Where is the blood?
... Flow = CO (mL/min) CO at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Aortic flow at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Blood flows from high pressure to low pressure – Down the pressure gradient ...
... Flow = CO (mL/min) CO at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Aortic flow at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Blood flows from high pressure to low pressure – Down the pressure gradient ...
Chap 5 Instruments
... Only give an estimate of flow Float can be magnetized inside steel tube Designed for specific small range ...
... Only give an estimate of flow Float can be magnetized inside steel tube Designed for specific small range ...
UNDERVISNING I TPM VED HiB
... r = Fluid Density [kg/m3] V = Fluid Velocity [m/s] g = Gravitational Acceleration Constant [m/s2] h = Pressure Height or Submergence [m] ...
... r = Fluid Density [kg/m3] V = Fluid Velocity [m/s] g = Gravitational Acceleration Constant [m/s2] h = Pressure Height or Submergence [m] ...
The flow meter to be used in the _____ project is a device that
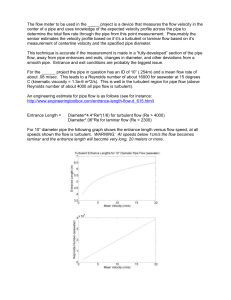
... flow, away from pipe entrances and exits, changes in diameter, and other deviations from a smooth pipe. Entrance and exit conditions are probably the biggest issue. For the ______ project the pipe in question has an ID of 10” (.254m) and a mean flow rate of about .08 m/sec. This leads to a Reynolds ...
... flow, away from pipe entrances and exits, changes in diameter, and other deviations from a smooth pipe. Entrance and exit conditions are probably the biggest issue. For the ______ project the pipe in question has an ID of 10” (.254m) and a mean flow rate of about .08 m/sec. This leads to a Reynolds ...
Linear Algebra
... layer x y and 2 x 2 2 y 2 . Distances in the x direction over which the velocity varies appreciably are of order L, but those of the y direction are of order δ, which is much smaller than L. o u v Schematic of airfoil without and with circulation: ...
... layer x y and 2 x 2 2 y 2 . Distances in the x direction over which the velocity varies appreciably are of order L, but those of the y direction are of order δ, which is much smaller than L. o u v Schematic of airfoil without and with circulation: ...
Template for the Design Expo Poster (PowerPoint)
... SUGGESTED HEADER SIZE: BELOW IS A SUGGESTED TEXT SIZE AND COLOR ...
... SUGGESTED HEADER SIZE: BELOW IS A SUGGESTED TEXT SIZE AND COLOR ...
FLUID MECHANICS Q3 Solutions
... FD = f(d1, d2, V, μ, ρ) where d1 is the outer diameter, d2 the inner diameter, V the fluid velocity, μ the fluid viscosity, and ρ the fluid density. Some experiments are to be performed in a wind tunnel to determine the drag force. By dimensional analysis, find the dimensionless parameters that you ...
... FD = f(d1, d2, V, μ, ρ) where d1 is the outer diameter, d2 the inner diameter, V the fluid velocity, μ the fluid viscosity, and ρ the fluid density. Some experiments are to be performed in a wind tunnel to determine the drag force. By dimensional analysis, find the dimensionless parameters that you ...
FLUID MECHANICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
... materials, petroleum, pharmaceutical, polymers and waste-processing industries. So what is a Fluid? A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear for ...
... materials, petroleum, pharmaceutical, polymers and waste-processing industries. So what is a Fluid? A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear for ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... GOALS (STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES): By the end of this course, the student will be able to: ...
... GOALS (STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES): By the end of this course, the student will be able to: ...
Fluid Mechanics - ODU - Old Dominion University
... Liquid: A state of matter in which the molecules are relatively free to change their positions with respect to each other but restricted by cohesive forces so as to maintain a relatively fixed volume Gas: a state of matter in which the molecules are practically unrestricted by cohesive forces. A gas ...
... Liquid: A state of matter in which the molecules are relatively free to change their positions with respect to each other but restricted by cohesive forces so as to maintain a relatively fixed volume Gas: a state of matter in which the molecules are practically unrestricted by cohesive forces. A gas ...
Fluid Mechanics Intro Slides.
... Liquid: A state of matter in which the molecules are relatively free to change their positions with respect to each other but restricted by cohesive forces so as to maintain a relatively fixed volume Gas: a state of matter in which the molecules are practically unrestricted by cohesive forces. A gas ...
... Liquid: A state of matter in which the molecules are relatively free to change their positions with respect to each other but restricted by cohesive forces so as to maintain a relatively fixed volume Gas: a state of matter in which the molecules are practically unrestricted by cohesive forces. A gas ...
Aula Teórica 17
... Adverse pressure gradient • In case of the adverse pressure gradient pressure force decreases the velocity and can invert the sense of the flow. • For layers close to the wall the forward shear stress (above) is larger that the backward shear (below) and thus friction contribute to keep the forward ...
... Adverse pressure gradient • In case of the adverse pressure gradient pressure force decreases the velocity and can invert the sense of the flow. • For layers close to the wall the forward shear stress (above) is larger that the backward shear (below) and thus friction contribute to keep the forward ...
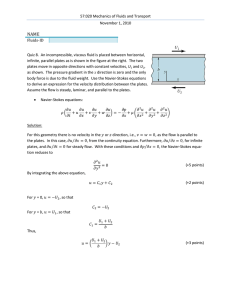
57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport
... 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport November 1, 2010 ...
... 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport November 1, 2010 ...
A Measure of Stream Turbulence
... Reynolds numbers less than 500 refer to laminar flow, which is steady and smooth. Under conditions of laminar flow, flow behavior is determined primarily by the fluid viscosity. Reynolds numbers greater than 2000 (or 2500 depending on the reference source) refer to turbulent flow, which is unsteady ...
... Reynolds numbers less than 500 refer to laminar flow, which is steady and smooth. Under conditions of laminar flow, flow behavior is determined primarily by the fluid viscosity. Reynolds numbers greater than 2000 (or 2500 depending on the reference source) refer to turbulent flow, which is unsteady ...
Types of sediment load
... • saltation (hopping)--grains are temporarily suspended by fluid vortices or by ballistic impact and then released • Grain movement may be continuous or intermittent depending on the flow regime (strength of flow as defined by Froude Number). ...
... • saltation (hopping)--grains are temporarily suspended by fluid vortices or by ballistic impact and then released • Grain movement may be continuous or intermittent depending on the flow regime (strength of flow as defined by Froude Number). ...
Document
... Physical meaning of fluid stress components σxy and σxx ? (a) σxy is the shear stress acting on the surface element perpendicular to the x-axis. σxy is parallel to the surface and points to the y direction .σxx is the normal stress pointing to the x direction and acting on the surface element perpen ...
... Physical meaning of fluid stress components σxy and σxx ? (a) σxy is the shear stress acting on the surface element perpendicular to the x-axis. σxy is parallel to the surface and points to the y direction .σxx is the normal stress pointing to the x direction and acting on the surface element perpen ...
There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and
... Ch-3. There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and sediments deposits. Reynolds Number Froude Number ...
... Ch-3. There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and sediments deposits. Reynolds Number Froude Number ...