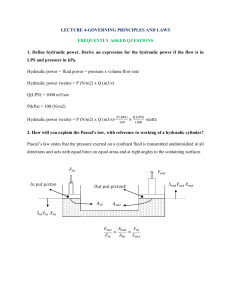
Electricity and Magnetism
... What kind of electricity is caused by a continuous flow of electrons? ...
... What kind of electricity is caused by a continuous flow of electrons? ...
Dynamics and Control of A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
... transfer of hat to and from process fluids is an essential part of most The tube chemical processes . among several types of heat exchangers ,shell and equipment heat exchanger , is by far the most common type of heat transfer concerned with the used in the chemical and allied industries the present ...
... transfer of hat to and from process fluids is an essential part of most The tube chemical processes . among several types of heat exchangers ,shell and equipment heat exchanger , is by far the most common type of heat transfer concerned with the used in the chemical and allied industries the present ...
Voltage The force motivating electrons to "flow" in a circuit It is
... In a conductor, electric current can flow freely, in an insulator it cannot. Metals such as copper typify conductors, while most non-metallic solids are said to be good insulators, having extremely high resistance to the flow of charge through them. "Conductor" implies that the outer electrons of th ...
... In a conductor, electric current can flow freely, in an insulator it cannot. Metals such as copper typify conductors, while most non-metallic solids are said to be good insulators, having extremely high resistance to the flow of charge through them. "Conductor" implies that the outer electrons of th ...
The properties of p-type cuprous oxide films prepared by reactive
... in solar cells to product semitranslucent glass, have some beneficial heat insulation and electronic generation layers. Cuprous oxide (Cu2O) is a direct bend gap and is p-type semiconductor at without doping. To understand Cu2O characteristics can provide useful and foundamental datum to promote the ...
... in solar cells to product semitranslucent glass, have some beneficial heat insulation and electronic generation layers. Cuprous oxide (Cu2O) is a direct bend gap and is p-type semiconductor at without doping. To understand Cu2O characteristics can provide useful and foundamental datum to promote the ...
Fluid Mechanics Sample Exam 1 Please work at least three
... velocity distribution at the entrance to the tunnel test section is horizontal and uniform, i.e., flat, with a magnitude Uo . Assume that the test section entrance pressure is likewise spatially uniform and equal to Po . Using a pitot tube (or any device/devices that allows simultaneous measurement ...
... velocity distribution at the entrance to the tunnel test section is horizontal and uniform, i.e., flat, with a magnitude Uo . Assume that the test section entrance pressure is likewise spatially uniform and equal to Po . Using a pitot tube (or any device/devices that allows simultaneous measurement ...
Methodological Travails: Taling
... Much of Tantra is concerned with worship in a ritualistic form, using the three basic tools of mantra, yantra and mandala. ...
... Much of Tantra is concerned with worship in a ritualistic form, using the three basic tools of mantra, yantra and mandala. ...
02_fluid properties
... located at a distance of 0.01 cm from it, the fluid separating them being water with dynamic viscosity of 0.001 Pa-s. Find the force and power required to maintain the velocity. Prob: Determine the torque and power required to turn a 10 cm long, 5 cm diameter shaft at 500 rev/min in a 5.1 cm diamete ...
... located at a distance of 0.01 cm from it, the fluid separating them being water with dynamic viscosity of 0.001 Pa-s. Find the force and power required to maintain the velocity. Prob: Determine the torque and power required to turn a 10 cm long, 5 cm diameter shaft at 500 rev/min in a 5.1 cm diamete ...
flowing fluids and pressure variation!
... For your culture : The force balance for hurricanes is the pressure force vs. the Coriolis force. That s why hurricanes in the northern hemisphere always spin counter-clockwise. In a tornado, the balance is between pressure force and centrifugal acceleration; a tornado can spin either way…! ...
... For your culture : The force balance for hurricanes is the pressure force vs. the Coriolis force. That s why hurricanes in the northern hemisphere always spin counter-clockwise. In a tornado, the balance is between pressure force and centrifugal acceleration; a tornado can spin either way…! ...
Copy and answer. - St. Francis Xavier Convent School
... to flow through a 300 ohm resistor? 7. How much voltage is required to make 15 Amps flow through a 7.5 ohm resistance? 8. A battery causes 250 mA to flow when it is applied to a light bulb with a resistance of 50 ohms. How much current would flow if the same source were applied to a 12 ohm resistor? ...
... to flow through a 300 ohm resistor? 7. How much voltage is required to make 15 Amps flow through a 7.5 ohm resistance? 8. A battery causes 250 mA to flow when it is applied to a light bulb with a resistance of 50 ohms. How much current would flow if the same source were applied to a 12 ohm resistor? ...
Numerical Modeling of Lava Flow Behavior on Earth and Mars
... parameters are well known for any particular flow, and therefore lava flow modeling must make simplifying assumptions, such as utilizing an idealized rheology. Many studies have successfully used simplified models to characterize flow evolution [2], especially for cases of purely molten lava without ...
... parameters are well known for any particular flow, and therefore lava flow modeling must make simplifying assumptions, such as utilizing an idealized rheology. Many studies have successfully used simplified models to characterize flow evolution [2], especially for cases of purely molten lava without ...
Biofluids - Louisiana Tech University
... Newtonian vs. Non-Newtonian Fluids • Newtonian Fluids: Linear Viscosity Equation ...
... Newtonian vs. Non-Newtonian Fluids • Newtonian Fluids: Linear Viscosity Equation ...
Fluid Properties - Icivil-Hu
... in pressure in order to change the density. Thus, for most applications, liquids can be considered incompressible and can be assumed to have constant density. An exception to this occurs when different solutions, such as saline and fresh water, are mixed. A mixture of salt in water changes the densi ...
... in pressure in order to change the density. Thus, for most applications, liquids can be considered incompressible and can be assumed to have constant density. An exception to this occurs when different solutions, such as saline and fresh water, are mixed. A mixture of salt in water changes the densi ...
國立臺北科技大學九十一學年度
... U1 and U2 as shown. The pressure gradient in the x direction is zero and the only body force is the gravity force along the –y axis. In addition, there is no flow velocity in the y or z direction (v= 0, w= 0). Assuming laminar flow, please use the Navier-Stokes equations to determine the velocity di ...
... U1 and U2 as shown. The pressure gradient in the x direction is zero and the only body force is the gravity force along the –y axis. In addition, there is no flow velocity in the y or z direction (v= 0, w= 0). Assuming laminar flow, please use the Navier-Stokes equations to determine the velocity di ...
Chap09c - MSU Physics
... Surface tension allows the needle to float, even though the density of the steel in the needle is much higher than the density of the water The needle actually rests in a small depression in the liquid surface The vertical components of the force balance the weight ...
... Surface tension allows the needle to float, even though the density of the steel in the needle is much higher than the density of the water The needle actually rests in a small depression in the liquid surface The vertical components of the force balance the weight ...
8.1 – Viscosity and the effects of temperature
... 8.1 – Viscosity and the effects of temperature 1) Write a short paragraph to describe viscosity. Include at least 2 examples of fluids and the words “flow”, “fluid”, “particles” and “viscosity”. The Viscosity of a fluid affects the flow of a liquid. If a liquid flows at a slower rate it’s because ...
... 8.1 – Viscosity and the effects of temperature 1) Write a short paragraph to describe viscosity. Include at least 2 examples of fluids and the words “flow”, “fluid”, “particles” and “viscosity”. The Viscosity of a fluid affects the flow of a liquid. If a liquid flows at a slower rate it’s because ...