Study Guide: Egypt Test
... 12. What was the name of the Pharaoh who wanted to extend trade out past the Nile River Valley? 13. Who was the Pharaoh that took over at the age of 9? 14. The ancient Egyptians believed in many gods; they were ______. 15. Which Pharaoh tried to change the religion on the Egyptians into a monotheist ...
... 12. What was the name of the Pharaoh who wanted to extend trade out past the Nile River Valley? 13. Who was the Pharaoh that took over at the age of 9? 14. The ancient Egyptians believed in many gods; they were ______. 15. Which Pharaoh tried to change the religion on the Egyptians into a monotheist ...
No Slide Title
... Egyptian Proportion The Egyptians did not understand how to draw a person from the side perspective. When they drew a person’s side perspective they would draw the person’s body facing the front and the feet and head facing the side. ...
... Egyptian Proportion The Egyptians did not understand how to draw a person from the side perspective. When they drew a person’s side perspective they would draw the person’s body facing the front and the feet and head facing the side. ...
Davidson
... Some two hundred years later the rulers of Kush moved their capital southward to Meroe, whose ruins lie about a hundred miles to the north of modern Khartoum. Here they presided over a distinctive civilization which flourished for seven hundred years. The Greeks called it Ethiopian. This has confuse ...
... Some two hundred years later the rulers of Kush moved their capital southward to Meroe, whose ruins lie about a hundred miles to the north of modern Khartoum. Here they presided over a distinctive civilization which flourished for seven hundred years. The Greeks called it Ethiopian. This has confuse ...
Ancient Egypt
... A. Origins 1. 5000 B.C. – Neolithic hunter-gatherers began settling along the Nile River Valley 2. 4000 B.C. – Egypt consists of 2 large kingdoms: a. Lower Egypt – in the north, Nile Delta b. Upper Egypt – in the south, Nile Valley ...
... A. Origins 1. 5000 B.C. – Neolithic hunter-gatherers began settling along the Nile River Valley 2. 4000 B.C. – Egypt consists of 2 large kingdoms: a. Lower Egypt – in the north, Nile Delta b. Upper Egypt – in the south, Nile Valley ...
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Powerpoint
... in into L.E.- river turns into rapids for stretch and it difficult to navigate ...
... in into L.E.- river turns into rapids for stretch and it difficult to navigate ...
Section 1 Focus questions
... 4.) Predict: Why might the ruins of early Egyptian settlements lack evidence of protective walls? ...
... 4.) Predict: Why might the ruins of early Egyptian settlements lack evidence of protective walls? ...
2 Column Ch3 Sec2 Filled Out
... Egypt’s God-Kings 1.Hatshepsut, female ruler who encouraged trade. Famous expedition to Punt From Dynasty to Dynasty 1.3 Main time periods called Kingdoms (Old, Middle, New) 2.Menes united Lower (Red) and Upper (White) Egypt and built the city Memphis All Powerful Pharaohs 1.Absolute power over thei ...
... Egypt’s God-Kings 1.Hatshepsut, female ruler who encouraged trade. Famous expedition to Punt From Dynasty to Dynasty 1.3 Main time periods called Kingdoms (Old, Middle, New) 2.Menes united Lower (Red) and Upper (White) Egypt and built the city Memphis All Powerful Pharaohs 1.Absolute power over thei ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... United by King Narmer (King of Upper Egypt) King of Upper Egypt wore a white crown Lower Egypt wore a red crown Narmer Palette: both crowns as one Symbol of unification around 3000 BC ...
... United by King Narmer (King of Upper Egypt) King of Upper Egypt wore a white crown Lower Egypt wore a red crown Narmer Palette: both crowns as one Symbol of unification around 3000 BC ...
File - Trotopia: World History
... Egyptian traders made greater contacts with the peoples of the middle east and the island of Crete. Around 1700 BC the Hyksos overran the Egyptians with their horse-drawn war chariots The Hyksos were impressed by the Egyptians and they adapted Egyptian customs, beliefs, and names. ...
... Egyptian traders made greater contacts with the peoples of the middle east and the island of Crete. Around 1700 BC the Hyksos overran the Egyptians with their horse-drawn war chariots The Hyksos were impressed by the Egyptians and they adapted Egyptian customs, beliefs, and names. ...
ancient_egypt_1pp
... Nile river were united when the ruler of Upper Egypt conquered the kingdom in Lower Egypt. Thus began what is now generally accepted as the first of at least 30 Egyptian dynasties. Ancient Egyptian dynasties are grouped into periods of stability referred to as 'kingdoms' and periods of fragmentation ...
... Nile river were united when the ruler of Upper Egypt conquered the kingdom in Lower Egypt. Thus began what is now generally accepted as the first of at least 30 Egyptian dynasties. Ancient Egyptian dynasties are grouped into periods of stability referred to as 'kingdoms' and periods of fragmentation ...
Nile
... - The New Kingdom in Egypt weakens and by 1100 BC the Kush people were free from the Egyptians - In 750 BC a new Kushite kingdom comes in to power, the capital being Napata, Piankhi would invade north into Egypt and the Kushites would remain in power for 100 ...
... - The New Kingdom in Egypt weakens and by 1100 BC the Kush people were free from the Egyptians - In 750 BC a new Kushite kingdom comes in to power, the capital being Napata, Piankhi would invade north into Egypt and the Kushites would remain in power for 100 ...
Slide 1
... The Hyksos were the source of the new horse-drawn war-chariots introduced to Egypt in the second half of the Hyksos rule. This invention, never seen before in Egypt, was instrumental in the continued power of the Hyksos in this region. The Hyksos utilized superior bronze weapons, chariots, and comp ...
... The Hyksos were the source of the new horse-drawn war-chariots introduced to Egypt in the second half of the Hyksos rule. This invention, never seen before in Egypt, was instrumental in the continued power of the Hyksos in this region. The Hyksos utilized superior bronze weapons, chariots, and comp ...
Ancient Egypt Scavenger Hunt
... 9. What god is known as the god of the pharaohs? 10. What god is known as the god of the underworld? 11. Click on the following LINK. Write down a description for three other gods NOT listed on your study guide. a. b. c. 12. Watch this Horrible History on Ancient Egyptian gods. 13. Who became the r ...
... 9. What god is known as the god of the pharaohs? 10. What god is known as the god of the underworld? 11. Click on the following LINK. Write down a description for three other gods NOT listed on your study guide. a. b. c. 12. Watch this Horrible History on Ancient Egyptian gods. 13. Who became the r ...
silt. - SWR Global History
... – A pharaoh was considered to be the son of Amon-Re, the sun god. Therefore, the pharaoh was also a god. – The pharaoh was the chief politician, meaning, like a king, he controlled all decisions of law and the military. – However, he was also the chief priest of Egypt. – A government ruled by such r ...
... – A pharaoh was considered to be the son of Amon-Re, the sun god. Therefore, the pharaoh was also a god. – The pharaoh was the chief politician, meaning, like a king, he controlled all decisions of law and the military. – However, he was also the chief priest of Egypt. – A government ruled by such r ...
Notes: Ancient Egypt
... – Created new religion of one god-Aten – Controversy, disputes over his religious beliefs – Abandon Thebes & built new city – New spectacular, buildings, elaborate ceremonies, works of art – Married to Nefertiti – After death he was so unpopular that his city was abandoneddestroyed ...
... – Created new religion of one god-Aten – Controversy, disputes over his religious beliefs – Abandon Thebes & built new city – New spectacular, buildings, elaborate ceremonies, works of art – Married to Nefertiti – After death he was so unpopular that his city was abandoneddestroyed ...
Ancient Kush
... Physical geography helped develop the Kushite Kush and Egypt traded but they also fought Many factors led to the decline of their civilizations ...
... Physical geography helped develop the Kushite Kush and Egypt traded but they also fought Many factors led to the decline of their civilizations ...
The First Age of Empires
... Stepson-may have murdered Hatshepsut Thutmose III armies took Syria & n part of Euphrates Pushed into Nubia ► Conquered an empire ...
... Stepson-may have murdered Hatshepsut Thutmose III armies took Syria & n part of Euphrates Pushed into Nubia ► Conquered an empire ...
The Land of the Pharaohs
... 2040 BCE Egypt is united again under Mentuhotep of the 11th Dynasty from Thebes. Nobles were very powerful b/c they controlled the armies. After the assassination of Amenehat I pharaohs began to build their own armies and body guards. 13th Dynasty witnessed the short reign of numerous pharaohs. Fore ...
... 2040 BCE Egypt is united again under Mentuhotep of the 11th Dynasty from Thebes. Nobles were very powerful b/c they controlled the armies. After the assassination of Amenehat I pharaohs began to build their own armies and body guards. 13th Dynasty witnessed the short reign of numerous pharaohs. Fore ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... homes and crops would be destroyed The desert on both sides of the Nile hindered travel and interaction with other people – trade was limited ...
... homes and crops would be destroyed The desert on both sides of the Nile hindered travel and interaction with other people – trade was limited ...
Kingdom of the NIle - Pleasantville High School
... “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile” – Herodotus Why is the river so important???? 1) Deposited rich layer of silt (soil) used for farming 2) Used for transportation 3) Trade routes ...
... “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile” – Herodotus Why is the river so important???? 1) Deposited rich layer of silt (soil) used for farming 2) Used for transportation 3) Trade routes ...
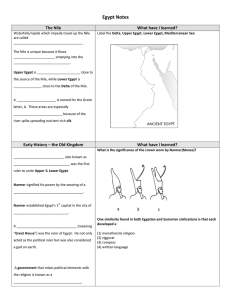
Egypt Notes
... ______________________________ was the first ruler to unite Upper & Lower Egypt. ...
... ______________________________ was the first ruler to unite Upper & Lower Egypt. ...
Grade 6 Study Guide Ancient Egypt Terms to Know Cataract: areas
... waters were diverted away from certain areas, such as cities and gardens, to keep them from flooding. Irrigation was also used to provide drinking water to Egyptians. Why Pharaohs had their pyramids built: Pharaohs had their pyramids built to serve as tombs where they would be buried and preserved ...
... waters were diverted away from certain areas, such as cities and gardens, to keep them from flooding. Irrigation was also used to provide drinking water to Egyptians. Why Pharaohs had their pyramids built: Pharaohs had their pyramids built to serve as tombs where they would be buried and preserved ...
egypt test study guide key
... 3. List the ways religion influenced every aspect of Egyptian life. Worshipped many powerful god and goddesses who they believed governed natural forces and human activities Believed in an afterlife that was better than life on Earth and though after a long journey the dead arrived at a place of ...
... 3. List the ways religion influenced every aspect of Egyptian life. Worshipped many powerful god and goddesses who they believed governed natural forces and human activities Believed in an afterlife that was better than life on Earth and though after a long journey the dead arrived at a place of ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.