Optical Fiber communication
... used in Fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are also immune to electromagnetic interference. ...
... used in Fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are also immune to electromagnetic interference. ...
Reflecting And Refracting Light
... Reflection Vocabulary • Real Image – – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears – Always inverted ...
... Reflection Vocabulary • Real Image – – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears – Always inverted ...
Anisotropic Minerals
... Refraction the light is bent when passing from one material to another, at an angle other than perpendicular. ...
... Refraction the light is bent when passing from one material to another, at an angle other than perpendicular. ...
Soft x-ray laser holography with wavelength resolution *
... temporal and spatial coherence of the illuminating source, the resolution of the medium in which the hologram is recorded, and the digitization process used are also factors that influence the ultimate resolution. The experimental setup described in this paper was optimized to limit the degrading ef ...
... temporal and spatial coherence of the illuminating source, the resolution of the medium in which the hologram is recorded, and the digitization process used are also factors that influence the ultimate resolution. The experimental setup described in this paper was optimized to limit the degrading ef ...
INTERFERENCE
... Two beams of microwaves of wavelength 6.00x10-3m are emitted by a source. They both travel 5cm to a detector, but one passes though air while the other through quartz of refractive index 1.54. Do they cause constructive or destructive interference? Path difference = (nquartz - nair) x d ...
... Two beams of microwaves of wavelength 6.00x10-3m are emitted by a source. They both travel 5cm to a detector, but one passes though air while the other through quartz of refractive index 1.54. Do they cause constructive or destructive interference? Path difference = (nquartz - nair) x d ...
Real-time digital holographic microscopy Ventseslav Sainov and Elena Stoykova
... Digital holography which implements numerical reconstruction of the holographic image from digitally recorded interfering object and reference beams has witnessed a real progress as a result of recent advances in laser sources, two dimensional photo sensors (CCD or CMOS cameras) and digital signal p ...
... Digital holography which implements numerical reconstruction of the holographic image from digitally recorded interfering object and reference beams has witnessed a real progress as a result of recent advances in laser sources, two dimensional photo sensors (CCD or CMOS cameras) and digital signal p ...
Beam Splitters A beam splitter is a device that`s used to divide an
... A mirror is a smooth surface that can reflect enough light to serve a useful purpose. Mirrors have been used since man first saw his image in a calm pool of water. They have progressed from the great silver-blackened hall mirrors of the eighteenth century to where, today, they are used to reflect li ...
... A mirror is a smooth surface that can reflect enough light to serve a useful purpose. Mirrors have been used since man first saw his image in a calm pool of water. They have progressed from the great silver-blackened hall mirrors of the eighteenth century to where, today, they are used to reflect li ...
Handout 7
... Even though our LX200s are generally referred to as relectors (as described in an upcoming section) the “corrector plate” is (as you may have suspected) in fact a lens, as are the eyepieces. These elements could in principle cause chromatic aberration,, but the corrector doesn’t bend light enough to ...
... Even though our LX200s are generally referred to as relectors (as described in an upcoming section) the “corrector plate” is (as you may have suspected) in fact a lens, as are the eyepieces. These elements could in principle cause chromatic aberration,, but the corrector doesn’t bend light enough to ...
Length poster
... Although the iodine-stabilised helium-neon laser provides a very stable optical frequency (or vacuum wavelength), it is already possible to build lasers with an optical frequency that is known around ten thousand times more accurately. The iodinestabilised laser is limited because the iodine molecul ...
... Although the iodine-stabilised helium-neon laser provides a very stable optical frequency (or vacuum wavelength), it is already possible to build lasers with an optical frequency that is known around ten thousand times more accurately. The iodinestabilised laser is limited because the iodine molecul ...
Quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry
... Wavefront sensing is a well known technology for studying the aberrations of a light-beam. In most applications, only the lower-order aberrations (like spherical aberration or coma) are considered, because the lower the aberration order is, the stronger is the effect on the beam [12] [13]. As a cons ...
... Wavefront sensing is a well known technology for studying the aberrations of a light-beam. In most applications, only the lower-order aberrations (like spherical aberration or coma) are considered, because the lower the aberration order is, the stronger is the effect on the beam [12] [13]. As a cons ...
OPTICAL MINERALOGY
... 1. Particle theory - release of a small amount of energy as a photon when an atom is excited. 2. Wave theory - radiant energy travels as a wave from one point to another. Waves have electrical and magnetic properties => electromagnetic variations. Wave theory effectively describes the phenomena of p ...
... 1. Particle theory - release of a small amount of energy as a photon when an atom is excited. 2. Wave theory - radiant energy travels as a wave from one point to another. Waves have electrical and magnetic properties => electromagnetic variations. Wave theory effectively describes the phenomena of p ...
HP Unit 11-light & optics - student handout
... With diffuse reflection, your eye sees reflected light at all angles. With specular reflection (from a mirror), your eye must be in the correct position. ...
... With diffuse reflection, your eye sees reflected light at all angles. With specular reflection (from a mirror), your eye must be in the correct position. ...
A. Menegolli
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
CP1: Investigation into the Feasibility of a Three Axis
... Crayfish axon which increased reflection, but unfortunately also decreased the fraction of light which reflected specularly. This technique also overcomes an issue often ignored in other experiments: the changing of the optical properties of the cell itself during a process of interest (in this case ...
... Crayfish axon which increased reflection, but unfortunately also decreased the fraction of light which reflected specularly. This technique also overcomes an issue often ignored in other experiments: the changing of the optical properties of the cell itself during a process of interest (in this case ...
Optics-Optical Instruments_ppt_RevW10
... objective mirror. The first real image is then viewed with a second short focal length (high diopter power) eyepiece lens • The first real image is brought to the side by means of a small flat mirror so that the eyepiece and observer can be out of the way of the incoming light ...
... objective mirror. The first real image is then viewed with a second short focal length (high diopter power) eyepiece lens • The first real image is brought to the side by means of a small flat mirror so that the eyepiece and observer can be out of the way of the incoming light ...
PDF
... micron-thick sample by producing 10 frames in less than 5 ms. For repetitive processes, one can use only xy-scanning, refocusing it at different depth step-by step. The speed of imaging depends on many additional factors, such as needed contrast (integration time), size of the scanned area, camera a ...
... micron-thick sample by producing 10 frames in less than 5 ms. For repetitive processes, one can use only xy-scanning, refocusing it at different depth step-by step. The speed of imaging depends on many additional factors, such as needed contrast (integration time), size of the scanned area, camera a ...
Will the Growth of the Microorganisms Bacteria and Mold Be
... The illumination that inhibited the bacterial colony growth the best was the 25 watt green light, with (2,1). The 25 watt U.V. light was the second best, but had excessive mold infiltration. Bacterial overgrowth was caused by the 60 watt incandescent. The blue 25 watt light was the best illumination ...
... The illumination that inhibited the bacterial colony growth the best was the 25 watt green light, with (2,1). The 25 watt U.V. light was the second best, but had excessive mold infiltration. Bacterial overgrowth was caused by the 60 watt incandescent. The blue 25 watt light was the best illumination ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction
... 6. Replace the mesh by the one with the smallest period. Observe the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern in the back focal plane F of L1. 7. Place the two slits in plane F. Fully open both of them. Center the slits on the diffraction pattern. 8. Close both slits so that only the (0, 0) diffraction order ...
... 6. Replace the mesh by the one with the smallest period. Observe the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern in the back focal plane F of L1. 7. Place the two slits in plane F. Fully open both of them. Center the slits on the diffraction pattern. 8. Close both slits so that only the (0, 0) diffraction order ...
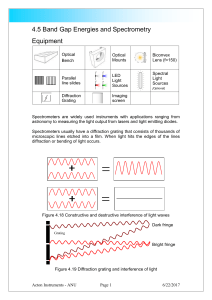
4.5 Band Gap Energies and Spectrometry
... Use the spectrometer to examine the white light LED and white light source. How might the white LED produce white light? LEDs are likely to replace incandescent lamps for many lighting applications such as car headlights. How does the white light LED compare to the normal light globe? For optical co ...
... Use the spectrometer to examine the white light LED and white light source. How might the white LED produce white light? LEDs are likely to replace incandescent lamps for many lighting applications such as car headlights. How does the white light LED compare to the normal light globe? For optical co ...
Chapter 23 Ray Optics
... The slight variation of index of refraction with wavelength is known as dispersion. Shown is the dispersion curves of two common glasses. Notice that n is larger when the wavelength is shorter, thus violet light refracts more than red light. ...
... The slight variation of index of refraction with wavelength is known as dispersion. Shown is the dispersion curves of two common glasses. Notice that n is larger when the wavelength is shorter, thus violet light refracts more than red light. ...
Introduction to Fiber Optics
... (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances. However, some of the light signal degrades within the fiber, mostly due to impurities in the glass. The extent that the signal ...
... (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances. However, some of the light signal degrades within the fiber, mostly due to impurities in the glass. The extent that the signal ...
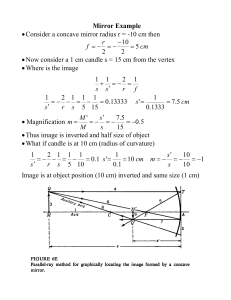
Mirror Example • Consider a concave mirror radius r =
... Draw line from object top Q to mirror parallel to axis (ray 4) Hits vertex line at T Then direct ray from T through focus point F (ray 5) and beyond Now direct ray from object top Q through radius C (ray 8) This intersects ray 5 at image Q’ (point 9) This correctly shows both position an ...
... Draw line from object top Q to mirror parallel to axis (ray 4) Hits vertex line at T Then direct ray from T through focus point F (ray 5) and beyond Now direct ray from object top Q through radius C (ray 8) This intersects ray 5 at image Q’ (point 9) This correctly shows both position an ...
PowerPoint version
... Light travels fast. In a vacuum it moves about 3 x 108 meters (186,000 miles) each second, a distance so large it’s difficult to comprehend. Here are some roughly equivalent distances: ...
... Light travels fast. In a vacuum it moves about 3 x 108 meters (186,000 miles) each second, a distance so large it’s difficult to comprehend. Here are some roughly equivalent distances: ...
PHYS 202 Notes, Week 10
... A camera is a device that is able to capture images and store them either on film or in a digital medium. Figure 1 shows a diagram of how a camera operates. The light coming off the object to be photographed passes through a lens, creating a real and inverted image on the film (for a traditional cam ...
... A camera is a device that is able to capture images and store them either on film or in a digital medium. Figure 1 shows a diagram of how a camera operates. The light coming off the object to be photographed passes through a lens, creating a real and inverted image on the film (for a traditional cam ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.