Single-Photon Synchronous Detection
... fact that the phase signal is analog and thus it needs amplification and A/D conversion on a pixel-by-pixel basis. As a result, several sources of noise and non-idealities are present and may be severe. Moreover, in this approach background illumination can in principle be eliminated by virtue of th ...
... fact that the phase signal is analog and thus it needs amplification and A/D conversion on a pixel-by-pixel basis. As a result, several sources of noise and non-idealities are present and may be severe. Moreover, in this approach background illumination can in principle be eliminated by virtue of th ...
LxxA, Overview of Microscopy methods, part a
... the resolving power of 100 and 300 keV electron microscopes will be about 0.0025 nm and 0.0017 nm respectively. These values are not realistic! ...
... the resolving power of 100 and 300 keV electron microscopes will be about 0.0025 nm and 0.0017 nm respectively. These values are not realistic! ...
(等倾干涉) — equal thickness interference.
... The interference only occurs for rays reflected by the top and button surfaces of the air film. ...
... The interference only occurs for rays reflected by the top and button surfaces of the air film. ...
Focusing of light through a stratified medium: a practical
... glass to specimen) separating the microscope objective from the specimen. Even if one considers randomly or circularly polarized light, which would have for effect of averaging the various polarization contributions, these extremal rays are considered to be transmitted without reflections, namely wi ...
... glass to specimen) separating the microscope objective from the specimen. Even if one considers randomly or circularly polarized light, which would have for effect of averaging the various polarization contributions, these extremal rays are considered to be transmitted without reflections, namely wi ...
McDonald-etal-OE-2015-3D-mapping-of-intensity
... optical elements are known. In this work we devise a scheme that allows interrogation of the focus while illuminating a mirror with a collimated laser beam, Fig. 2. This arrangement means that the intensity distribution that would be formed in an optical tweezing experiment [22], for example, can be ...
... optical elements are known. In this work we devise a scheme that allows interrogation of the focus while illuminating a mirror with a collimated laser beam, Fig. 2. This arrangement means that the intensity distribution that would be formed in an optical tweezing experiment [22], for example, can be ...
FTIR Instrumentation
... field. But with commercial development of the optical null dispersive spectrophotometer, later that decade, chemical infrared spectroscopy came into widespread use. Dispersive instruments proved the tremendous value of infrared analysis, and soon became the mainstay of organic characterization labor ...
... field. But with commercial development of the optical null dispersive spectrophotometer, later that decade, chemical infrared spectroscopy came into widespread use. Dispersive instruments proved the tremendous value of infrared analysis, and soon became the mainstay of organic characterization labor ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
Optics - Mr. Gallagher's Physics
... Optical Devices • Lenses: bend light in a specific way. ▫ Converging lens (convex): bends light to a point. ▫ Diverging lens (concave): Spreads light out. ...
... Optical Devices • Lenses: bend light in a specific way. ▫ Converging lens (convex): bends light to a point. ▫ Diverging lens (concave): Spreads light out. ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
Generalizing the Confocal Microscope via Heterodyne Interferometry and Digital Filtering
... The confocal microscope is finding wide use in semiconductor metrology, biology, and other fields, because of its excellent resolution, depth discrimination, and lack of edge artifacts (ringing). The classical confocal microscope measures only intensity, and like an ordinary bright-field microscope, ...
... The confocal microscope is finding wide use in semiconductor metrology, biology, and other fields, because of its excellent resolution, depth discrimination, and lack of edge artifacts (ringing). The classical confocal microscope measures only intensity, and like an ordinary bright-field microscope, ...
MPE Tutorial Multiphoton Excitation Microscopy 5100 Patrick Henry Drive
... When working with biological samples, serious problems can occur with normal confocal fluorescence microscopy. One problem is photobleaching of the fluorescent label (fluorophore). In many cases, researchers are interested in observing living specimens, often at several stages during development. Be ...
... When working with biological samples, serious problems can occur with normal confocal fluorescence microscopy. One problem is photobleaching of the fluorescent label (fluorophore). In many cases, researchers are interested in observing living specimens, often at several stages during development. Be ...
High-resolution retinal microscopy using MEMS
... retinal disease, and can play a critical role for diagnosing systemic diseases such as diabetes and eye-specific diseases such as macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, the leading causes of blindness. It is demonstrated in this work that the µDM can enable diffraction-limited imaging of mic ...
... retinal disease, and can play a critical role for diagnosing systemic diseases such as diabetes and eye-specific diseases such as macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, the leading causes of blindness. It is demonstrated in this work that the µDM can enable diffraction-limited imaging of mic ...
ECEN 4616/5616 Optoelectronic Design
... For detecting planets around other stars, the angular requirements result in extremely long focal lengths (100’s of km), so another approach is to use a phase mask at the prime focal plane in order to null out the star image: ...
... For detecting planets around other stars, the angular requirements result in extremely long focal lengths (100’s of km), so another approach is to use a phase mask at the prime focal plane in order to null out the star image: ...
Ultrahigh-resolution full-field optical coherence microscopy using
... Full-field optical coherence microscopy (FFOCM), also termed full-field optical coherence tomography (FFOCT), is an interferometric technique that utilizes spatially incoherent illumination and array detection to provide high-resolution transverse images of reflected light within biological specimen ...
... Full-field optical coherence microscopy (FFOCM), also termed full-field optical coherence tomography (FFOCT), is an interferometric technique that utilizes spatially incoherent illumination and array detection to provide high-resolution transverse images of reflected light within biological specimen ...
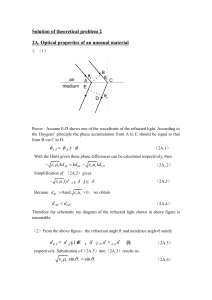
Solution of theoretical problem 2
... Further taking the symmetry about the y axis into consideration we obtain that if the ...
... Further taking the symmetry about the y axis into consideration we obtain that if the ...
Nanophotonics Lecture 1 - Groups
... in optical cross-connect OXC module, and multiplexed back into another fiber with new headers in WDM multiplexer. Data packets are buffered in optical delay line if necessary. Channels are monitored with ...
... in optical cross-connect OXC module, and multiplexed back into another fiber with new headers in WDM multiplexer. Data packets are buffered in optical delay line if necessary. Channels are monitored with ...
Opt001
... The key to its operation is a glass prism, which disperses light into a spectrum. Experiment 1 develops your understanding of how the prism spectrometer works, as well as the skills necessary to using it - adjustment of the components which make up the spectrometer and reading its vernier scales. Yo ...
... The key to its operation is a glass prism, which disperses light into a spectrum. Experiment 1 develops your understanding of how the prism spectrometer works, as well as the skills necessary to using it - adjustment of the components which make up the spectrometer and reading its vernier scales. Yo ...
Scanning Electron Microscope - i-Explore International Research
... features of both the pinhole and the immersion lenses. Its magnetic field extends outside the lens and reaches the specimen. This design puts restrictions for imaging of magnetic specimens, which could be drawn inside lens with negative consequences for the samples and the SEM. The advantage is that ...
... features of both the pinhole and the immersion lenses. Its magnetic field extends outside the lens and reaches the specimen. This design puts restrictions for imaging of magnetic specimens, which could be drawn inside lens with negative consequences for the samples and the SEM. The advantage is that ...
PhotoAcoustic Schlieren Elastography II
... waves in a silicone phantom. A for 50 ns durations. The abstract figure shows the layout of the PhASE strobed-source, transmissive system. The light source of the schlieren system is a high power, 2000+ schlieren imaging system is lumen LED with a 10 ns rise time. A 100 ns output signal from the use ...
... waves in a silicone phantom. A for 50 ns durations. The abstract figure shows the layout of the PhASE strobed-source, transmissive system. The light source of the schlieren system is a high power, 2000+ schlieren imaging system is lumen LED with a 10 ns rise time. A 100 ns output signal from the use ...
The Intermediate Optical System of Laser
... given in the Melles Griot catalogue (Chapter 1, 1999); the performance of real lenses is found in Melles Griot, Chapters 6 and 11, this volume). One goal of the optical system is to generate a light spot in the image plane that is smaller than actually required. This is equivalent to overfilling the ...
... given in the Melles Griot catalogue (Chapter 1, 1999); the performance of real lenses is found in Melles Griot, Chapters 6 and 11, this volume). One goal of the optical system is to generate a light spot in the image plane that is smaller than actually required. This is equivalent to overfilling the ...
9.Wave Properties
... Optical fibres are thin strands of solid glass, about the size of a human hair. They are widely used in communication, medicine, lighting and as sensors. The first transatlantic telephone cable to use optical fibres went into operation in 1988. Optical fibres can transmit light signals at high speed ...
... Optical fibres are thin strands of solid glass, about the size of a human hair. They are widely used in communication, medicine, lighting and as sensors. The first transatlantic telephone cable to use optical fibres went into operation in 1988. Optical fibres can transmit light signals at high speed ...
WINDOWS During the Apollo (manned lunar exploration) space
... probably will be air (n1 = 1.0). The other probably will be some other glass (n2 ~ 1.5). Using Equation 3, you can calculate a reflection of ~ 4%. This calculation is for one side of the window. When the rays emerge from the other side, another 4% reflection loss is encountered. In summary, we reali ...
... probably will be air (n1 = 1.0). The other probably will be some other glass (n2 ~ 1.5). Using Equation 3, you can calculate a reflection of ~ 4%. This calculation is for one side of the window. When the rays emerge from the other side, another 4% reflection loss is encountered. In summary, we reali ...
Soft X-ray tomography and cryogenic light microscopy - X
... Soft x-ray microscopes have three clear advantages over light and electron microscopes. Firstly, the short wavelength allows cells to be imaged at significantly higher spatial resolution than is possible with light. Secondly, fully hydrated specimens up to 10 mm thick can be imaged without the need ...
... Soft x-ray microscopes have three clear advantages over light and electron microscopes. Firstly, the short wavelength allows cells to be imaged at significantly higher spatial resolution than is possible with light. Secondly, fully hydrated specimens up to 10 mm thick can be imaged without the need ...
Behavior Of Waves
... 5. Can reflect off the bottom and top surfaces of thin film, such as oil on water or bubbles, and produce a color pattern due to interference. 6. Can diffract through small slits or around lines to produce light and dark patterns or color patterns due to the interference of light waves. ...
... 5. Can reflect off the bottom and top surfaces of thin film, such as oil on water or bubbles, and produce a color pattern due to interference. 6. Can diffract through small slits or around lines to produce light and dark patterns or color patterns due to the interference of light waves. ...
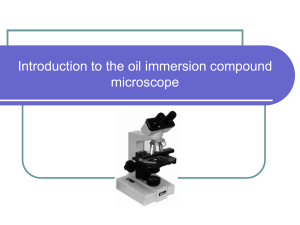
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.