermal (heat) energy, light energy, mechanical energy, and electrical energy (dry cell batteries). The energy involved in chemical reactions is from breaking and making chemical bonds. Internal energy is the sum of all of the energy contained in a chemical system. The ...
... energy. Some examples would be thermal (heat) energy, light energy, mechanical energy, and electrical energy (dry cell batteries). The energy involved in chemical reactions is from breaking and making chemical bonds. Internal energy is the sum of all of the energy contained in a chemical system. The ...
29.2 Chemical Bonds
... The concept of temperature and changes of phase between solid, liquid, and gas are traditionally considered part of chemistry, as are the gas laws. These kinds of changes in matter are called physical changes, because matter changes physical form but one substance does not change into a complete ...
... The concept of temperature and changes of phase between solid, liquid, and gas are traditionally considered part of chemistry, as are the gas laws. These kinds of changes in matter are called physical changes, because matter changes physical form but one substance does not change into a complete ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 x = 12.3 g Cd 1.3 2.24845 ×12 u
... Silver and gold are in the same periodic table group as copper, so they might well be expected to occur together in nature, because of their similar properties and tendencies to form similar compounds. ...
... Silver and gold are in the same periodic table group as copper, so they might well be expected to occur together in nature, because of their similar properties and tendencies to form similar compounds. ...
Cosmetology Learning Module 12
... A change in the form or physical properties of a substance without the formation of a new substance No chemical reaction involved No new chemicals are formed Solid ice changes into water Temporary hair color changes the appearance of hair by physically adding color to the surface of the ha ...
... A change in the form or physical properties of a substance without the formation of a new substance No chemical reaction involved No new chemicals are formed Solid ice changes into water Temporary hair color changes the appearance of hair by physically adding color to the surface of the ha ...
Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home Work
... Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home ...
... Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home ...
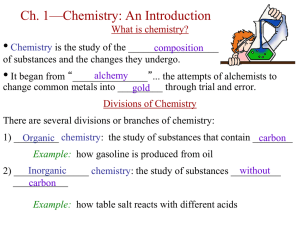
chemical reaction?
... • A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed very much. • Catalysts usually ____________ reaction rate by bringing together reactants • _____________ are an example of a catalyst found in living things ...
... • A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed very much. • Catalysts usually ____________ reaction rate by bringing together reactants • _____________ are an example of a catalyst found in living things ...
II. Classification of Matter
... Law vs. theory Scientific (natural) _____________: a general statement based on the observed behavior of matter to which no exceptions are known. __________________: a broad generalization that explains a body of facts or phenomena. Quantitative vs. qualitative data Quantitative: numerical (________ ...
... Law vs. theory Scientific (natural) _____________: a general statement based on the observed behavior of matter to which no exceptions are known. __________________: a broad generalization that explains a body of facts or phenomena. Quantitative vs. qualitative data Quantitative: numerical (________ ...
Quantum Mechanics_chemical potential
... three states of equilibrium, i.e. "necessarily stable", "neutral", and "unstable", and whether or not changes will ensue. In 1876, Gibbs built on this framework by introducing the concept of chemical potential so to take into account chemical reactions and states of bodies that are chemically differ ...
... three states of equilibrium, i.e. "necessarily stable", "neutral", and "unstable", and whether or not changes will ensue. In 1876, Gibbs built on this framework by introducing the concept of chemical potential so to take into account chemical reactions and states of bodies that are chemically differ ...