The Egyptian Civilization
... • Historians divide Ancient Egyptian history into three periods: – Old Kingdom (2700 – 2200 BC) – Middle Kingdom (2055 – 1650 BC) – New Kingdom (1550 – 1070 BC) ...
... • Historians divide Ancient Egyptian history into three periods: – Old Kingdom (2700 – 2200 BC) – Middle Kingdom (2055 – 1650 BC) – New Kingdom (1550 – 1070 BC) ...
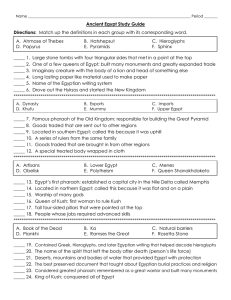
Ancient Egypt Study Guide
... - Describe the class system (social order) - Why did the Egyptians mummify their dead? - Why were tombs filled with art, jewelry and treasures? - Why was the Egyptian Middle Kingdom so short? - Why did Egypt become so wealthy during the New Kingdom? - List three reasons why Kush declines: ...
... - Describe the class system (social order) - Why did the Egyptians mummify their dead? - Why were tombs filled with art, jewelry and treasures? - Why was the Egyptian Middle Kingdom so short? - Why did Egypt become so wealthy during the New Kingdom? - List three reasons why Kush declines: ...
Egypt Notes page Geography • Nile River – 4,100 miles long, flows
... Wealthy or middle class women could own and trade property Women could propose marriage or seek divorce Intellectual The earliest form of writing was pictographs, then developed a more flexible system called hieroglyphics developed papyrus, a paper-like substance made from reeds. developed cal ...
... Wealthy or middle class women could own and trade property Women could propose marriage or seek divorce Intellectual The earliest form of writing was pictographs, then developed a more flexible system called hieroglyphics developed papyrus, a paper-like substance made from reeds. developed cal ...
Chapter 3
... a. Violence between Egypt and Nubia led to Nubian leaders organizing farther South in Upper Nubia. b. By 2500 bce they est. the kingdom of Kush c. Even though there were tensions both sought political diplomacies, alliances w/ each other and commercial relationships. d. Mercenaries prominent in Old ...
... a. Violence between Egypt and Nubia led to Nubian leaders organizing farther South in Upper Nubia. b. By 2500 bce they est. the kingdom of Kush c. Even though there were tensions both sought political diplomacies, alliances w/ each other and commercial relationships. d. Mercenaries prominent in Old ...
The Middle and New Kingdoms in ancient Egypt
... - Ahmose rises to power and brings Egypt back to glory - The New Kingdom lasts from 1550 BCE to 1050 BCE - How would the Egyptians prevent invasions in the future? - Egypt began to make a name for themselves across their region, and became very rich - With all of this conquered territory, Egyptians ...
... - Ahmose rises to power and brings Egypt back to glory - The New Kingdom lasts from 1550 BCE to 1050 BCE - How would the Egyptians prevent invasions in the future? - Egypt began to make a name for themselves across their region, and became very rich - With all of this conquered territory, Egyptians ...
Document
... like a castle. This citadel has served as the administrative center and as a military base. ...
... like a castle. This citadel has served as the administrative center and as a military base. ...
First Age of Empires 1570 B.C.–200 B.C..
... – The pharaohs of the Eighteenth Dynasty • A new army of archers, charioteers, and infantry ...
... – The pharaohs of the Eighteenth Dynasty • A new army of archers, charioteers, and infantry ...
Unit #3: Cradles of Civilization
... • Upper and Lower Egypt are united in 3200 BCE by Narmer, who settles the capital in Memphis near the 1st cataract and establishes the 1st dynasty (sequence of rulers from the same family) • Ancient Egypt would go on to have nearly 30 different dynasties, spanning a period of over 2600 years. ...
... • Upper and Lower Egypt are united in 3200 BCE by Narmer, who settles the capital in Memphis near the 1st cataract and establishes the 1st dynasty (sequence of rulers from the same family) • Ancient Egypt would go on to have nearly 30 different dynasties, spanning a period of over 2600 years. ...
ancient of egypt
... the Otherworld. It contained magic spells, prayers and hymns to the gods which were to be spoken on the journey into the afterlife. ...
... the Otherworld. It contained magic spells, prayers and hymns to the gods which were to be spoken on the journey into the afterlife. ...
TOPIC 2 READING GUIDE
... Egypt is often called “the gift of the Nile”. Why do you think this is? How are cataracts created along the Nile? What geographic features protected the Egyptians? Describe the flood patterns of the Nile. Explain how the Egyptians controlled the Nile’s flood waters. How did the Egyptians use geometr ...
... Egypt is often called “the gift of the Nile”. Why do you think this is? How are cataracts created along the Nile? What geographic features protected the Egyptians? Describe the flood patterns of the Nile. Explain how the Egyptians controlled the Nile’s flood waters. How did the Egyptians use geometr ...
2016-17 HISTORY-GRADE: VI THE EGYPTIAN
... The Egyptian deserts served as natural barriers to foreign invasions. So the early Egyptian settlers enjoyed many years of peace and security during which they learnt to build huts, grow crops, domesticate animals and establish a society of their own. Egypt was divided into two parts –Lower Egypt an ...
... The Egyptian deserts served as natural barriers to foreign invasions. So the early Egyptian settlers enjoyed many years of peace and security during which they learnt to build huts, grow crops, domesticate animals and establish a society of their own. Egypt was divided into two parts –Lower Egypt an ...
Notes from sept 3 B
... from mountains of eastcentral Africa – Nile River rose and spilled over its banks – Egyptians worshiped Nile River like a god ...
... from mountains of eastcentral Africa – Nile River rose and spilled over its banks – Egyptians worshiped Nile River like a god ...
Early Civilizations: Mesopotamia
... 4. Unification: Two kingdoms unified around ________ BC; Upper Egypt ruler ______________ conquered north, ______________ capital city, adopted both symbols (snake and vulture). First of ______ dynasties. E. The Old Kingdom 1. Many of the institutions for which the Egyptian civilization is known wer ...
... 4. Unification: Two kingdoms unified around ________ BC; Upper Egypt ruler ______________ conquered north, ______________ capital city, adopted both symbols (snake and vulture). First of ______ dynasties. E. The Old Kingdom 1. Many of the institutions for which the Egyptian civilization is known wer ...
Name Period Date Chapter 5: Egypt Review Packet Lesson 1 ____
... 1. The ruler who wore the Double Crown reigned over both ____________________ and ____________________ Egypt. 2. More than 30 dynasties ruled ancient Egypt. Historians divide Egypt’s history into the ____________________ Kingdom, ____________________ Kingdom, and ____________________ Kingdom. 3. Bec ...
... 1. The ruler who wore the Double Crown reigned over both ____________________ and ____________________ Egypt. 2. More than 30 dynasties ruled ancient Egypt. Historians divide Egypt’s history into the ____________________ Kingdom, ____________________ Kingdom, and ____________________ Kingdom. 3. Bec ...
Ancient Egypt notes
... 1. The Old Kingdom is sometimes called the Pyramid Age because during this time the Egyptians built the majestic pyramid that still stands at Giza, near present day Cairo. The pyramids were tombs for eternity. Because the Egyptians believed in an afterlife, they preserved the bodies of their dead ru ...
... 1. The Old Kingdom is sometimes called the Pyramid Age because during this time the Egyptians built the majestic pyramid that still stands at Giza, near present day Cairo. The pyramids were tombs for eternity. Because the Egyptians believed in an afterlife, they preserved the bodies of their dead ru ...
The Nile Valley
... 1. Nubia arose in the region of present-day Libya. 2. Powerful Nubian villages created the kingdom of Kerma. 3. After being conquered by the Egyptian forces under Thutmose III, the people of Nubia adopted many Egyptian ways. 4. The Kushite kingdom was formed at the high point of Egypt’s power. 5. Fo ...
... 1. Nubia arose in the region of present-day Libya. 2. Powerful Nubian villages created the kingdom of Kerma. 3. After being conquered by the Egyptian forces under Thutmose III, the people of Nubia adopted many Egyptian ways. 4. The Kushite kingdom was formed at the high point of Egypt’s power. 5. Fo ...
Capitalization, Punctuation, and Compound Words
... Nile River The longest river in the world; flows from Eastern Africa to a delta in northeastern Egypt ...
... Nile River The longest river in the world; flows from Eastern Africa to a delta in northeastern Egypt ...
The Middle and New Kingdom
... The wealth and power of the pharaohs began to decline at the end of the Old Kingdom. At the same time ambitious nobles used their positions to take power from the pharaohs. Over time they took all of the power from the pharaohs and for 160 years the kingdom did not have a central ruler. ...
... The wealth and power of the pharaohs began to decline at the end of the Old Kingdom. At the same time ambitious nobles used their positions to take power from the pharaohs. Over time they took all of the power from the pharaohs and for 160 years the kingdom did not have a central ruler. ...
Ancient Nile Civ - Myers World History
... Two Kingdoms of Egypt Unite Into One • Monarchy- Kingdom headed by one ruler (Both Upper and Lower Egypt were Monarchies) • Menes, king of upper Egypt unites them(3200 B.C.) • Successors crush rebellions, gain new territories, regulate irrigation, and encouraged trade ...
... Two Kingdoms of Egypt Unite Into One • Monarchy- Kingdom headed by one ruler (Both Upper and Lower Egypt were Monarchies) • Menes, king of upper Egypt unites them(3200 B.C.) • Successors crush rebellions, gain new territories, regulate irrigation, and encouraged trade ...
Chapter 3 - Ancient Egypt and Nubia MP
... • Nubia was a kingdom to the south of Egypt • They were separated by a cataract on the Nile • Since their land was very rocky, they developed sturdy farming tools • Nubians grew food, used irrigation and had their own language • Written language, Merotic, had not been decoded • Egypt and Nubia had s ...
... • Nubia was a kingdom to the south of Egypt • They were separated by a cataract on the Nile • Since their land was very rocky, they developed sturdy farming tools • Nubians grew food, used irrigation and had their own language • Written language, Merotic, had not been decoded • Egypt and Nubia had s ...
Invasions and Empires in Egypt
... the Egyptian way of life, they were still considered unwelcome outsiders. They were only able to control the region around the Nile Delta. The rest of the Nile valley was divided between two other kingdoms— Thebes and a kingdom ruled by Nubian princes. Under the leadership of Kamose, the Thebans mas ...
... the Egyptian way of life, they were still considered unwelcome outsiders. They were only able to control the region around the Nile Delta. The rest of the Nile valley was divided between two other kingdoms— Thebes and a kingdom ruled by Nubian princes. Under the leadership of Kamose, the Thebans mas ...
Pyramids - WordPress.com
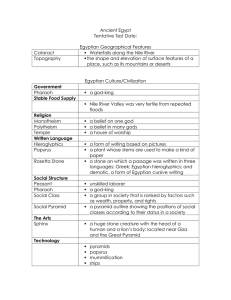
... a plant whose stems are used to make a kind of paper a stone on which a passage was written in three languages: Greek; Egyptian hieroglyphics; and demotic, a form of Egyptian cursive writing unskilled laborer a god-king a group in society that is ranked by factors such as wealth, property, ...
... a plant whose stems are used to make a kind of paper a stone on which a passage was written in three languages: Greek; Egyptian hieroglyphics; and demotic, a form of Egyptian cursive writing unskilled laborer a god-king a group in society that is ranked by factors such as wealth, property, ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.