Chapter 3 Study Guide Ancient Egypt and Nubia
... 22. The Nile River flows to the _________________________. 23. What two rivers come together to create the Nile River? 24. Define Nile DELTA – ...
... 22. The Nile River flows to the _________________________. 23. What two rivers come together to create the Nile River? 24. Define Nile DELTA – ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... and sentences. At first they wrote on stone. Later they began to make a kind of paper from the papyrus plant. The Egyptians invented a system of written numbers and a calendar. Their calendar had 12 months, each of which had 30 days. They were famous in the ancient world for their ideas in medicine. ...
... and sentences. At first they wrote on stone. Later they began to make a kind of paper from the papyrus plant. The Egyptians invented a system of written numbers and a calendar. Their calendar had 12 months, each of which had 30 days. They were famous in the ancient world for their ideas in medicine. ...
Early_African_Civili.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... In 2650 B.C.E the ruler Zoser ordered the construction of Egypt’s first pyramid. His chief advisor Imhotep built the structure, which rose more than 200 feet. It was made of six stone platforms. Today the so-called ‘Step Pyramid’, located at Saqqara, is the oldest standing building in the ...
... In 2650 B.C.E the ruler Zoser ordered the construction of Egypt’s first pyramid. His chief advisor Imhotep built the structure, which rose more than 200 feet. It was made of six stone platforms. Today the so-called ‘Step Pyramid’, located at Saqqara, is the oldest standing building in the ...
The Geography of Egypt, Kush, and Canaan
... 1. What were the different social classes that made up the social pyramid of Ancient Egypt? Describe 2 - 3 details about each. (6 groups) 2. What did the Egyptians believe the afterlife would be like? How was the body and tomb prepared? The Kingdom of Kush: Chapter 10 1. Where was Kush located? Was ...
... 1. What were the different social classes that made up the social pyramid of Ancient Egypt? Describe 2 - 3 details about each. (6 groups) 2. What did the Egyptians believe the afterlife would be like? How was the body and tomb prepared? The Kingdom of Kush: Chapter 10 1. Where was Kush located? Was ...
Chapter 2 / Section 3
... About 2300 B.C., pharaohs lost control of Egypt due to nobles fighting over power. Finally, a new dynasty of pharaohs came to power and moved the capital south, from Memphis to Thebes (theebz). This began the Middle Kingdom which lasted from about 2050 B.C. to 1670 B.C. and was a time of stabi ...
... About 2300 B.C., pharaohs lost control of Egypt due to nobles fighting over power. Finally, a new dynasty of pharaohs came to power and moved the capital south, from Memphis to Thebes (theebz). This began the Middle Kingdom which lasted from about 2050 B.C. to 1670 B.C. and was a time of stabi ...
File - Mr. Butts World History
... Scholars divide the history of ancient Egypt into three main periods: the Old Kingdom (about 2575 B.C. to 2130 B.C.), the Middle Kingdom (about 1938 B.C. to 1630 B.C.), and the New Kingdom (about 1539 B.C. to 1075 B.C.). Although power passed from one dynasty, or ruling family, to another, the land ...
... Scholars divide the history of ancient Egypt into three main periods: the Old Kingdom (about 2575 B.C. to 2130 B.C.), the Middle Kingdom (about 1938 B.C. to 1630 B.C.), and the New Kingdom (about 1539 B.C. to 1075 B.C.). Although power passed from one dynasty, or ruling family, to another, the land ...
Ancient Egypt Review
... • A great pharaoh from the time of the New Kingdom of Egypt • Defended Egypt against enemies ...
... • A great pharaoh from the time of the New Kingdom of Egypt • Defended Egypt against enemies ...
Egyptian civilization last 3000 years.
... life-enriching and not threatening Civilization was rural with many small population centers along a narrow band on both sides of the river The river splits into two major branches in the end forming the delta, called the Lower Egypt ...
... life-enriching and not threatening Civilization was rural with many small population centers along a narrow band on both sides of the river The river splits into two major branches in the end forming the delta, called the Lower Egypt ...
Ancient Egypt - Maple River Schools
... United Egypt • Skillful farming leads to a surplus • Less workers needed in the fields and skilled workers develop( artisans make pottery, cloth, copper tools and weapons, and carved ...
... United Egypt • Skillful farming leads to a surplus • Less workers needed in the fields and skilled workers develop( artisans make pottery, cloth, copper tools and weapons, and carved ...
Ancient Egypt
... in order to be able to serve his king when the Pharaoh awoke in the afterlife. Ma’at: The Pharoah possessed complete authority. The king ruled as a living god. His chief responsibility was to rule according to “Ma’at.” Ma’at is an untranslatable Egyptian concept that includes justice, right, truth, ...
... in order to be able to serve his king when the Pharaoh awoke in the afterlife. Ma’at: The Pharoah possessed complete authority. The king ruled as a living god. His chief responsibility was to rule according to “Ma’at.” Ma’at is an untranslatable Egyptian concept that includes justice, right, truth, ...
Egypt
... Another benefit for the Egyptians was a plant called _____________________, which was used to make paper. 8) In 3100 BCE, Upper and Lower Egypt ___________________ and ______________________ was the ruler. 9) Use the timeline to answer these questions A) Old Kingdom B) Middle Kingdom C) New Kingdom ...
... Another benefit for the Egyptians was a plant called _____________________, which was used to make paper. 8) In 3100 BCE, Upper and Lower Egypt ___________________ and ______________________ was the ruler. 9) Use the timeline to answer these questions A) Old Kingdom B) Middle Kingdom C) New Kingdom ...
Ancient mapping challenge
... fertile soil was about six miles wide along each side of the river. Egyptians called the land surrounding the river banks Kemet or “black land” because the soil was rich and fertile. Draw three rakes along the river to show that they used that area for farming. 5. The Nile has many cataracts that ma ...
... fertile soil was about six miles wide along each side of the river. Egyptians called the land surrounding the river banks Kemet or “black land” because the soil was rich and fertile. Draw three rakes along the river to show that they used that area for farming. 5. The Nile has many cataracts that ma ...
Class Notes / Learning Log / Textbook Notes
... to grow their crops. Around 3100 B.C., Egypt’s two major kingdoms, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, were combined into one Egyptian society was divided into social groups based on wealth and power. Egypt was ruled by allpowerful pharaohs. The Egyptians believed in many gods and goddesses and in life aft ...
... to grow their crops. Around 3100 B.C., Egypt’s two major kingdoms, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, were combined into one Egyptian society was divided into social groups based on wealth and power. Egypt was ruled by allpowerful pharaohs. The Egyptians believed in many gods and goddesses and in life aft ...
blank student outlines for notes, if lost.
... 2. _______________ system needed for taxes, but clumsy 3. From need to survey after each flood, the Egyptians developed the origin of __________________ 4. A calendar to help with planting was created based on the ...
... 2. _______________ system needed for taxes, but clumsy 3. From need to survey after each flood, the Egyptians developed the origin of __________________ 4. A calendar to help with planting was created based on the ...
History Study Guide Ch_ 4 _ 5 blank
... 41. How were Kushites different from the Egyptians? True and False: Write out the whole word Mesopotamia means "the land between two rivers" in Greek Mesopotamia began between the Euphrates and Nile river The farmers in Mesopotamia did not know when the Tigris and Euphrates rivers would flood or dry ...
... 41. How were Kushites different from the Egyptians? True and False: Write out the whole word Mesopotamia means "the land between two rivers" in Greek Mesopotamia began between the Euphrates and Nile river The farmers in Mesopotamia did not know when the Tigris and Euphrates rivers would flood or dry ...
File
... and Isis was more emotional and more Egyptians felt connected to it; Osiris once ruled Egypt until his jealous brother Set killed him and cast pieces of him across the Nile. Isis retrieved all the pieces and resurrected him. But because Osiris was partially dead, he could no longer rule the living a ...
... and Isis was more emotional and more Egyptians felt connected to it; Osiris once ruled Egypt until his jealous brother Set killed him and cast pieces of him across the Nile. Isis retrieved all the pieces and resurrected him. But because Osiris was partially dead, he could no longer rule the living a ...
Chapter 2 / Section 3 - Ms-Jernigans-SS
... About 2300 B.C., pharaohs lost control of Egypt due to nobles fighting over power. Finally, a new dynasty of pharaohs came to power and moved the capital south, from Memphis to Thebes (theebz). This began the Middle Kingdom which lasted from about 2050 B.C. to 1670 B.C. and was a time of stabi ...
... About 2300 B.C., pharaohs lost control of Egypt due to nobles fighting over power. Finally, a new dynasty of pharaohs came to power and moved the capital south, from Memphis to Thebes (theebz). This began the Middle Kingdom which lasted from about 2050 B.C. to 1670 B.C. and was a time of stabi ...
3. Complete the cloze passage below.
... Defeated forces in southern Syria and fought off the Hittites. He had a major building program where he constructed gardens, orchards, and temples---including the famous Temple of Karnak. ...
... Defeated forces in southern Syria and fought off the Hittites. He had a major building program where he constructed gardens, orchards, and temples---including the famous Temple of Karnak. ...
Background of the Nile and Egyptians
... Egyptian tradition credits the uniting of Upper and Lower Egypt to a king called Menes. But that is merely a word meaning 'founder'. It is possible that the real historical figure is a ruler by the name of Narmer, who features in warlike mood on an early slate plaque. Whatever the name, the first hi ...
... Egyptian tradition credits the uniting of Upper and Lower Egypt to a king called Menes. But that is merely a word meaning 'founder'. It is possible that the real historical figure is a ruler by the name of Narmer, who features in warlike mood on an early slate plaque. Whatever the name, the first hi ...
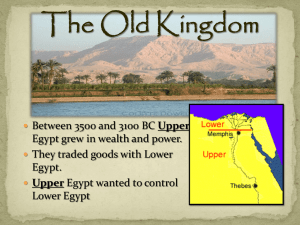
The Old Kingdom - Kingdom of Reese
... By 2500 BC, Egyptians had invented new techniques for making a mummy. They removed all the organs and placed them in jars, however, the heart they returned to the body. ...
... By 2500 BC, Egyptians had invented new techniques for making a mummy. They removed all the organs and placed them in jars, however, the heart they returned to the body. ...
Chapter 2, Section 3 – The Egyptian Empire The Middle Kingdom
... Chapter 2, Section 3 – The Egyptian Empire ...
... Chapter 2, Section 3 – The Egyptian Empire ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.