P1X
... Lecture 7: Lasers and their applications (II) Requirements for Laser action (Y&F 38.6): Theoretical laser: • We want a three level system in which the intermediate state is metastable (ie. the time for transition is much longer than the time for transition to other states). • If we can optically p ...
... Lecture 7: Lasers and their applications (II) Requirements for Laser action (Y&F 38.6): Theoretical laser: • We want a three level system in which the intermediate state is metastable (ie. the time for transition is much longer than the time for transition to other states). • If we can optically p ...
Dunlap Institute Summer School: Fourier Transform Spectroscopy Lab
... beams of light meet in space, these fields add according to the principle of superposition. At each point in space, the resultant electric and magnetic fields are the vector sum of the fields of the separate beams. If the two beams of light originate from separate sources, there is generally no fixe ...
... beams of light meet in space, these fields add according to the principle of superposition. At each point in space, the resultant electric and magnetic fields are the vector sum of the fields of the separate beams. If the two beams of light originate from separate sources, there is generally no fixe ...
Theoretical and experimental characterization of coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy
... pump field’s intensity and a linear dependence on the Stokes field’s intensity, the signal is generated in a small focal volume under the tight-focusing condition. Tight focusing permits three-dimensional sectioning of thick samples with high spatial resolution, similarly to multiphoton fluorescence ...
... pump field’s intensity and a linear dependence on the Stokes field’s intensity, the signal is generated in a small focal volume under the tight-focusing condition. Tight focusing permits three-dimensional sectioning of thick samples with high spatial resolution, similarly to multiphoton fluorescence ...
Full-field refractive index measurement with simultaneous phase
... Therefore, according to Eqs. (12) and (13), when the phase difference is accurately measured, the refractive index of the tested specimen n2 can be obtained using Eq. (7). 3. Experimental setup and results To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, various mixtures of the tested specimen ...
... Therefore, according to Eqs. (12) and (13), when the phase difference is accurately measured, the refractive index of the tested specimen n2 can be obtained using Eq. (7). 3. Experimental setup and results To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, various mixtures of the tested specimen ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
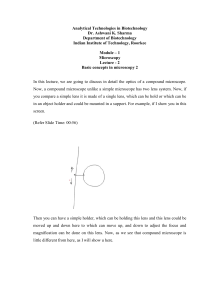
... Now, after objective there is a tube here, which connects the objective to the eye piece? The objective forms, which will be real and inverted image because the specimen is placed just one focal length away little farther from one focal length from the ah specimen. So, a real inverted image is form ...
... Now, after objective there is a tube here, which connects the objective to the eye piece? The objective forms, which will be real and inverted image because the specimen is placed just one focal length away little farther from one focal length from the ah specimen. So, a real inverted image is form ...
Raman Spectroscopy - University of Arizona
... spectrograph. This device bounce the light around reflecting out any remaining Rayleigh scattering and converts the Raman scattering into a detectable spectra of light wavelengths. A charged couple device then converts the light signal into electric signal, amplifies the signal and sends the signal ...
... spectrograph. This device bounce the light around reflecting out any remaining Rayleigh scattering and converts the Raman scattering into a detectable spectra of light wavelengths. A charged couple device then converts the light signal into electric signal, amplifies the signal and sends the signal ...
EDS system
... possible to low energy X-rays. • There are two main types of window materials. • Beryllium (Be) is highly robust, but strongly absorbs low energy X-rays meaning that only elements from sodium (Na) can be detected. • Polymer-based thin windows can be made much thinner than Be windows and therefore ar ...
... possible to low energy X-rays. • There are two main types of window materials. • Beryllium (Be) is highly robust, but strongly absorbs low energy X-rays meaning that only elements from sodium (Na) can be detected. • Polymer-based thin windows can be made much thinner than Be windows and therefore ar ...
Paper
... with HBT and that are to be taken into account to develop a HPT. It appears that high speed HPTs need thin base/collector layers and a small area like high speed HBTs. These features are important; however we would like to focus on the HPT specificity. A cautious design of the device should lead to ...
... with HBT and that are to be taken into account to develop a HPT. It appears that high speed HPTs need thin base/collector layers and a small area like high speed HBTs. These features are important; however we would like to focus on the HPT specificity. A cautious design of the device should lead to ...
Chapter 12: Light
... does not spread out Incoherent light - can contain more than one wavelength, and the electromagnetic waves are not aligned Light from ordinary light bulbs is incoherent ...
... does not spread out Incoherent light - can contain more than one wavelength, and the electromagnetic waves are not aligned Light from ordinary light bulbs is incoherent ...
Instructional Software for Visualizing Optical Phenomena
... past 40 years, and many of the textbook illustrations have remained essentially the same over this time. In particular, the illustrations rely heavily on line drawings and 2D graphs. Certain key concepts in the study of optics possess fundamentally 3D aspects, which are typically demonstrated in a c ...
... past 40 years, and many of the textbook illustrations have remained essentially the same over this time. In particular, the illustrations rely heavily on line drawings and 2D graphs. Certain key concepts in the study of optics possess fundamentally 3D aspects, which are typically demonstrated in a c ...
A Practical Guide to Optical Trapping
... In the last few decades, novel microscopy techniques have been developed to monitor the activity of single enzymes as they perform their biological functions in vitro. Motor proteins such as kinesin, myosin, F1 Fo ATPase, and RNA polymerase have been mercilessly subjected to magnetic, elastic, and o ...
... In the last few decades, novel microscopy techniques have been developed to monitor the activity of single enzymes as they perform their biological functions in vitro. Motor proteins such as kinesin, myosin, F1 Fo ATPase, and RNA polymerase have been mercilessly subjected to magnetic, elastic, and o ...
unit 9: imaging
... A radio telescope receives and detects EM waves in the radiofrequency region. What types of objects are known to radiate in this region? Properties of single-dish radio telescopes: 1) Since frequencies are small, their wavelengths are large, so the diameter of the radio telescope has to be large as ...
... A radio telescope receives and detects EM waves in the radiofrequency region. What types of objects are known to radiate in this region? Properties of single-dish radio telescopes: 1) Since frequencies are small, their wavelengths are large, so the diameter of the radio telescope has to be large as ...
Di raction and Interference PRECAUTION
... This experiment is greatly facilitated by the use of a laser as a light source. The laser light is highly monochromatic and coherent. Coherence means that there are surfaces, in this experiment approximately planes, in which the light is in phase. When such light falls on a ~ oscillates in phase ove ...
... This experiment is greatly facilitated by the use of a laser as a light source. The laser light is highly monochromatic and coherent. Coherence means that there are surfaces, in this experiment approximately planes, in which the light is in phase. When such light falls on a ~ oscillates in phase ove ...
Strategies for the compensation of specimen
... particular imaging depth, it is possible to create a significant increase in intensity and a better focal distribution than using an uncorrected lens. The maximum intensities in these three plots are approximately 20 times larger than those using a lens without correction. Many objectives are design ...
... particular imaging depth, it is possible to create a significant increase in intensity and a better focal distribution than using an uncorrected lens. The maximum intensities in these three plots are approximately 20 times larger than those using a lens without correction. Many objectives are design ...
INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front
... surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. ...
... surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. ...
Colorimeters
... absorb light for a variety of reasons. Pigments absorb light at different wavelengths. A cloudy solution will simply scatter/block the passage of light (sometimes a colorimeter is used to monitor the growth of a bacterial or yeast culture). The % transmission or the % absorbance is recorded (you c ...
... absorb light for a variety of reasons. Pigments absorb light at different wavelengths. A cloudy solution will simply scatter/block the passage of light (sometimes a colorimeter is used to monitor the growth of a bacterial or yeast culture). The % transmission or the % absorbance is recorded (you c ...
21. Specific rotation of sugar solution
... Partially polarized light is also distinguished. In this case, one of the directions of oscillations of the Evector is preferable compared to the others. That’s why partly polarized light can to be observed as a straight-line polarized and natural light mixture. Natural light can be polarized by the ...
... Partially polarized light is also distinguished. In this case, one of the directions of oscillations of the Evector is preferable compared to the others. That’s why partly polarized light can to be observed as a straight-line polarized and natural light mixture. Natural light can be polarized by the ...
An accurate technique to record the angular distribution of
... cone because these waves have no counterpropagating counterparts. This light will however contribute to the background and will therefore also lower the observed enhancement factor. To reduce the above effects, the glass window must be thick (1 cmj and its front side must be antireflection coated. M ...
... cone because these waves have no counterpropagating counterparts. This light will however contribute to the background and will therefore also lower the observed enhancement factor. To reduce the above effects, the glass window must be thick (1 cmj and its front side must be antireflection coated. M ...
Optical response of plasmonic relief meta-surfaces
... from an unstructured metal and in this instance for x-polarized light). In this range the continuously metallic metamaterial functions as a high impedance surface, or ‘optical magnetic mirror’ [20] for the y-polarization. Optical magnetic mirrors impose extremely unusual electromagnetic boundary con ...
... from an unstructured metal and in this instance for x-polarized light). In this range the continuously metallic metamaterial functions as a high impedance surface, or ‘optical magnetic mirror’ [20] for the y-polarization. Optical magnetic mirrors impose extremely unusual electromagnetic boundary con ...
Computational photography with plenoptic camera and light field
... Photography is a cornerstone of imaging. Ever since cameras became consumer products more than a century ago, we have witnessed great technological progress in optics and recording mediums, with digital sensors replacing photographic films in most instances. The latest revolution is computational ph ...
... Photography is a cornerstone of imaging. Ever since cameras became consumer products more than a century ago, we have witnessed great technological progress in optics and recording mediums, with digital sensors replacing photographic films in most instances. The latest revolution is computational ph ...
Lecture 21: Polarisation of light and other waves
... were initially equal, are out of step when they emerge from the plate. The extent to which they are out of step depends on the difference in refractive indices and on the thickness of the plate (and on the wavelength of the light). If the thickness is chosen such that the difference is π/2 then plan ...
... were initially equal, are out of step when they emerge from the plate. The extent to which they are out of step depends on the difference in refractive indices and on the thickness of the plate (and on the wavelength of the light). If the thickness is chosen such that the difference is π/2 then plan ...
Optics-Diffraction - The Wave Nature of Light
... waves arriving at the same place from different sources. When two waves combine the effect is called interference. The same rule applies when more than two waves arrive in the same place: the resulting amplitude is always the sum of the amplitudes of the arriving individual waves at each instant of ...
... waves arriving at the same place from different sources. When two waves combine the effect is called interference. The same rule applies when more than two waves arrive in the same place: the resulting amplitude is always the sum of the amplitudes of the arriving individual waves at each instant of ...
document
... • When you take a picture with a camera, a shutter opens to allow light to enter the camera for a specific length of time. • The light reflected off your subject enters the camera through an opening called the aperture. ...
... • When you take a picture with a camera, a shutter opens to allow light to enter the camera for a specific length of time. • The light reflected off your subject enters the camera through an opening called the aperture. ...
Vol. 26. Is. 5 - Society for Experimental Mechanics
... The entire event is immersed in a medium that has a refractive index n0. The first wave leaves the starting line, and arrives at point A at time t1. The second wave leaves the start line at the same instant the first wave left. But, this wave is required to pass through a slab of refractive material ...
... The entire event is immersed in a medium that has a refractive index n0. The first wave leaves the starting line, and arrives at point A at time t1. The second wave leaves the start line at the same instant the first wave left. But, this wave is required to pass through a slab of refractive material ...
Fourier Optics
... of the screen. In this way, the picture is passed unchanged and the lines are eliminated. 4. Image correlation. More complicated filters can be made by photography. One interesting application is the comparison of various objects with a reference one, for example, a set of alphanumeric characters. W ...
... of the screen. In this way, the picture is passed unchanged and the lines are eliminated. 4. Image correlation. More complicated filters can be made by photography. One interesting application is the comparison of various objects with a reference one, for example, a set of alphanumeric characters. W ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.