Properties of Solids and Fluids
... • Viscosity is a measure of the material’s resistance to flow. • High viscosity fluids take longer to pour from their containers than low viscosity fluids. • Demonstration ...
... • Viscosity is a measure of the material’s resistance to flow. • High viscosity fluids take longer to pour from their containers than low viscosity fluids. • Demonstration ...
turbulent flow - SNS Courseware
... 2. over a sharp expansion corner, entropy can increase 3. over a gradual compression, entropy can remain constant ...
... 2. over a sharp expansion corner, entropy can increase 3. over a gradual compression, entropy can remain constant ...
Conservation of Energy Due to the fact that in a nonviscous flow
... Equation. However, the following restrictions have to be made: 1. The motion is irrotational, (where v is velocity field) 2. The external force is conservative, (where U is potential energy/unit mass) 3. The fluid is incompressible with fixed constant density, For an isentropic irrotational flow, Be ...
... Equation. However, the following restrictions have to be made: 1. The motion is irrotational, (where v is velocity field) 2. The external force is conservative, (where U is potential energy/unit mass) 3. The fluid is incompressible with fixed constant density, For an isentropic irrotational flow, Be ...
10.7 Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle 10.8 Fluids in Motion
... 1. Students will explain the principles associated to Archimedes Principle. 2. Students will relate the various flow rates to forces and motion. 3. Students will explain how Bernoulli’s equation is applied. 4. Students will relate viscosity to flow in tubes. ...
... 1. Students will explain the principles associated to Archimedes Principle. 2. Students will relate the various flow rates to forces and motion. 3. Students will explain how Bernoulli’s equation is applied. 4. Students will relate viscosity to flow in tubes. ...
Lab 5 - Wright State University
... pipe, and a bank of manometers. The centrifugal pump forces the water from the recirculation tank through the valve and past the orifice plate flow meter, which was calibrated in Lab 4. Downstream from the flow meter is a length of ½ inch copper pipe, a length of ½ inch stainless steel pipe, and a l ...
... pipe, and a bank of manometers. The centrifugal pump forces the water from the recirculation tank through the valve and past the orifice plate flow meter, which was calibrated in Lab 4. Downstream from the flow meter is a length of ½ inch copper pipe, a length of ½ inch stainless steel pipe, and a l ...
OH 5: Fluid Dynamics
... Increasing Stability in Dynamic Equilibrium Enlarge the body’s base of support in the direction of the external horizontal forces Adopt a starting position in which the centre of pressure is close to the edge of the base of support whenever a quick acceleration is important When slowing down o ...
... Increasing Stability in Dynamic Equilibrium Enlarge the body’s base of support in the direction of the external horizontal forces Adopt a starting position in which the centre of pressure is close to the edge of the base of support whenever a quick acceleration is important When slowing down o ...
Determination of viscosity with Ostwald viscometer
... The liquid is added to the viscometer, pulled into the upper reservoir by suction, and then allowed to drain by gravity back into the lower reservoir. The time that it takes for the liquid to pass between two etched marks, one above and one bellow the upper reservoir, is measured. If the level of th ...
... The liquid is added to the viscometer, pulled into the upper reservoir by suction, and then allowed to drain by gravity back into the lower reservoir. The time that it takes for the liquid to pass between two etched marks, one above and one bellow the upper reservoir, is measured. If the level of th ...
SCALE UP OF HIGH SHEAR WET GRANULATION PROCESS
... flow uniformity of mixture before tableting.The high shear mixers are widely used for wet granulation process, because it permits to obtain uniformity in the size distribution of the granules. The granulation process is sensitive to change in powder characteristics and process factors. During the de ...
... flow uniformity of mixture before tableting.The high shear mixers are widely used for wet granulation process, because it permits to obtain uniformity in the size distribution of the granules. The granulation process is sensitive to change in powder characteristics and process factors. During the de ...
Conductors and Insulators
... this means that the electric current produces a magnetic field When this wire is twisted into loops, the magnetism gets stronger. this is called a solenoid ...
... this means that the electric current produces a magnetic field When this wire is twisted into loops, the magnetism gets stronger. this is called a solenoid ...
3Feb05_lec
... Where D = depth and gD = speed (celerity) of the gravitational wave. Fr >1 occurs in fast and/or shallow flows; Fr <1 occurs in slow and/or deep flows) What is a gravity wave? Throw a stone into a standing body of water and watch the waves move out in concentric paths – this is a gravity wave; now t ...
... Where D = depth and gD = speed (celerity) of the gravitational wave. Fr >1 occurs in fast and/or shallow flows; Fr <1 occurs in slow and/or deep flows) What is a gravity wave? Throw a stone into a standing body of water and watch the waves move out in concentric paths – this is a gravity wave; now t ...
Important Engineering and HydroGeologic Properties of
... Under relatively low loads of relatively short duration, nearly all solid materials, including rocks, deform in a recoverable manner. In other words, if the loads are relaxed, the material rebounds to its original shape. This is called elastic deformation. Under sufficiently large loads or over suff ...
... Under relatively low loads of relatively short duration, nearly all solid materials, including rocks, deform in a recoverable manner. In other words, if the loads are relaxed, the material rebounds to its original shape. This is called elastic deformation. Under sufficiently large loads or over suff ...
Document
... Definition of “Mechanics” Science concerned with the motion of bodies under the action of forces, including the special case in which a body remains at rest. Of first concern in the problem of motion are the forces that bodies exert on one another. This leads to the study of such topics as gravitati ...
... Definition of “Mechanics” Science concerned with the motion of bodies under the action of forces, including the special case in which a body remains at rest. Of first concern in the problem of motion are the forces that bodies exert on one another. This leads to the study of such topics as gravitati ...
Fully Developed Couette Flow - Pharos University in Alexandria
... • For the given geometry and BC’s, calculate the velocity and pressure fields, and estimate the shear force per unit area acting on the bottom plate • Step 1: Geometry, dimensions, and properties ...
... • For the given geometry and BC’s, calculate the velocity and pressure fields, and estimate the shear force per unit area acting on the bottom plate • Step 1: Geometry, dimensions, and properties ...
2014 Award for Outstanding Graduate Research in Polymer Chemistry will... Ph.D. in Chemical Engineering in 2012 at the University of... Felix S. Kim
... The 2014 Award for Outstanding Graduate Research in Polymer Chemistry will be presented to Dr. Felix S. Kim at the ACS National Meeting in San Francisco August 10-14, 2014. Dr. Kim completed the Ph.D. in Chemical Engineering in 2012 at the University of Washington with Prof. Samson Jenekhe. His Ph.D ...
... The 2014 Award for Outstanding Graduate Research in Polymer Chemistry will be presented to Dr. Felix S. Kim at the ACS National Meeting in San Francisco August 10-14, 2014. Dr. Kim completed the Ph.D. in Chemical Engineering in 2012 at the University of Washington with Prof. Samson Jenekhe. His Ph.D ...
Fluid Mechanics Primer
... Important fluid properties -2 • If one element of a fluid moves, it tends to carry other elements with it… that is, a fluid tends to stick to itself. • Dynamic viscosity represents the rate at which motion or momentum can be transferred through the flow. • Fluids can not have an abrupt discontinuit ...
... Important fluid properties -2 • If one element of a fluid moves, it tends to carry other elements with it… that is, a fluid tends to stick to itself. • Dynamic viscosity represents the rate at which motion or momentum can be transferred through the flow. • Fluids can not have an abrupt discontinuit ...
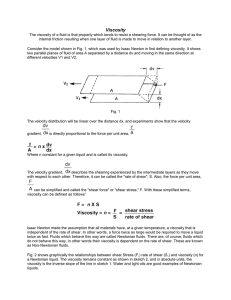
Introduction to Viscosity
... There are two basic viscosity parameters: dynamic (or absolute) viscosity and kinematic viscosity. Dynamic viscosities are given in terms of force requiredto move a unit area a unit distance. This is usually expressed in pound-seconds per square foot in the English system which is equal to slugs per ...
... There are two basic viscosity parameters: dynamic (or absolute) viscosity and kinematic viscosity. Dynamic viscosities are given in terms of force requiredto move a unit area a unit distance. This is usually expressed in pound-seconds per square foot in the English system which is equal to slugs per ...
Sample Paper
... (c) The two inertial terms are of the same order (d) Viscous term(s) are of the same order as inertial term(s) 8. For steady, uniform flow over a sufficiently long plate: (a) Flow will always transit from laminar to turbulent (b) Boundary layer will separate at the transition point (c) Laminar bound ...
... (c) The two inertial terms are of the same order (d) Viscous term(s) are of the same order as inertial term(s) 8. For steady, uniform flow over a sufficiently long plate: (a) Flow will always transit from laminar to turbulent (b) Boundary layer will separate at the transition point (c) Laminar bound ...
FLUID MECHANICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
... materials, petroleum, pharmaceutical, polymers and waste-processing industries. So what is a Fluid? A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear for ...
... materials, petroleum, pharmaceutical, polymers and waste-processing industries. So what is a Fluid? A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear for ...