The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4th ed Donald R
... of only one crystal (there are no grain boundaries). Grains are the crystals in a polycrystalline material. Polycrystalline material is a material comprised of many crystals (as opposed to a single-crystal material that has only one crystal). Grain boundaries are regions between grains of a ...
... of only one crystal (there are no grain boundaries). Grains are the crystals in a polycrystalline material. Polycrystalline material is a material comprised of many crystals (as opposed to a single-crystal material that has only one crystal). Grain boundaries are regions between grains of a ...
Chapter 2 - CP Physics
... enters one end of the tube in a given time interval equals the volume of fluid leaving the tube in the same interval • Assumes the fluid is incompressible and there are no leaks ...
... enters one end of the tube in a given time interval equals the volume of fluid leaving the tube in the same interval • Assumes the fluid is incompressible and there are no leaks ...
Section 4-2b
... 2. Scan the first vertex and check each incoming and outgoing edge and label if they are unlabeled. 3. Choose another labeled vertex to scan and label. 4. Find an a-z chain K of slack edges by backtracking. 5. Increase the flow in the edges of K by ( z ) units. ...
... 2. Scan the first vertex and check each incoming and outgoing edge and label if they are unlabeled. 3. Choose another labeled vertex to scan and label. 4. Find an a-z chain K of slack edges by backtracking. 5. Increase the flow in the edges of K by ( z ) units. ...
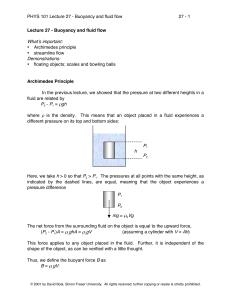
Buoyancy and fluid flow
... The net force from the surrounding fluid on the object is equal to the upward force, (P2 - P1)A = ρLghA = ρLgV (assuming a cylinder with V = Ah) This force applies to any object placed in the fluid. Further, it is independent of the shape of the object, as can be verified with a little thought. Thus ...
... The net force from the surrounding fluid on the object is equal to the upward force, (P2 - P1)A = ρLghA = ρLgV (assuming a cylinder with V = Ah) This force applies to any object placed in the fluid. Further, it is independent of the shape of the object, as can be verified with a little thought. Thus ...
Problem 1. Water flows steadily from a large closed tank as shown in
... I will choose F, T, L as few of my variables will look simpler in terms of force. Please recall, I have to choose d as a non-repeating, the rest is more or less up to me. As a result I find: ...
... I will choose F, T, L as few of my variables will look simpler in terms of force. Please recall, I have to choose d as a non-repeating, the rest is more or less up to me. As a result I find: ...
V-NLH-048 2013 NLH General Rate Application Page 1 of 2 Q.
... Reference: Section 4: Rates and Regulation, Section 4.6 Rate Stabilization Plan, ...
... Reference: Section 4: Rates and Regulation, Section 4.6 Rate Stabilization Plan, ...
Lecture Presentation Chp-10
... analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a).The tube is cantilevered out from a rigidly supported base. An electromechanical driver is use ...
... analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a).The tube is cantilevered out from a rigidly supported base. An electromechanical driver is use ...
Eudaimonia - ScottMacLeod
... 7. A loss of self-consciousness; 8. And often a sense of loss of time, because one is absorbed in enjoyment. 'Flow' can happen in yoga-related movement. Exploring your 'inner body' in movement is a very enjoyable kind of 'flow.' 'Flow' leads to greater complexity, as one engages challenges at the ri ...
... 7. A loss of self-consciousness; 8. And often a sense of loss of time, because one is absorbed in enjoyment. 'Flow' can happen in yoga-related movement. Exploring your 'inner body' in movement is a very enjoyable kind of 'flow.' 'Flow' leads to greater complexity, as one engages challenges at the ri ...
Get Way to GATE
... circle for plane stress and plane strain, thin cylinders; shear force and bending moment diagrams; bending and shear stresses; deflection of beams; torsion of circular shafts; Euler’s theory of columns; strain energy methods; thermal stresses. ...
... circle for plane stress and plane strain, thin cylinders; shear force and bending moment diagrams; bending and shear stresses; deflection of beams; torsion of circular shafts; Euler’s theory of columns; strain energy methods; thermal stresses. ...
Normal version 1.00
... and lithium ion battery electrodes and strain control in strained more difficult to make mechanical measurements of such small silicon/silicon germanium substrates for high speed microelectronic volumes of material. Nanoindentation is one of the few methods devices. available that can measure the e ...
... and lithium ion battery electrodes and strain control in strained more difficult to make mechanical measurements of such small silicon/silicon germanium substrates for high speed microelectronic volumes of material. Nanoindentation is one of the few methods devices. available that can measure the e ...
Extrusion of Sections with Varying Thickness Through Pocket Dies
... Appropriate shape Dimensional tolerances Surface quality Homogenous structure Uniform mechanical properties ...
... Appropriate shape Dimensional tolerances Surface quality Homogenous structure Uniform mechanical properties ...
sensors homework 3
... MECHANICS MEAUREMENTS. In this paper we learn the a novel about micro machined hot-film flow sensor system, by using film depositing process and incorporating a standard printed circuit techniques. It is divided into different categories such as: 1. Introduction The silicon-based flow sensor was fir ...
... MECHANICS MEAUREMENTS. In this paper we learn the a novel about micro machined hot-film flow sensor system, by using film depositing process and incorporating a standard printed circuit techniques. It is divided into different categories such as: 1. Introduction The silicon-based flow sensor was fir ...
An Opportunity
... (0.0603 m3) × (725 kg/m3) = 43.72 kg. When fully immersed in water, the buoyant force on a log is: Fb = (1000 kg/m3) × (0.0603 m3)g = 590.9 N With n logs, the total buoyant force is 590.9n and the total weight, including the people, is W = (4×80 + 43.72n)g. Set these forces to be equal: 590.9n = (32 ...
... (0.0603 m3) × (725 kg/m3) = 43.72 kg. When fully immersed in water, the buoyant force on a log is: Fb = (1000 kg/m3) × (0.0603 m3)g = 590.9 N With n logs, the total buoyant force is 590.9n and the total weight, including the people, is W = (4×80 + 43.72n)g. Set these forces to be equal: 590.9n = (32 ...
Mechanical Rate - U
... Drag forces increase linearly with velocity until turbulence takes place. ...
... Drag forces increase linearly with velocity until turbulence takes place. ...
Electricity images
... Electricity is the flow of electric charge Electric charges can flow in wires, light bulbs, and even in salt water. In some ways, the flow of electric charges acts like the flow of water, so we will often make an analogy between electricity and water flow. Nonetheless, this is only an analogy. Elect ...
... Electricity is the flow of electric charge Electric charges can flow in wires, light bulbs, and even in salt water. In some ways, the flow of electric charges acts like the flow of water, so we will often make an analogy between electricity and water flow. Nonetheless, this is only an analogy. Elect ...
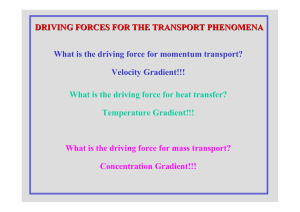
DRIVING FORCES FOR THE TRANSPORT PHENOMENA What is
... What is the driving force for heat transfer? Temperature Gradient!!! ...
... What is the driving force for heat transfer? Temperature Gradient!!! ...
Dragedit - Physics Forums
... We now have a simple equation for the force due to air resistance. In practice this equation is not very accurate as modelling the drag force is an incredibly complex procedure that is usually dependent on two complex factors; drag pressure and drag friction. We can however say “As the size and/or s ...
... We now have a simple equation for the force due to air resistance. In practice this equation is not very accurate as modelling the drag force is an incredibly complex procedure that is usually dependent on two complex factors; drag pressure and drag friction. We can however say “As the size and/or s ...