Mirrors form images by reflecting light.
... instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine optical tools to extend vision far into space. As you will see, some of the latest optical technology—lasers— use visible light in ways t ...
... instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine optical tools to extend vision far into space. As you will see, some of the latest optical technology—lasers— use visible light in ways t ...
Geometric optics
... Figure for use in showing how to find answer (I would draw this on the board) ...
... Figure for use in showing how to find answer (I would draw this on the board) ...
Superior Pointing Stability Simplifies MPE Imaging
... lasers, it is very important to understand how the pointing is being specified. The microscope input aperture has a circular cross section, so at Coherent, we use a radial specification, i.e. 80 μrad/100 nm in any axis. That’s because with a circular aperture, it doesn’t matter which direction the b ...
... lasers, it is very important to understand how the pointing is being specified. The microscope input aperture has a circular cross section, so at Coherent, we use a radial specification, i.e. 80 μrad/100 nm in any axis. That’s because with a circular aperture, it doesn’t matter which direction the b ...
F045033337
... method. The gradient-based methods detect edges by first computing a measure of edge strength, usually a first-order derivative expression such as the gradient magnitude, and then searching for local directional maxima of the gradient magnitude using a computed estimate of the local orientation of t ...
... method. The gradient-based methods detect edges by first computing a measure of edge strength, usually a first-order derivative expression such as the gradient magnitude, and then searching for local directional maxima of the gradient magnitude using a computed estimate of the local orientation of t ...
lecture_five_2016
... refraction and reflection including polarization. And I will take no attempt to derive this for ou in detail but I will present you wit some results so that you can a least appreciate the far-reaching consequences of the reflection in which we can produce a hundred percent polarized light. Suppose w ...
... refraction and reflection including polarization. And I will take no attempt to derive this for ou in detail but I will present you wit some results so that you can a least appreciate the far-reaching consequences of the reflection in which we can produce a hundred percent polarized light. Suppose w ...
Fundamentals of Optical Interferometry for Thermal Expansion
... single laser beam and one or two photodetectors to record the phase changes caused by the movement of a single spot. Full field imaging techniques use a laser beam to illuminate a larger area and CCD cameras to record the information. Each pixel of the camera becomes an interferometer by combining t ...
... single laser beam and one or two photodetectors to record the phase changes caused by the movement of a single spot. Full field imaging techniques use a laser beam to illuminate a larger area and CCD cameras to record the information. Each pixel of the camera becomes an interferometer by combining t ...
Non-invasive ophthalmic imaging of adult zebrafish eye using
... topic of considerable current interest. This is motivated by the potential of optical techniques to provide sub-millimetre resolution imaging without the need for ionizing radiation and associated risks1. The fundamental problem with optical imaging is that in contrast to X-rays, optical photons are ...
... topic of considerable current interest. This is motivated by the potential of optical techniques to provide sub-millimetre resolution imaging without the need for ionizing radiation and associated risks1. The fundamental problem with optical imaging is that in contrast to X-rays, optical photons are ...
Homework Set #6 Due: 3-28-14
... exist for which there is a definite index of refraction. These are referred to as the extraordinary and ordinary modes. When light is incident on an anisotropic medium at non-normal incidence it will in general refract into two beams, each at a different angle, inside the medium. This is because, so ...
... exist for which there is a definite index of refraction. These are referred to as the extraordinary and ordinary modes. When light is incident on an anisotropic medium at non-normal incidence it will in general refract into two beams, each at a different angle, inside the medium. This is because, so ...
Structure and Imaging of a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
... electron has rotation and focusing in a form of a shrinking spiral form along the optical axis. This focusing action occurs for electrons emitted from a paraxial point near the optical axis, and they are focused on another paraxial point in the opposite side of the lens for forming a reversed image. ...
... electron has rotation and focusing in a form of a shrinking spiral form along the optical axis. This focusing action occurs for electrons emitted from a paraxial point near the optical axis, and they are focused on another paraxial point in the opposite side of the lens for forming a reversed image. ...
PDF Link
... second-order statistics is of particular interest. Field cross-correlation functions are measured whenever we study the relative properties of two fields, one of which is modified by a sample of interest, e.g., in interferometry, holography, and microscopy [5]. Field auto-correlation functions are u ...
... second-order statistics is of particular interest. Field cross-correlation functions are measured whenever we study the relative properties of two fields, one of which is modified by a sample of interest, e.g., in interferometry, holography, and microscopy [5]. Field auto-correlation functions are u ...
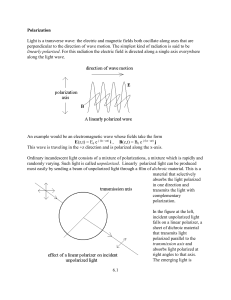
6.1 Polarization Light is a transverse wave: the electric and magnetic
... Light polarized along the x-axis moves through the birefringent material at a speed c/n1 while light polarized along the y-axis moves at speed c/n2. If n1 < n2 , the x-axis is called the fast axis of the material, the y-axis the slow one. The fast and slow axes refer to directions within the birefri ...
... Light polarized along the x-axis moves through the birefringent material at a speed c/n1 while light polarized along the y-axis moves at speed c/n2. If n1 < n2 , the x-axis is called the fast axis of the material, the y-axis the slow one. The fast and slow axes refer to directions within the birefri ...
Optical Interferometers
... surfaces, creating a large number of reflections. Interference of these multiple beams produces sharp spikes in the transmission for certain light frequencies. Thanks to the large number of interfering rays, this type of interferometer has extremely high resolution, much better than, for example, a ...
... surfaces, creating a large number of reflections. Interference of these multiple beams produces sharp spikes in the transmission for certain light frequencies. Thanks to the large number of interfering rays, this type of interferometer has extremely high resolution, much better than, for example, a ...
Holographic Metalens for Switchable Focusing of Surface Plasmons
... accomplished by simple experimental configurations, typically by using prism geometries or diffractive gratings. In addition, the development of high-resolution lithography and milling techniques allows for the design of structures that can be integrated into complex optoelectronic circuits whose func ...
... accomplished by simple experimental configurations, typically by using prism geometries or diffractive gratings. In addition, the development of high-resolution lithography and milling techniques allows for the design of structures that can be integrated into complex optoelectronic circuits whose func ...
(FT-IR) Microspectroscopic Measurements of Intact Spheres
... An infrared spectrum recorded from a microscopic sample depends on spectral properties of the constituent material as well as on morphology. Many samples or domains within heterogeneous materials can be idealized as spheres, in which both scattering and absorption from the three-dimensional shape af ...
... An infrared spectrum recorded from a microscopic sample depends on spectral properties of the constituent material as well as on morphology. Many samples or domains within heterogeneous materials can be idealized as spheres, in which both scattering and absorption from the three-dimensional shape af ...
The Fundamentals of Infrared Spectroscopy
... L = sample pathlength An absorption band can be characterized by two parameters; the wavelength at which maximum absorption occurs, and the intensity of absorption at this wavelength. In an absorption spectrum, the intensity of the band is proportional to the number of molecules (i.e. the concentrat ...
... L = sample pathlength An absorption band can be characterized by two parameters; the wavelength at which maximum absorption occurs, and the intensity of absorption at this wavelength. In an absorption spectrum, the intensity of the band is proportional to the number of molecules (i.e. the concentrat ...
00 Fourier optics – 4f Arrangement – Filtering and reconstruction
... parallel to the water’s surface such that it is immersed in the liquid by about 5 mm without bubble formation. (Caution: Do not immerse the transducer too deeply!) Connect the sonic transducer with the ultrasonic generator. In its switched-off state, one does not observe any changes on the screen Sc ...
... parallel to the water’s surface such that it is immersed in the liquid by about 5 mm without bubble formation. (Caution: Do not immerse the transducer too deeply!) Connect the sonic transducer with the ultrasonic generator. In its switched-off state, one does not observe any changes on the screen Sc ...
C. Huang, X. Wu, H. Liu, B. Aldalali, J.A. Rogers and H. Jiang
... artificial RSCEs from the rest of the compound eye devices is the cruciform pattern (i.e. the blue cross on the detector surface in Figure 1b) around every focused image, which is attributed to the even number of reflections (i.e. blue rays) on the mirrored sidewalls in only one of the X and Y coord ...
... artificial RSCEs from the rest of the compound eye devices is the cruciform pattern (i.e. the blue cross on the detector surface in Figure 1b) around every focused image, which is attributed to the even number of reflections (i.e. blue rays) on the mirrored sidewalls in only one of the X and Y coord ...
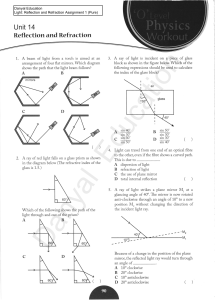
Assignment 1A
... The diagram shows four lamps in front of and behind an opaque plane mirror.The card prevents the observer at X from seeing the lamps directly, although the image of one lamp can be seen in the mirror. Which lamp's image can be seen in the mirror? ...
... The diagram shows four lamps in front of and behind an opaque plane mirror.The card prevents the observer at X from seeing the lamps directly, although the image of one lamp can be seen in the mirror. Which lamp's image can be seen in the mirror? ...
A Laser Module for 100Gbps Digital Coherent Optical Transmission System
... order to simultaneously realize a linewidth of no more than 500 kHz and high optical output, we used a long DFB LD cavity that has a length of 1.2 mm, and also optimally designed the shape of the waveguide of the SOA. Figure 4 shows the dependency of the output power of the optical fiber to which th ...
... order to simultaneously realize a linewidth of no more than 500 kHz and high optical output, we used a long DFB LD cavity that has a length of 1.2 mm, and also optimally designed the shape of the waveguide of the SOA. Figure 4 shows the dependency of the output power of the optical fiber to which th ...
Images and Plane Mirrors
... virtual image of a light source (said to be the object, O) by redirecting light rays emerging from the source. The image can be seen where backward extensions of reflected rays pass through one another. The object’s distance p from the mirror is related to the (apparent) image distance i from the mi ...
... virtual image of a light source (said to be the object, O) by redirecting light rays emerging from the source. The image can be seen where backward extensions of reflected rays pass through one another. The object’s distance p from the mirror is related to the (apparent) image distance i from the mi ...
... Diverging (negative) lens: bends the light rays away from the axis. It has a negative focal length. An object placed anywhere to the left of a diverging lens results in an erect virtual image. It is not possible to construct a negative magnetic lens although negative electrostatic lenses can be mad ...
LCI
... The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and directed toward two mirrors, M1 and M2, which reflect the field back. Mirror M2 has an adjustable position, such that the phase delay between the two fields can be tuned. Finally, the two beams are recombined at the detector, via the BS (note that pow ...
... The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and directed toward two mirrors, M1 and M2, which reflect the field back. Mirror M2 has an adjustable position, such that the phase delay between the two fields can be tuned. Finally, the two beams are recombined at the detector, via the BS (note that pow ...
The Faraday Effect
... These are identical, so either may serve a polarizer, and the other as analyzer. The fine adjust screws of one has been damaged however, so it is best to use this as the polarizer. Do not change the setting of this during a series of measurements. Anisotropy provides selective absorption in Polaroid ...
... These are identical, so either may serve a polarizer, and the other as analyzer. The fine adjust screws of one has been damaged however, so it is best to use this as the polarizer. Do not change the setting of this during a series of measurements. Anisotropy provides selective absorption in Polaroid ...
Scanning Electron Microscopy Primer - CharFac
... An electromagnetic lens [2] consists of a coil of copper wires inside an iron pole piece. A current through the coils creates a magnetic field (symbolized by red lines) in the bore of the pole pieces which is used to converge the electron beam. When an electron passes through an electromagnetic lens ...
... An electromagnetic lens [2] consists of a coil of copper wires inside an iron pole piece. A current through the coils creates a magnetic field (symbolized by red lines) in the bore of the pole pieces which is used to converge the electron beam. When an electron passes through an electromagnetic lens ...
Convex Mirrors
... The amount of refraction depends upon the difference between the speeds of light in the two media. The index of refraction for a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of the light in the material. • A low index of refraction (near 1) causes light to slow ...
... The amount of refraction depends upon the difference between the speeds of light in the two media. The index of refraction for a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of the light in the material. • A low index of refraction (near 1) causes light to slow ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.