Ancient Egypt
... Also farmed but were most known for their warrior skills. More powerful Nubian villages took control over weaker ones and organized the kingdom of Kerma. ...
... Also farmed but were most known for their warrior skills. More powerful Nubian villages took control over weaker ones and organized the kingdom of Kerma. ...
Sample Questions for Chapter 1
... e. prevent decomposition during immersion in the Nile. 28. Egyptian hieroglyphs a. used sacred characters as picture signs. b. was entirely alphabetic (phonetic) c. were written only on a paper made from papyrus reed and oak bark. d. were introduced by the Amorites. e. both a and c 31. Which of the ...
... e. prevent decomposition during immersion in the Nile. 28. Egyptian hieroglyphs a. used sacred characters as picture signs. b. was entirely alphabetic (phonetic) c. were written only on a paper made from papyrus reed and oak bark. d. were introduced by the Amorites. e. both a and c 31. Which of the ...
Ancient Egypt - Spectrum Loves Social Studies
... – Corruption and rebellions were common – 1700 BC: Hyksos people invaded and took over the government for 100 years • Egypt and Hyksos shared technology and ideas ...
... – Corruption and rebellions were common – 1700 BC: Hyksos people invaded and took over the government for 100 years • Egypt and Hyksos shared technology and ideas ...
Ancient Egypt
... • The Nile is surrounded by deserts. • But the land near the river is perfect for farming. • The Nile also was used for trading and for the Pharaoh to move his soldiers. ...
... • The Nile is surrounded by deserts. • But the land near the river is perfect for farming. • The Nile also was used for trading and for the Pharaoh to move his soldiers. ...
First Age of Empires - Elizabeth School District C-1
... Hatshepsut—pharaoh whose reign most noted for her trade expeditions, not war. ...
... Hatshepsut—pharaoh whose reign most noted for her trade expeditions, not war. ...
Ancient Egypt
... 3. Thebes – An ancient city on the Nile River; Became the capital of the Egyptian Empire after the Hyksos period. 4. Kush – An ancient kingdom in Northeastern Africa, which flourished from about 751 B.C. to A.D. 400. 5. Valley of the Kings – An ancient burial place near the Nile River. Many ancient ...
... 3. Thebes – An ancient city on the Nile River; Became the capital of the Egyptian Empire after the Hyksos period. 4. Kush – An ancient kingdom in Northeastern Africa, which flourished from about 751 B.C. to A.D. 400. 5. Valley of the Kings – An ancient burial place near the Nile River. Many ancient ...
Blue Nile and White Nile 2) How
... up their settlements? The Nubians formed settlements before they began to farm, while the Mesopotamians developed their agriculture and then established settlements 9) Since Nubia had a shortage of farmland, how did the Nubians get the food that they needed? They added fish, ducks, and other birds t ...
... up their settlements? The Nubians formed settlements before they began to farm, while the Mesopotamians developed their agriculture and then established settlements 9) Since Nubia had a shortage of farmland, how did the Nubians get the food that they needed? They added fish, ducks, and other birds t ...
Egypt study guide answers
... 26) Who was the first pharaoh of Egypt? Menes 27) What group in the social hierarchy makes up the majority of people? Farmers and unskilled ...
... 26) Who was the first pharaoh of Egypt? Menes 27) What group in the social hierarchy makes up the majority of people? Farmers and unskilled ...
File - Dameron`s World History
... • King in Lower Egypt had a red crown • King in Upper Egypt had a white crown • When two become one…a new crown! • The two were united by king Narmer • A new capital was created at Memphis, where the kingdoms met…was the first of 31 dynasties for 2,600 years • Egyptians pharaohs (god kings) were wor ...
... • King in Lower Egypt had a red crown • King in Upper Egypt had a white crown • When two become one…a new crown! • The two were united by king Narmer • A new capital was created at Memphis, where the kingdoms met…was the first of 31 dynasties for 2,600 years • Egyptians pharaohs (god kings) were wor ...
Geography and Early Egypt
... form • all power was concentrated in the Pharaoah • the pharaoh was the head of a planned and organized economy • modern comparisons ??? ...
... form • all power was concentrated in the Pharaoah • the pharaoh was the head of a planned and organized economy • modern comparisons ??? ...
Ancient Egypt
... of spiritual characteristics unique to each individual.[30] Unlike the ka, the ba remained attached to the body after death. Egyptian funeral rituals were intended to release the ba from the body so that it could move freely, and to rejoin it with the ka so that it could live on as an akh. However, ...
... of spiritual characteristics unique to each individual.[30] Unlike the ka, the ba remained attached to the body after death. Egyptian funeral rituals were intended to release the ba from the body so that it could move freely, and to rejoin it with the ka so that it could live on as an akh. However, ...
cataract
... 11. The Nile River is the world’s longest river. 12. The Nile River flows from South to North. 13. The Nile flooded about the same time every year. 14. The Nile’s flood pattern was predictable. 15. The Nile River was used for trade and travel. 16. The hot desert protected Egypt from foreign attacks. ...
... 11. The Nile River is the world’s longest river. 12. The Nile River flows from South to North. 13. The Nile flooded about the same time every year. 14. The Nile’s flood pattern was predictable. 15. The Nile River was used for trade and travel. 16. The hot desert protected Egypt from foreign attacks. ...
History 4.3 Notes - The Wesley School
... History 4.3 Notes - The Middle Kingdom Reuniting the Kingdom - pg.151 ● 2181 B.C. - Old Kingdom ended with a ____________ war and drought which caused ________________, or food shortages. ● Middle Kingdom begins about __________ B.C. and lasts until _______ B.C. ● Dynasty 12 - greatest period in Mid ...
... History 4.3 Notes - The Middle Kingdom Reuniting the Kingdom - pg.151 ● 2181 B.C. - Old Kingdom ended with a ____________ war and drought which caused ________________, or food shortages. ● Middle Kingdom begins about __________ B.C. and lasts until _______ B.C. ● Dynasty 12 - greatest period in Mid ...
Notes sheet for 4.3
... History 4.3 Notes - The Middle Kingdom Reuniting the Kingdom - pg.151 ● 2181 B.C. - Old Kingdom ended with a ____________ war and drought which caused ________________, or food shortages. ● Middle Kingdom begins about __________ B.C. and lasts until _______ B.C. ● Dynasty 12 - greatest period in Mid ...
... History 4.3 Notes - The Middle Kingdom Reuniting the Kingdom - pg.151 ● 2181 B.C. - Old Kingdom ended with a ____________ war and drought which caused ________________, or food shortages. ● Middle Kingdom begins about __________ B.C. and lasts until _______ B.C. ● Dynasty 12 - greatest period in Mid ...
Study Guide - Teachers.AUSD.NET
... 6. What type of artisans existed in Egyptian society? What was daily life like for these artisans? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 7. In what way did the daily lives of peasants revolve around the Nile River? _________ ...
... 6. What type of artisans existed in Egyptian society? What was daily life like for these artisans? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 7. In what way did the daily lives of peasants revolve around the Nile River? _________ ...
1 Egyptian Culture 2 Geography of Egypt 3 4 The Gift of the Nile 5
... remarkable engineering built by people who had not even begun to use the wheel. in the pyramid at Giza, built mostly by peasants Egyptians mummified the body so the soul could return to it later. They were so good that archaeologists have found mummies that still have hair, skin, and teeth ...
... remarkable engineering built by people who had not even begun to use the wheel. in the pyramid at Giza, built mostly by peasants Egyptians mummified the body so the soul could return to it later. They were so good that archaeologists have found mummies that still have hair, skin, and teeth ...
Ch. 4 – Ancient Egypt and Kush – Review Sheet
... Rising to power in Upper Egypt, who wanted to unify Upper and Lower Egypt? _________________________________________ Historians believe Menes to be the first _______________________________, or _______________________________________________________________________________ Menes also started Egypt’s ...
... Rising to power in Upper Egypt, who wanted to unify Upper and Lower Egypt? _________________________________________ Historians believe Menes to be the first _______________________________, or _______________________________________________________________________________ Menes also started Egypt’s ...
Review for Egypt Unit Test: February 6th Ahmose: an Egyptian
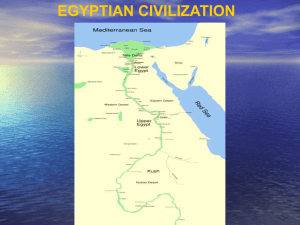
... Tutankhamen: son-in-law of Amenhotep IV, became pharaoh at age 9, he died at age 18 and during his reign, Egypt returned to honoring Amon-Re. Known as King Tut The area of rich fertile land where the Nile River flows into the Mediterranean Sea , the Nile Delta, was known as Lower Egypt. The land of ...
... Tutankhamen: son-in-law of Amenhotep IV, became pharaoh at age 9, he died at age 18 and during his reign, Egypt returned to honoring Amon-Re. Known as King Tut The area of rich fertile land where the Nile River flows into the Mediterranean Sea , the Nile Delta, was known as Lower Egypt. The land of ...
Ancient Egypt Presentation
... Nile is the longest river in the world Lower Egypt or the Nile delta = the area where the Nile splits in two, before it empties into the Mediterranean Upper Egypt = the land upstream ...
... Nile is the longest river in the world Lower Egypt or the Nile delta = the area where the Nile splits in two, before it empties into the Mediterranean Upper Egypt = the land upstream ...
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa
... the Hittite Empire,Assyrian Empire and Mitanni Empire, after which it entered a period of slow decline. Egypt was invaded or conquered by a succession of foreign powers (such as the Canaanites/Hyksos, Libyans , Nubians, Assyria, Babylonia, Persian rule and MacedonianGreece) in the Third Intermediate ...
... the Hittite Empire,Assyrian Empire and Mitanni Empire, after which it entered a period of slow decline. Egypt was invaded or conquered by a succession of foreign powers (such as the Canaanites/Hyksos, Libyans , Nubians, Assyria, Babylonia, Persian rule and MacedonianGreece) in the Third Intermediate ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.