Inter 1-4
... Now, let reflected and refracted (transmitted) rays be reversed. Then amplitude of refracted ray = t1r1E. ...
... Now, let reflected and refracted (transmitted) rays be reversed. Then amplitude of refracted ray = t1r1E. ...
The Polarization of Light
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
Highly parallel CMOS lock-in optical sensor array for hyperspectral
... carried out slowly to reduce noise6,7. Fluorescence lifetime imaging is another area where the detected light intensities are very low. In these applications, however, fast data acquisition is necessary. Cameras designed for time resolved single photon counting are now being produced for use in fluo ...
... carried out slowly to reduce noise6,7. Fluorescence lifetime imaging is another area where the detected light intensities are very low. In these applications, however, fast data acquisition is necessary. Cameras designed for time resolved single photon counting are now being produced for use in fluo ...
Determination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids
... Precision of 10−5 of refractive index of a liquid sample would simply be meaningless if the temperature of the sample was not known with high accuracy. As the temperature coefficients of most liquid samples are of the order of ∂n/∂T ≈ 10−4 K−1 a measured index with 6 significant digits is only meani ...
... Precision of 10−5 of refractive index of a liquid sample would simply be meaningless if the temperature of the sample was not known with high accuracy. As the temperature coefficients of most liquid samples are of the order of ∂n/∂T ≈ 10−4 K−1 a measured index with 6 significant digits is only meani ...
Lecture 7 Optical Lithography
... • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatial frequency components). ...
... • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatial frequency components). ...
An Optical ‘‘Janus’’ Device for Integrated Photonics By Xiang Zhang*
... couplers are fabricated where a typical geometry for the total structure is shown as an scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image in Figure 2c. The gratings are designed to launch a TM mode at 1500 nm into the waveguide. However, the finite size of the gratings provides a coupling range over a wide f ...
... couplers are fabricated where a typical geometry for the total structure is shown as an scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image in Figure 2c. The gratings are designed to launch a TM mode at 1500 nm into the waveguide. However, the finite size of the gratings provides a coupling range over a wide f ...
Use of Broadband, Continuous-Wave Diode Lasers in Cavity Ring
... 10 6 cm 2 1 (one s). This corresponds to detecting ppb to ppt for good absorbers. This detection limit is only slightly higher than the limit reported for a standard CRDS setup with a pulsed dye laser under similar conditions.5 Changes in experimental setup, particularly solvent and wavelength, have ...
... 10 6 cm 2 1 (one s). This corresponds to detecting ppb to ppt for good absorbers. This detection limit is only slightly higher than the limit reported for a standard CRDS setup with a pulsed dye laser under similar conditions.5 Changes in experimental setup, particularly solvent and wavelength, have ...
External visual interface for a Nikon 6D autocollimator
... the eyepiece area (where the final image is formed), generating radial lighting saturated zones in the image center and dark areas at the image contour (see Fig. 4). If this incoming light has an offset and it is not centered in the reticle, the final image will have a wrong structure. Because of th ...
... the eyepiece area (where the final image is formed), generating radial lighting saturated zones in the image center and dark areas at the image contour (see Fig. 4). If this incoming light has an offset and it is not centered in the reticle, the final image will have a wrong structure. Because of th ...
Interference with monochromatic light
... the observation screen only if the source consists of a point. As soon as the source is laterally extended, the same point x, y on the screen is attained by many light rays, all with different ϑ. It is obvious that the contrast in the interference pattern then must decrease. Loss of contrast will al ...
... the observation screen only if the source consists of a point. As soon as the source is laterally extended, the same point x, y on the screen is attained by many light rays, all with different ϑ. It is obvious that the contrast in the interference pattern then must decrease. Loss of contrast will al ...
Green's function formulation for third-harmonic generation microscopy
... third-harmonic generation (THG) microscopy7–12 for biology and materials science. THG microscopy was demonstrated by Barad et al. in 1997.7 This technique has been applied for imaging transparent objects,7,8 laser-induced breakdown,9 and biological samples.10–12 The advantages of this technique are ...
... third-harmonic generation (THG) microscopy7–12 for biology and materials science. THG microscopy was demonstrated by Barad et al. in 1997.7 This technique has been applied for imaging transparent objects,7,8 laser-induced breakdown,9 and biological samples.10–12 The advantages of this technique are ...
lecture plan
... Fresnel Biprism in detail, Interference with White Light, Idea of Stokes Theorem. T1: ...
... Fresnel Biprism in detail, Interference with White Light, Idea of Stokes Theorem. T1: ...
A high resolution ion microscope for cold atoms
... plane behind the lens, which is further magnified by the next lens and finally imaged onto the MCP plane. In order to achieve a sharp image, the focal length of each lens is matched to the position of the image plane of the previous lens. The position of the image planes is determined by simulating ...
... plane behind the lens, which is further magnified by the next lens and finally imaged onto the MCP plane. In order to achieve a sharp image, the focal length of each lens is matched to the position of the image plane of the previous lens. The position of the image planes is determined by simulating ...
Sample Pages
... Flexible endoscopes use imaging fiber bundles to transfer the image from the distal end of the endoscope to the imaging lens or eyepiece, as shown in Fig. 8.4. With fiber bundles, the diameter of the space required for the image relay is reduced significantly, leaving more space for other instrument ...
... Flexible endoscopes use imaging fiber bundles to transfer the image from the distal end of the endoscope to the imaging lens or eyepiece, as shown in Fig. 8.4. With fiber bundles, the diameter of the space required for the image relay is reduced significantly, leaving more space for other instrument ...
Diffraction limited resolution - X-ray and Observational Astronomy
... • This is due to the turbulent nature of the Earth’s atmosphere • Local changes in atmospheric T and density over small distances create regions where the light is refracted in random directions • This causes a point source to become blurred • Since stars are effectively point sources, they twinkle ...
... • This is due to the turbulent nature of the Earth’s atmosphere • Local changes in atmospheric T and density over small distances create regions where the light is refracted in random directions • This causes a point source to become blurred • Since stars are effectively point sources, they twinkle ...
Conference title, upper and lower case, bolded, 18 point type
... Fig. S3. Sketch of the experimental setup. The laser beam from a fiber coupled laser is collimated by means of a fiber collimator (Thorlabs RC04APC-P01) with a beam diameter of about 4 mm. The collimated beam then passes through a Glan-Thompson polarizer (Thorlabs GTH10) and a quarter waveplate (ach ...
... Fig. S3. Sketch of the experimental setup. The laser beam from a fiber coupled laser is collimated by means of a fiber collimator (Thorlabs RC04APC-P01) with a beam diameter of about 4 mm. The collimated beam then passes through a Glan-Thompson polarizer (Thorlabs GTH10) and a quarter waveplate (ach ...
Utilizing a 4-F Fourier Optical System to Learn More About Image
... We then attempted to test what would happen to images if we applied differently shaped filters to the Fourier plane. We decided to experiment with two more shapes: a triangle and a square. To do this for a high-pass filter, we drew a small triangle on a transparent film and a small square on another ...
... We then attempted to test what would happen to images if we applied differently shaped filters to the Fourier plane. We decided to experiment with two more shapes: a triangle and a square. To do this for a high-pass filter, we drew a small triangle on a transparent film and a small square on another ...
Physics 228 Today: Polarization, Scattering
... Polarizing Visible Light Although the wavelength of visible light is < 1 μm, we can linearly polarize it using arrays of molecules, as in a polaroid filter. We can think of this similarly to microwaves and the metal plate: if the electric field orientation can accelerate electrons in the material - ...
... Polarizing Visible Light Although the wavelength of visible light is < 1 μm, we can linearly polarize it using arrays of molecules, as in a polaroid filter. We can think of this similarly to microwaves and the metal plate: if the electric field orientation can accelerate electrons in the material - ...
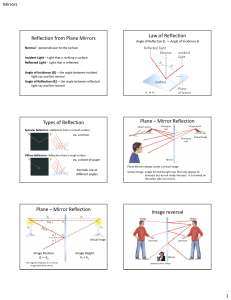
Reflection from Plane Mirrors Law of Reflection Types of Reflection
... 2. Draw a line parallel to the optical axis from where this line hits the mirror and draw the line out past the back of the mirror. 3. Draw a line from the tip of the object straight to the mirror. 4. Draw a line from the F, through the point where the last line hit the mirror, and out past the ...
... 2. Draw a line parallel to the optical axis from where this line hits the mirror and draw the line out past the back of the mirror. 3. Draw a line from the tip of the object straight to the mirror. 4. Draw a line from the F, through the point where the last line hit the mirror, and out past the ...
PDF
... were visualized using the three-photon excitation fluorescence polarized microscopy (3PEFPM) that utilizes fluorescence signals from the LC molecules excited through a three-photon absorption process [20]. The advantage of using this technique is that, unlike fluorescence confocal polarizing microsc ...
... were visualized using the three-photon excitation fluorescence polarized microscopy (3PEFPM) that utilizes fluorescence signals from the LC molecules excited through a three-photon absorption process [20]. The advantage of using this technique is that, unlike fluorescence confocal polarizing microsc ...
lecture5web
... the air above it, we see the upside down version of the road mirage, as the ray travels from cool to warm air, and is bent away from normal. Again, we interpret rays as traveling in straight lines, and thus the island appears to float above the ocean ...
... the air above it, we see the upside down version of the road mirage, as the ray travels from cool to warm air, and is bent away from normal. Again, we interpret rays as traveling in straight lines, and thus the island appears to float above the ocean ...
219_cha.pdf
... etc. have been developed [1-9]. Optical surface contouring method using interferometry fulfills the condition of non-contacting and whole field measurement of surface shape with high resolution. Fizeau and Twyman-Green interferometers can be used only for continuous mirror surfaces, on the other han ...
... etc. have been developed [1-9]. Optical surface contouring method using interferometry fulfills the condition of non-contacting and whole field measurement of surface shape with high resolution. Fizeau and Twyman-Green interferometers can be used only for continuous mirror surfaces, on the other han ...
3 The concept of diffraction limit
... beam falling on the objective and let NA denote the numerical aperture of the focusing lens. lλ Then the critical dimension can be roughly given as CD = . In modern photolithograNA phy, for optimized ring shaped illumination, the value of l can be as small as 0.36. Thus with NA = 0.9, near-ultraviol ...
... beam falling on the objective and let NA denote the numerical aperture of the focusing lens. lλ Then the critical dimension can be roughly given as CD = . In modern photolithograNA phy, for optimized ring shaped illumination, the value of l can be as small as 0.36. Thus with NA = 0.9, near-ultraviol ...
Graphene-like optical light field and its interaction with two
... in Eq. (1) as it originates from disks rather than points spaced around the vertices of a hexagon. This is necessary to increase efficiency, but results in a pattern with an intensity that is falling off rapidly around the beam waist, as shown in Fig. 2. Figure 3 shows the hologram pattern. Ideally, ...
... in Eq. (1) as it originates from disks rather than points spaced around the vertices of a hexagon. This is necessary to increase efficiency, but results in a pattern with an intensity that is falling off rapidly around the beam waist, as shown in Fig. 2. Figure 3 shows the hologram pattern. Ideally, ...
Interferometric near-infrared spectroscopy directly quantifies optical
... Consequently, iNIRS measures both the TPSF and TOFresolved field and intensity autocorrelations, overcoming ambiguities inherent in intensity-based DSCL techniques. This allows verification of the Siegert relation, and potentially, the study of non-Gaussian and non-ergodic light scattering where Eq. ...
... Consequently, iNIRS measures both the TPSF and TOFresolved field and intensity autocorrelations, overcoming ambiguities inherent in intensity-based DSCL techniques. This allows verification of the Siegert relation, and potentially, the study of non-Gaussian and non-ergodic light scattering where Eq. ...
to - UCL Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering
... optical excitation is used as it enables the large variation in the optical absorption and scattering properties of different tissue constituents to be exploited. Sources of naturally occurring absorption contrast include chromophores such as haemaglobin (and its various oxygenated states), melanin, ...
... optical excitation is used as it enables the large variation in the optical absorption and scattering properties of different tissue constituents to be exploited. Sources of naturally occurring absorption contrast include chromophores such as haemaglobin (and its various oxygenated states), melanin, ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.