* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pyramids on the Nile
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
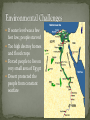
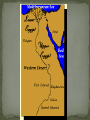
Chapter 2 Section 2 Do Now: Take out HW and switch with a partner; discuss your answers in a group Obj: Discuss environmental challenges surrounding the civilizations along the Nile Egyptian Life & Religion Compare/Contrast hieroglyphics and cuneiform HW: Active Reading pgs. #44- 49 Crit. Thinking #3-5 Delta Narmer Pharaoh Theocrasy Pyramid Mumification Hieroglyphics papyrus The Nile River supported early life in Egypt Yearly flooding left behind rich silt (farming) Egyptians viewed the Nile as a god Greek historian called Egypt, “the gift of the Nile” If water level was a few feet low; people starved Too high destroy homes and flood crops Forced people to live on very small area of Egypt Desert protected the people from constant warfare Upper Egypt: Southern part of Egypt above the first cataract Elevation is higher Boats can flow up river with the rivers current Lower Egypt: Northern Egypt where elevation is lower Leads to the Nile delta region Strong winds can bring boats down the river against the current Makes contact and trade very possible Upper and lower Egypt ruled by two kingdoms (3200 BC) United by King Narmer (King of Upper Egypt) King of Upper Egypt wore a white crown Lower Egypt wore a red crown Narmer Palette: both crowns as one Symbol of unification around 3000 BC Narmer settled his capital in Memphis, near where Upper and Lower Egypt met. Egyptian kings known as pharaohs ruled as gods Government ruled by religious authority is called theocracy Pharaohs had full responsibility for kingdoms well being Pharaohs reign was expected to last forever; so their tombs had to be as important as their palaces. Egyptians built massive structures called pyramids to honor their dead kings Religion: Polytheistic Over 2,000 gods Belief in after life Judged for their deeds If passed lived in Other World forever\ People of all classes planned their burials to ensure their passage to the Other World Royal Egyptians would be mummified, so that the body would not decay over time. Body would be placed in a tomb filled with material belongings to be used in the after life Social Pyramid Pharaohs Merchants and artisans Peasant Farmers and laborers Hieroglyphics: Greek- sacred carving Early writing; picture represented ideas Then pictures represented sounds Developed papyrus: Reeds from the Nile dried together to make paper like material Developed a calendar Using astronomy to predict time between flooding of the Nile. Solar Year: 365 days divided into 12 months of 30 days. Was accurate to a true solar year within 6 hours! Mathematics: Number system to help asses collecting taxes Geometry helped to reset boundary lines after floods and make accurate measurements for building pyramids