Microscopy corrected
... The two key properties of a microscope that allow you to see microbes are resolution and magnification. Magnification refers to the enlargement of the specimen when seen through the microscope. For a compound light microscope like we will use in this lab, magnification is achieved through the use of ...
... The two key properties of a microscope that allow you to see microbes are resolution and magnification. Magnification refers to the enlargement of the specimen when seen through the microscope. For a compound light microscope like we will use in this lab, magnification is achieved through the use of ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS In geometric
... a parameter used to characterize prisms. The refractive index of the prism is then related to the apex angle, σ of the prism and δ as in the equation above. δ can be found by adjusting the angle of the incident light so that the light passes through the prism parallel to the base of the prism. ...
... a parameter used to characterize prisms. The refractive index of the prism is then related to the apex angle, σ of the prism and δ as in the equation above. δ can be found by adjusting the angle of the incident light so that the light passes through the prism parallel to the base of the prism. ...
Lecture 5
... The MTF uses the power density (W/cm2 or (J/sec)/cm2). The resist responds to the total amount of energy absorbed. Thus, we need to define the Dose, with units of energy density (mJ/cm2), as the Intensity (or power density) times the exposure time. • We can also define D100= the minimum dose for whi ...
... The MTF uses the power density (W/cm2 or (J/sec)/cm2). The resist responds to the total amount of energy absorbed. Thus, we need to define the Dose, with units of energy density (mJ/cm2), as the Intensity (or power density) times the exposure time. • We can also define D100= the minimum dose for whi ...
visible spectroscopy - Purdue University Chemistry Department
... The Spectronic educator is designed to emit different wavelengths of light. You may select specific wavelengths of light by turning the wavelength control knob (next to the wavelength scale). Light having wavelengths of approximately 350 nm to 650 nm is visible to the naked eye. To see how this work ...
... The Spectronic educator is designed to emit different wavelengths of light. You may select specific wavelengths of light by turning the wavelength control knob (next to the wavelength scale). Light having wavelengths of approximately 350 nm to 650 nm is visible to the naked eye. To see how this work ...
Entry Task
... • Rainbows are cause by refraction and reflection of light through spherical water drops which act as prisms. – Like a prism, water drops separate the wavelengths of sunlight to produce a spectrum. – Unlike a prism, only one color reaches your eye from each drop. • Red appears at the top of a rainbo ...
... • Rainbows are cause by refraction and reflection of light through spherical water drops which act as prisms. – Like a prism, water drops separate the wavelengths of sunlight to produce a spectrum. – Unlike a prism, only one color reaches your eye from each drop. • Red appears at the top of a rainbo ...
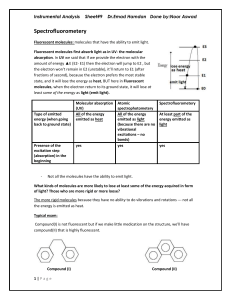
L09 Instru Spectrofluorometery
... Conclusion: the absorbed light in UV range (shorter wavelength) may be emitted as light in visible range (longer wavelength) and this is the most common case. In other cases: maybe both of them (absorbed+emitted) in UV range or both in visible range. Is it the same case of the spontaneous decay of r ...
... Conclusion: the absorbed light in UV range (shorter wavelength) may be emitted as light in visible range (longer wavelength) and this is the most common case. In other cases: maybe both of them (absorbed+emitted) in UV range or both in visible range. Is it the same case of the spontaneous decay of r ...
Geometrical and diffraction optics
... Since the refractive index n = f(LJ), the focal length of a lens = f(LJ) and different wavelengths have different foci. (Mirrors are usually achromatic). ...
... Since the refractive index n = f(LJ), the focal length of a lens = f(LJ) and different wavelengths have different foci. (Mirrors are usually achromatic). ...
Dark fringes
... =Distance of light traveling through vacuum at the same time For a monochromatic light, f is same in different medium, but and v are different. ...
... =Distance of light traveling through vacuum at the same time For a monochromatic light, f is same in different medium, but and v are different. ...
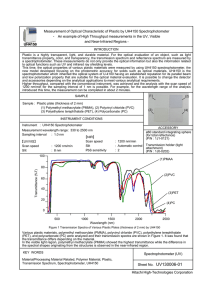
Measurement of Optical Characteristic of Plastic by UH4150
... Plastic is a highly transparent, light, and durable material. For the optical evaluation of an object, such as light transmittance property, color, and transparency, the transmission spectrum and reflectance spectrum are measured by a spectrophotometer. These measurements do not only provide the opt ...
... Plastic is a highly transparent, light, and durable material. For the optical evaluation of an object, such as light transmittance property, color, and transparency, the transmission spectrum and reflectance spectrum are measured by a spectrophotometer. These measurements do not only provide the opt ...
FT-IR Glossary - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... Birefringence Optically anisotropic substances are double refracting. In birefringent crystals, light is resolved into two components that are polarized at right angles to each other and that travel at different velocities through the substance. Thus, the crystal exhibits two refractive indices (one ...
... Birefringence Optically anisotropic substances are double refracting. In birefringent crystals, light is resolved into two components that are polarized at right angles to each other and that travel at different velocities through the substance. Thus, the crystal exhibits two refractive indices (one ...
Glossary (PDF file)
... reflect To bounce back from a surface. We can see things because light reflects off of them and travels to our eyes. Some objects reflect light better than others. refraction The bending of light when it moves from one material to another. Light travels at different speeds through different materials. ...
... reflect To bounce back from a surface. We can see things because light reflects off of them and travels to our eyes. Some objects reflect light better than others. refraction The bending of light when it moves from one material to another. Light travels at different speeds through different materials. ...
Optimizing Fluorescence Signal Quality
... An object should already be placed in the microscope. This object need not be fluorescent or biological; lens paper for example may work fine. All or some of the following excitation hardware should be adjusted to maximize illumination while minimizing background. Software control of the light sourc ...
... An object should already be placed in the microscope. This object need not be fluorescent or biological; lens paper for example may work fine. All or some of the following excitation hardware should be adjusted to maximize illumination while minimizing background. Software control of the light sourc ...
Prisms Lab - Mr. Ahearn`s Science
... • Prisms are typically made out of glass, but can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelength for which they are designed. • A prism can be used to break light up into its spectral colors (ROY G BIV). Prisms can also be used to reflect light, or to split light into components. ...
... • Prisms are typically made out of glass, but can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelength for which they are designed. • A prism can be used to break light up into its spectral colors (ROY G BIV). Prisms can also be used to reflect light, or to split light into components. ...
Chapter 20-Light The Nature of Light Visible Light Is a Form of
... e. Lenses are used in many kinds of instruments i. Camera=parts of a camera are lightproof box, opening in front of the camera, shutter over the opening, convex lens behind the opening, film at the back of the camera, device to hold and turn the film ii. Light microscope= two convex lenses one at ea ...
... e. Lenses are used in many kinds of instruments i. Camera=parts of a camera are lightproof box, opening in front of the camera, shutter over the opening, convex lens behind the opening, film at the back of the camera, device to hold and turn the film ii. Light microscope= two convex lenses one at ea ...
IX71/IX81 - Olympus Microscopy Resource Center
... As new fluorochromes are developed and new methods of light excitation and manipulation become more popular for live cell experiments, more and more researchers will require the use of low phototoxicity near-IR wavelengths in addition to the conventional visible spectrum. Olympus has equipped its IX ...
... As new fluorochromes are developed and new methods of light excitation and manipulation become more popular for live cell experiments, more and more researchers will require the use of low phototoxicity near-IR wavelengths in addition to the conventional visible spectrum. Olympus has equipped its IX ...
Adiabatic far-field sub-diffraction imaging ARTICLE Hu Cang *, Alessandro Salandrino
... lthough a tsunami is devastating near land, it is barely noticeable in the open ocean. This is because the sea floor near the land slows down the tsunami, compressing its wavelength from hundreds of kilometres1 to metres and rapidly increasing its amplitude to be destructive. Recently, a similar opti ...
... lthough a tsunami is devastating near land, it is barely noticeable in the open ocean. This is because the sea floor near the land slows down the tsunami, compressing its wavelength from hundreds of kilometres1 to metres and rapidly increasing its amplitude to be destructive. Recently, a similar opti ...
PochPHYS104-Obj_Chapt23Sp13
... draw a ray diagram for an image given the object’s distance and focal length of the lens and describe the image’s character, i.e. relative size, erect or inverted, real or virtual. using the lens equation, solve for the object distance, image distance and/or focal length (radius) in terms of the oth ...
... draw a ray diagram for an image given the object’s distance and focal length of the lens and describe the image’s character, i.e. relative size, erect or inverted, real or virtual. using the lens equation, solve for the object distance, image distance and/or focal length (radius) in terms of the oth ...
refraction ppt_2010
... Note the reflection of the man facing her. He must be you! Because reflection shows that he is directly in front of the woman, and thus he must be the viewer of the painter. You are looking into Manet’s work and seeing your reflection well off to your right. The effect is errie because it is not wha ...
... Note the reflection of the man facing her. He must be you! Because reflection shows that he is directly in front of the woman, and thus he must be the viewer of the painter. You are looking into Manet’s work and seeing your reflection well off to your right. The effect is errie because it is not wha ...
Modulation Transfer Function
... where C(s) is the object contrast and C 0 (s0 ) the image contrast. A value of 1 means that frequency is perfectly transferred to the image plane, which is the best possible outcome in a passive system. A value of 0 means that frequency will not appear at all in the image. The object- and image-spac ...
... where C(s) is the object contrast and C 0 (s0 ) the image contrast. A value of 1 means that frequency is perfectly transferred to the image plane, which is the best possible outcome in a passive system. A value of 0 means that frequency will not appear at all in the image. The object- and image-spac ...
Michelson Lab Guide UTSA
... into it. This change is one indication that you have passed through the equal path condition. Using the law of cosines: L2 + (m)2 – 2 mL cosk = (L + (m – k) from which it follows that k = [2k/m]½ once corrections of order /L have been ignored. Exercise: Complete the derivation of k = [k/2m ...
... into it. This change is one indication that you have passed through the equal path condition. Using the law of cosines: L2 + (m)2 – 2 mL cosk = (L + (m – k) from which it follows that k = [2k/m]½ once corrections of order /L have been ignored. Exercise: Complete the derivation of k = [k/2m ...
Technology for a better society
... The resolving power of an optical system is limited by the diffraction occurring at the optical path every time there is an aperture/diaphragm/lens. The aperture causes interference of the radiation (the path difference between the green waves results in destructive interference while the path diffe ...
... The resolving power of an optical system is limited by the diffraction occurring at the optical path every time there is an aperture/diaphragm/lens. The aperture causes interference of the radiation (the path difference between the green waves results in destructive interference while the path diffe ...
Head-Mounted Display
... eye and receives the image formed by the lens of the eye. Fovea - The part of the human retina that possesses the best spatial resolution or visual acuity. ...
... eye and receives the image formed by the lens of the eye. Fovea - The part of the human retina that possesses the best spatial resolution or visual acuity. ...
Chapter 35 – Interference and Diffraction
... Note that the light traveling from the slits to point P on the screen travel different distances. Because of this, there is a phase difference between the two waves at P, the resulting amplitude can vary from zero to a maximum magnitude of two times the amplitude of the waves reaching point P. Digr ...
... Note that the light traveling from the slits to point P on the screen travel different distances. Because of this, there is a phase difference between the two waves at P, the resulting amplitude can vary from zero to a maximum magnitude of two times the amplitude of the waves reaching point P. Digr ...
Extinction Coefficient Measurements of Turbid Media
... a spectral range from 390 nm (UV) to 1150 nm (IR) . In order to avoid the optical noise we let the whole path of the laser beam be within black-walled cylindrical tubes until it entered the photodetector . This has eliminated the optical noise to about zero. To avoid the entrance of scattered light ...
... a spectral range from 390 nm (UV) to 1150 nm (IR) . In order to avoid the optical noise we let the whole path of the laser beam be within black-walled cylindrical tubes until it entered the photodetector . This has eliminated the optical noise to about zero. To avoid the entrance of scattered light ...
Light Study Guide
... Any lens refracts parallel light rays so they cross or appear to cross at a __________ __________. A converging lens is ______________ in the middle than at the edges, and a diverging lens is ______________ in the middle than at the edges. A converging lens forms virtual, enlarged images when the ob ...
... Any lens refracts parallel light rays so they cross or appear to cross at a __________ __________. A converging lens is ______________ in the middle than at the edges, and a diverging lens is ______________ in the middle than at the edges. A converging lens forms virtual, enlarged images when the ob ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.