Protein Synthesis
... • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) ...
... • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) ...
The molecular architecture, macro-organization and functions of the
... controlled dissipation governed by low lumenal pH, they are capable of transiently downregulating their light-harvesting function; via reversible phosphorylation they participate in regulation of the distribution of excitation energy between the two photosystems. Although the crystal structure of LH ...
... controlled dissipation governed by low lumenal pH, they are capable of transiently downregulating their light-harvesting function; via reversible phosphorylation they participate in regulation of the distribution of excitation energy between the two photosystems. Although the crystal structure of LH ...
G Protein Coupled Receptors
... switch region. This leads to dissociation of Gß and it destabilizes the region where the G protein N- and Cterminus come together with the GPCR C-terminus, which leads to G protein dissociation. ...
... switch region. This leads to dissociation of Gß and it destabilizes the region where the G protein N- and Cterminus come together with the GPCR C-terminus, which leads to G protein dissociation. ...
Protein Origami
... at the structures of thousands of proteins at once. These resources are helping move the field toward accurately predicting and designing protein structures and protein complexes, eventually with specific functions or disease targets in mind. Protein molecules are the workhorses of cells in all livi ...
... at the structures of thousands of proteins at once. These resources are helping move the field toward accurately predicting and designing protein structures and protein complexes, eventually with specific functions or disease targets in mind. Protein molecules are the workhorses of cells in all livi ...
Document
... - figure out what it looks like (structure or form) - understand what it does (function) ...
... - figure out what it looks like (structure or form) - understand what it does (function) ...
Homology Modeling Zinc Fingers – Introduction zf
... most of the residues reach an equilibrium point that is highly similar to the crystal structure. Cluster analysis revealed that the cluster with the most amount of neighbors is in general highly similar to the crystal structure. There are a few residues that are seen in the simulation that seem to f ...
... most of the residues reach an equilibrium point that is highly similar to the crystal structure. Cluster analysis revealed that the cluster with the most amount of neighbors is in general highly similar to the crystal structure. There are a few residues that are seen in the simulation that seem to f ...
You have worked for 2 years to isolate a gene involved in axon
... - Function…. Can it complement? (h ras into yeast) - Protein structure - degenerate PCR over similarity regions. ...
... - Function…. Can it complement? (h ras into yeast) - Protein structure - degenerate PCR over similarity regions. ...
Machine Learning in the Study of Protein Structure
... Structures (back) • X-ray crystallography The interaction of x-rays with electrons arranged in a crystal can produce electron-density map, which can be interpreted to an atomic model. Crystal is very hard to grow. ...
... Structures (back) • X-ray crystallography The interaction of x-rays with electrons arranged in a crystal can produce electron-density map, which can be interpreted to an atomic model. Crystal is very hard to grow. ...
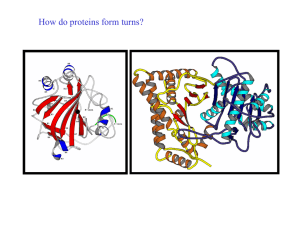
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
TIM barrel proteins (ie
... Putative Orf2-mediated electrophilic geranylation mechanism of aromatic substrates A carbocation is proposed to result from the ionization of the diphosphate moiety, triggered by Mg2+ coordination, hydrogen bonds with Lys 119, Arg 228, Asn 173 and Lys 284, and cosubstrate binding. The positively cha ...
... Putative Orf2-mediated electrophilic geranylation mechanism of aromatic substrates A carbocation is proposed to result from the ionization of the diphosphate moiety, triggered by Mg2+ coordination, hydrogen bonds with Lys 119, Arg 228, Asn 173 and Lys 284, and cosubstrate binding. The positively cha ...
Crystallizing a clearer understanding of the protein
... tion between them. Among the proteins in this matrix is netrin, which guides the growth and repair of axons, or nerve fibres. Damaged or dysfunctional axons can’t properly communicate information throughout the brain and body, resulting in neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis (MS). Stetefe ...
... tion between them. Among the proteins in this matrix is netrin, which guides the growth and repair of axons, or nerve fibres. Damaged or dysfunctional axons can’t properly communicate information throughout the brain and body, resulting in neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis (MS). Stetefe ...
Shin-ichi Tate Research Group Activity ・ Protein dynamics and
... ・ Protein dynamics and function relationships revealed through nuclear spin relaxation analyses Protein dynamics, in the time regime in sec-msec, can be revealed by nuclear spin relaxations. Systematic analyses on the dynamical modulations caused by single site-directed mutation will give us experi ...
... ・ Protein dynamics and function relationships revealed through nuclear spin relaxation analyses Protein dynamics, in the time regime in sec-msec, can be revealed by nuclear spin relaxations. Systematic analyses on the dynamical modulations caused by single site-directed mutation will give us experi ...
Slide 1
... Cystic Fibrosis ,affects lungs and digestive system and cause early death Alzheimers’s and Parkinson's disease It may help us to understand the structure of proteins which has not been known ...
... Cystic Fibrosis ,affects lungs and digestive system and cause early death Alzheimers’s and Parkinson's disease It may help us to understand the structure of proteins which has not been known ...
A1987J365500002
... regions that could undergo conformational changes! We suggested that by changing residues, it should be possible to change potentialsand thus lock either the a-helix or fl-structure in this 19-29 region. Recently, V.1. Hruby° performed experiments that yielded a glucagon with 500 times the activity ...
... regions that could undergo conformational changes! We suggested that by changing residues, it should be possible to change potentialsand thus lock either the a-helix or fl-structure in this 19-29 region. Recently, V.1. Hruby° performed experiments that yielded a glucagon with 500 times the activity ...
A1980JC93500001
... know why there should be more than scattered citations of my review in the literature. “In the 1960s there was a valid biological reason for investigating denatured proteins. There was a growing conviction that the three-dimensional structure and biological activity of proteins are uniquely determin ...
... know why there should be more than scattered citations of my review in the literature. “In the 1960s there was a valid biological reason for investigating denatured proteins. There was a growing conviction that the three-dimensional structure and biological activity of proteins are uniquely determin ...
PSCF Poster
... Simple Westerns by Size or Charge Consultation with the director on sample preparation, experimental design and ...
... Simple Westerns by Size or Charge Consultation with the director on sample preparation, experimental design and ...
Using the standardized (normally distributed with a mean of zero
... metrics for allelic pairs of 15-mers and 9-mers the minimum value for the pair was computed within a window ±4 from each position within the protein sequence. A least-squares mean was calculated over all permuted pairs to arrive at a number for each position in the protein sequence. Statistics for t ...
... metrics for allelic pairs of 15-mers and 9-mers the minimum value for the pair was computed within a window ±4 from each position within the protein sequence. A least-squares mean was calculated over all permuted pairs to arrive at a number for each position in the protein sequence. Statistics for t ...
Probabilistic Approaches to Predicting the Secondary Structure of Proteins
... existing structures to hypothesize whether or not new sequences could acquire ...
... existing structures to hypothesize whether or not new sequences could acquire ...
2016 N1 Week 4
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
Dynamical Analysis of Networks: How to Identify Important Nodes with
... ♦ The major targets of prescription drugs are proteins. ...
... ♦ The major targets of prescription drugs are proteins. ...
Protein structure
... sequence of 20 different L-α-amino acids, also referred to as residues. For chains under 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used instead of protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one, or more, specific spatial conformations, driven by a number of noncova ...
... sequence of 20 different L-α-amino acids, also referred to as residues. For chains under 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used instead of protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one, or more, specific spatial conformations, driven by a number of noncova ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.