Lesson 2 Study Guide The Kingdoms of Egypt
... E. The title used by the rulers of ancient Egypt. F. A French scholar who figured out how to read the hieroglyphics on the Rosetta Stone. G. The way a country manages money and resources for the production of goods and services. H. The joining of separate parts, such as kingdoms, into one. I. A reed ...
... E. The title used by the rulers of ancient Egypt. F. A French scholar who figured out how to read the hieroglyphics on the Rosetta Stone. G. The way a country manages money and resources for the production of goods and services. H. The joining of separate parts, such as kingdoms, into one. I. A reed ...
WH4
... knew how to read and write. Being a scribe was an extremely difficult job because in total, there were hundreds of different hieroglyphs to remember. A scribe's job was highly regarded in Ancient Egypt. Although being a scribe was rewarding, the training could take as long as twelve years. ...
... knew how to read and write. Being a scribe was an extremely difficult job because in total, there were hundreds of different hieroglyphs to remember. A scribe's job was highly regarded in Ancient Egypt. Although being a scribe was rewarding, the training could take as long as twelve years. ...
Ancient Egypt Unit Test
... 4. The process of ____________________________ preserved the bodies of pharaohs for thousands of years. 5. Large triangular tombs of some pharaohs are ___________________________. 6. _______________________ are rapids in the south prevented the Nile from being used to invade Egypt. 7. Egyptian paper ...
... 4. The process of ____________________________ preserved the bodies of pharaohs for thousands of years. 5. Large triangular tombs of some pharaohs are ___________________________. 6. _______________________ are rapids in the south prevented the Nile from being used to invade Egypt. 7. Egyptian paper ...
Impact of Geography
... 23. In obeying their ___________________________, subjects believed that they were helping to maintain a ______________________ world order. 24. A ___________________________ in royal power could only mean that citizens were ______________________________ the gods and weakening that order. 25. Egypt ...
... 23. In obeying their ___________________________, subjects believed that they were helping to maintain a ______________________ world order. 24. A ___________________________ in royal power could only mean that citizens were ______________________________ the gods and weakening that order. 25. Egypt ...
Egyptian Civilization
... demotic, and Greek script Scholars found hieroglyphics to be a mystical form of writing ...
... demotic, and Greek script Scholars found hieroglyphics to be a mystical form of writing ...
Nile Civilizations-3
... After the reign of Ramses the Great, Egyptian power over Kush declined. By about 1100 BC, Kush was free from Egypt. In around 750 BC, a new Kushite kingdom grew up. Its ruler, Piankhi, decided to expand the kingdom to the north, into Egypt. In the end, Piankhi conquered all of Egypt and declared him ...
... After the reign of Ramses the Great, Egyptian power over Kush declined. By about 1100 BC, Kush was free from Egypt. In around 750 BC, a new Kushite kingdom grew up. Its ruler, Piankhi, decided to expand the kingdom to the north, into Egypt. In the end, Piankhi conquered all of Egypt and declared him ...
Egypt - LaVergne Middle School
... (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). Starts 1st Dynasty in Egypt; ...
... (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). Starts 1st Dynasty in Egypt; ...
Notes - 6th Grade Social Studies
... need in the spirit world, including clothing, furniture, jewelry, and food. Most of the work was done by ________________ during the Nile floods, when they could not tend their fields. In addition, surveyors, engineers, carpenters, and stonecutters lent their skills. Square base, with the entranc ...
... need in the spirit world, including clothing, furniture, jewelry, and food. Most of the work was done by ________________ during the Nile floods, when they could not tend their fields. In addition, surveyors, engineers, carpenters, and stonecutters lent their skills. Square base, with the entranc ...
Unit 4 Study Guide with answers
... Who were some of the gods that Ancient Egyptians believed in? ( list at least 3) Osiris, Ra, Isis, Amun, Hathor, Anubis ...
... Who were some of the gods that Ancient Egyptians believed in? ( list at least 3) Osiris, Ra, Isis, Amun, Hathor, Anubis ...
Egypt Test 2
... a. Cataract b. Akhet c. Menes d. Akkad 2. The kingdom of Kush arose south of Egypt in a land called what? a. Asswan b. Kushdom c. Nubia d. Assyria 3. In Chapter 3 we learned about Sargon I, who first united Mesopotamia under one ruler. Which Egyptian ruler’s accomplishments were most similar to Sarg ...
... a. Cataract b. Akhet c. Menes d. Akkad 2. The kingdom of Kush arose south of Egypt in a land called what? a. Asswan b. Kushdom c. Nubia d. Assyria 3. In Chapter 3 we learned about Sargon I, who first united Mesopotamia under one ruler. Which Egyptian ruler’s accomplishments were most similar to Sarg ...
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE
... KEY LEARNING(S): Egypt achieved many accomplishments such as great architecture. hieroglyphics, medicine, religious beliefs, and military conquests due to its location along the Nile River. UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S): What were the many achievements throughout Egypt’s Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms ? ...
... KEY LEARNING(S): Egypt achieved many accomplishments such as great architecture. hieroglyphics, medicine, religious beliefs, and military conquests due to its location along the Nile River. UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S): What were the many achievements throughout Egypt’s Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms ? ...
Ancient Egypt
... buy/sell/inherit property, right to divorce; but still expected to be subservient to men • Egyptians married young; The husband was the master, but the wife ran the household and educated the children (boys received a better education) • Marriages could end in divorce, which included compensation fo ...
... buy/sell/inherit property, right to divorce; but still expected to be subservient to men • Egyptians married young; The husband was the master, but the wife ran the household and educated the children (boys received a better education) • Marriages could end in divorce, which included compensation fo ...
Egypt GRAPES - LaVergne Middle School
... (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). Starts 1st Dynasty in Egypt; ...
... (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). Starts 1st Dynasty in Egypt; ...
Study Questions on Egypt on 5 Deben a Day Terms to define
... 48. Name 10 Egyptian gods and what they were god/ goddess of. 49. Why is Aketaten a ghost town and abandoned? 50. What was different about Aten? 51. How did Akhenaten attempt to change Egypt? How long did it last? 52. What happened toTutankhamun’s tomb? 53. Why was Abydos so sacred to the Egyptians? ...
... 48. Name 10 Egyptian gods and what they were god/ goddess of. 49. Why is Aketaten a ghost town and abandoned? 50. What was different about Aten? 51. How did Akhenaten attempt to change Egypt? How long did it last? 52. What happened toTutankhamun’s tomb? 53. Why was Abydos so sacred to the Egyptians? ...
File - Mr. Belter`s World History Virtual Classroom
... After the reign of Ramses the Great, Egyptian power over Kush declined. By about 1100 BC, Kush was free from Egypt. In around 750 BC, a new Kushite kingdom grew up. Its ruler, Piankhi, decided to expand the kingdom to the north, into Egypt. In the end, Piankhi conquered all of Egypt and declared him ...
... After the reign of Ramses the Great, Egyptian power over Kush declined. By about 1100 BC, Kush was free from Egypt. In around 750 BC, a new Kushite kingdom grew up. Its ruler, Piankhi, decided to expand the kingdom to the north, into Egypt. In the end, Piankhi conquered all of Egypt and declared him ...
Ancient Egypt
... They had advanced cities…. • Cities developed along the Nile River (longest river in the world). • The Nile River helped to unify Egypt’s cities and promote trade. • Each city had its own rituals, gods, and ruler. ...
... They had advanced cities…. • Cities developed along the Nile River (longest river in the world). • The Nile River helped to unify Egypt’s cities and promote trade. • Each city had its own rituals, gods, and ruler. ...
Egypitian civilization
... An advanced civilization: towns along Nile, temples, stone tombs, writing, potters, copper and gold for decorative art Farming key to civilization: surplus crops: wheat and barley, trading Sinai Peninsula: crossroad for trade between Egyptians and southwestern Asia Nile served as a “highway” for tra ...
... An advanced civilization: towns along Nile, temples, stone tombs, writing, potters, copper and gold for decorative art Farming key to civilization: surplus crops: wheat and barley, trading Sinai Peninsula: crossroad for trade between Egyptians and southwestern Asia Nile served as a “highway” for tra ...
Study Guide: Egypt and Kush
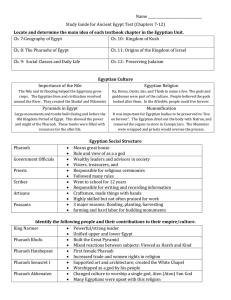
... Middle Class = scribes and craftspeople, lesser govt officials;Lower Class – 80% people and mostly farmers – worked on pharaoh projects in off season. Slaves and servants Trade with Nubia and Suria – materials for building Religion: all worship same gods, tons of them too, temples built and they col ...
... Middle Class = scribes and craftspeople, lesser govt officials;Lower Class – 80% people and mostly farmers – worked on pharaoh projects in off season. Slaves and servants Trade with Nubia and Suria – materials for building Religion: all worship same gods, tons of them too, temples built and they col ...
Chapter 3
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
Chapter 3
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
Answers - Schoolwires.net
... Supported art and architecture; created the White Chapel Worshipped as a god by his people Changed culture to worship a single god, Aten (Aton) Sun God Pharaoh Akhenaten Many Egyptians were upset with this religion ...
... Supported art and architecture; created the White Chapel Worshipped as a god by his people Changed culture to worship a single god, Aten (Aton) Sun God Pharaoh Akhenaten Many Egyptians were upset with this religion ...
Ancient Egypt Study Guide
... o Pyramids: huge stone tombs with four triangle shaped walls that met at a point on top o Rosetta Stone: a stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, text in Greek and a later form of Egyptian which helped scientists to decode the hieroglyphics o Hieroglyphics: Egyptian writing system of symbols which ...
... o Pyramids: huge stone tombs with four triangle shaped walls that met at a point on top o Rosetta Stone: a stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, text in Greek and a later form of Egyptian which helped scientists to decode the hieroglyphics o Hieroglyphics: Egyptian writing system of symbols which ...
Ancient Egypt
... Trade flourished, arts and literature flourished. Egypt built strong armies to defend herself against her neighbors. During the time period of the middle kingdom, pharaohs were expected to be good kings and wise rulers. • Pyramid building declined and stopped. • Orisis became the most important god, ...
... Trade flourished, arts and literature flourished. Egypt built strong armies to defend herself against her neighbors. During the time period of the middle kingdom, pharaohs were expected to be good kings and wise rulers. • Pyramid building declined and stopped. • Orisis became the most important god, ...
Early Civilizations: Nile, Eastern Mediterranean
... built an elaborate tomb mummification – the preservation of dead bodies by embalming and wrapping them in cloth Pyramids were built as ...
... built an elaborate tomb mummification – the preservation of dead bodies by embalming and wrapping them in cloth Pyramids were built as ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.