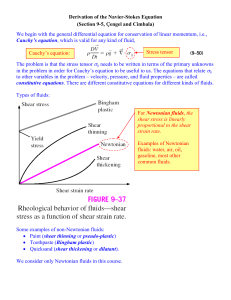
Newtonian, Non-Newtonian Fluids and Viscosity
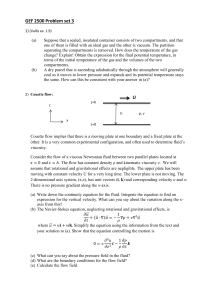
... Q.3) For the figure given below and for the given equation, u = 3y-4y3 calculate the shear stress, 0.15m from the wall if the dynamic viscosity of the fluid is 0.001N.s/m2? ...
... Q.3) For the figure given below and for the given equation, u = 3y-4y3 calculate the shear stress, 0.15m from the wall if the dynamic viscosity of the fluid is 0.001N.s/m2? ...
P16318 Poster
... • The cam profile can be tuned for different applications with different flow control requirements. ...
... • The cam profile can be tuned for different applications with different flow control requirements. ...
Cartridge Filter is designed for high viscosity liquid filtration, by
... ① This Cartridge has the high compressive strength against the viscous liquids, because of the structure of only molded layer. Also, it achieves the bigger filtration flow. ②All Cartridge products are rinsed up, so the no flow out of oils, and no foaming. ③Thickness of the fibers is uniformed, and t ...
... ① This Cartridge has the high compressive strength against the viscous liquids, because of the structure of only molded layer. Also, it achieves the bigger filtration flow. ②All Cartridge products are rinsed up, so the no flow out of oils, and no foaming. ③Thickness of the fibers is uniformed, and t ...
ME 101
... • Exact relationship among these variables discovered by British engineer Osborne Reynolds • Reynolds number – Dimensionless parameter describes that transition ...
... • Exact relationship among these variables discovered by British engineer Osborne Reynolds • Reynolds number – Dimensionless parameter describes that transition ...
Bernoulli - Cloudfront.net
... can undergo; We will also be • Laminar flow assuming no friction along the edges • Turbulent flow. ...
... can undergo; We will also be • Laminar flow assuming no friction along the edges • Turbulent flow. ...
Derive from first principles the Poiseuille equation for
... will move in bulk. However in viscous fluids, there will be a resistance to the fluid motion as shear force is induced between adjacent layers of fluid. In the figure, the shear force retarding the motion is acting on the surface of the fluid element and given by FT = τ2πrL In fully-developed steady ...
... will move in bulk. However in viscous fluids, there will be a resistance to the fluid motion as shear force is induced between adjacent layers of fluid. In the figure, the shear force retarding the motion is acting on the surface of the fluid element and given by FT = τ2πrL In fully-developed steady ...
Lecture Notes for First Quiz - Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
... The velocity gradient tensor has symmetric and antisymmetric parts: symmetric part includes divergence (trace; ignored) and shear strain elements (off-diagonal) antisymmetric part includes vorticities, which do not deform a fluid element and are ignored in defining the constitutive relationship 11. ...
... The velocity gradient tensor has symmetric and antisymmetric parts: symmetric part includes divergence (trace; ignored) and shear strain elements (off-diagonal) antisymmetric part includes vorticities, which do not deform a fluid element and are ignored in defining the constitutive relationship 11. ...
v 1
... The oxygen exchange in the lungs takes place across the membranes of small balloon-like structures called alveoli attached to the branches of the bronchial passages. These alveoli inflate and deflate with inhalation and exhalation It takes some effort to breathe in because these tiny balloons must b ...
... The oxygen exchange in the lungs takes place across the membranes of small balloon-like structures called alveoli attached to the branches of the bronchial passages. These alveoli inflate and deflate with inhalation and exhalation It takes some effort to breathe in because these tiny balloons must b ...
ME33: Fluid Flow Lecture 1: Information and Introduction
... These slides were developed1 during the spring semester 2005, as a teaching aid for the undergraduate Fluid Mechanics course (ME33: Fluid Flow) in the Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering at Penn State University. This course had two sections, one taught by myself and one taught by Prof. ...
... These slides were developed1 during the spring semester 2005, as a teaching aid for the undergraduate Fluid Mechanics course (ME33: Fluid Flow) in the Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering at Penn State University. This course had two sections, one taught by myself and one taught by Prof. ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-2011 - Rensselaer Hartford Campus
... • COMSOL Multi-physics has been used to model the steady laminar flow and convective heat transfer of an electrically conducting fluid subjected to an applied electromagnetic field in two simple flow configurations, namely, flow between parallel plates (Hartmann flow) and flow around a backward faci ...
... • COMSOL Multi-physics has been used to model the steady laminar flow and convective heat transfer of an electrically conducting fluid subjected to an applied electromagnetic field in two simple flow configurations, namely, flow between parallel plates (Hartmann flow) and flow around a backward faci ...
B12a - damtp - University of Cambridge
... the fluid. Calculate the velocity profile and find the volume flux (per unit width) of fluid down the wall. 3. A long, horizontal, two-dimensional container of depth h, filled with viscous fluid, has rigid, stationary bottom and end walls and a rigid top wall that moves with velocity (U, 0) in Carte ...
... the fluid. Calculate the velocity profile and find the volume flux (per unit width) of fluid down the wall. 3. A long, horizontal, two-dimensional container of depth h, filled with viscous fluid, has rigid, stationary bottom and end walls and a rigid top wall that moves with velocity (U, 0) in Carte ...
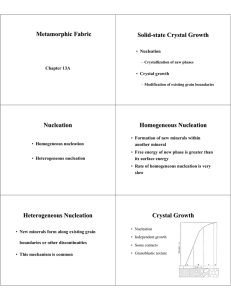
Metamorphic Fabric Solid-state Crystal Growth Nucleation
... • Migration facilitated by an intergranular fluid • Driving mechanism is a chemical potential • Evidenced by growth into pressure shadows ...
... • Migration facilitated by an intergranular fluid • Driving mechanism is a chemical potential • Evidenced by growth into pressure shadows ...
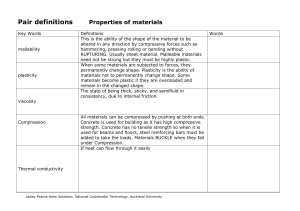
Applied Mechanics
... Deformable Body Mechanics The mechanics of deformable bodies is the field that is concerned with the deformability of objects. An elastic body is defined as one in which all deformations are recoverable upon removal of external forces. this feature of some materials can easily be visualized by obse ...
... Deformable Body Mechanics The mechanics of deformable bodies is the field that is concerned with the deformability of objects. An elastic body is defined as one in which all deformations are recoverable upon removal of external forces. this feature of some materials can easily be visualized by obse ...
L15 - University of Iowa Physics
... • Ketchup and molasses are also good examples • viscosity is sometimes referred to as the “thickness” of a liquid • viscosity is the most important property of ...
... • Ketchup and molasses are also good examples • viscosity is sometimes referred to as the “thickness” of a liquid • viscosity is the most important property of ...
Lecture 3 - fluid motion - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... He asks you how they can both be the same equation when they look so different? And what it’s the value of the constant in the second equation, anyway? What should you tell him? ...
... He asks you how they can both be the same equation when they look so different? And what it’s the value of the constant in the second equation, anyway? What should you tell him? ...