Chapter 2 Introduction to Chemistry
... chemical reactions and to form new substances (i.e. flammability, rusting) – can only be observed during the change Chemical changes can’t be observed without altering the ...
... chemical reactions and to form new substances (i.e. flammability, rusting) – can only be observed during the change Chemical changes can’t be observed without altering the ...
File
... Carried out in a Hoffman’s apparatus (shown to the right), it splits water compounds into oxygen molecules and hydrogen molecules Water Oxygen + Hydrogen H2O O2 +H2 The electrolysis reaction proves that compounds are made of more than one kind of element. Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1. All matte ...
... Carried out in a Hoffman’s apparatus (shown to the right), it splits water compounds into oxygen molecules and hydrogen molecules Water Oxygen + Hydrogen H2O O2 +H2 The electrolysis reaction proves that compounds are made of more than one kind of element. Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1. All matte ...
Notes matter energy
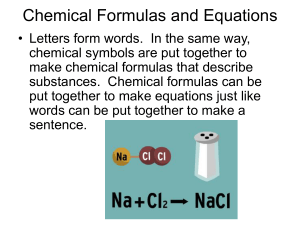
... indicate the number of atoms in the formula (when only one atom of a given type is present, no ‘1’ is written). The chemical formula can be written from a description of the composition. For example, the molecule niacin consists of 6 carbon atoms, 6 hydrogen atoms, 2 nitrogen atoms, and 1 oxygen ato ...
... indicate the number of atoms in the formula (when only one atom of a given type is present, no ‘1’ is written). The chemical formula can be written from a description of the composition. For example, the molecule niacin consists of 6 carbon atoms, 6 hydrogen atoms, 2 nitrogen atoms, and 1 oxygen ato ...
Chemical Formulas and Equations
... The Importance of Accuracy • CO2 is a colorless, odorless gas you exhale. • CO is a colorless, odorless, and poisonous gas. • Co is an element. ...
... The Importance of Accuracy • CO2 is a colorless, odorless gas you exhale. • CO is a colorless, odorless, and poisonous gas. • Co is an element. ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
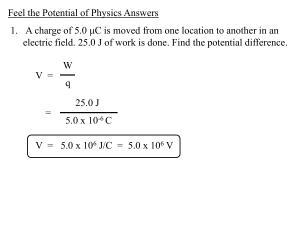
Feel the Potential of Physics Answers
... 3. If an electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 100 V, what is the final speed of the electron? Energy = KE = 1.6021 x 10-17 J KE = 1/2 mv2 ...
... 3. If an electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 100 V, what is the final speed of the electron? Energy = KE = 1.6021 x 10-17 J KE = 1/2 mv2 ...
Summary of Class 4 8.02 Tuesday 2/8/05 / Wednesday 2/9/05 Topics
... of electric potential. Just as electric fields are analogous to gravitational fields, electric potential is analogous to gravitational potential. We introduce from the point of view of calculating the electric potential given the electric field. At the end of this class we consider the opposite proc ...
... of electric potential. Just as electric fields are analogous to gravitational fields, electric potential is analogous to gravitational potential. We introduce from the point of view of calculating the electric potential given the electric field. At the end of this class we consider the opposite proc ...
2.4 Chemical Reactions
... 2. Describe how the interaction between an enzyme and its substrate changes a chemical reaction. 4. Suppose that the amino acids that make up an enzyme’s active site are changed. How might this change affect the enzyme? ...
... 2. Describe how the interaction between an enzyme and its substrate changes a chemical reaction. 4. Suppose that the amino acids that make up an enzyme’s active site are changed. How might this change affect the enzyme? ...
PowerPoint for Cornell Notes
... or a bee? Bee stings are acidic in nature, which is why a household remedy for a bee sting is baking soda or sodium bicarbonate, which is a basic substance. A wasp sting, on the other hand, is mildly basic, so a household remedy for this will be vinegar, also known as acetic acid. These simple treat ...
... or a bee? Bee stings are acidic in nature, which is why a household remedy for a bee sting is baking soda or sodium bicarbonate, which is a basic substance. A wasp sting, on the other hand, is mildly basic, so a household remedy for this will be vinegar, also known as acetic acid. These simple treat ...
Electric Potential Energy
... An even more general description looks at ∆PE per kilogram. That way the object’s mass is irrelevant. This would be like considering changes in “gh” not “mgh.” This isn’t useful for gravitational fields, but it’s very for electric fields. ...
... An even more general description looks at ∆PE per kilogram. That way the object’s mass is irrelevant. This would be like considering changes in “gh” not “mgh.” This isn’t useful for gravitational fields, but it’s very for electric fields. ...
chemical reaction
... water; however not all products formed from aqueous reactions are dissolved in water -In order for a product to be aqueous it must be soluble in water; this is determined using ...
... water; however not all products formed from aqueous reactions are dissolved in water -In order for a product to be aqueous it must be soluble in water; this is determined using ...