Proteins are biopolymers construced from similar building blocks
... Proteins are biopolymers construced from similar building blocks called amino acids. The unique feature is that these polypeptide chains are folded in a certain three-dimensional structure (called native structure), which enables them to perform their biological funtion. Studies on protein structure ...
... Proteins are biopolymers construced from similar building blocks called amino acids. The unique feature is that these polypeptide chains are folded in a certain three-dimensional structure (called native structure), which enables them to perform their biological funtion. Studies on protein structure ...
Topic 3
... a protein can influence the relative free energies of the cis and trans isomeric states, leading to wide variations in the ratio of cis:trans populations in different proteins. Although most structures require proline to adopt one or the other isomer in the context of native protein folds, several r ...
... a protein can influence the relative free energies of the cis and trans isomeric states, leading to wide variations in the ratio of cis:trans populations in different proteins. Although most structures require proline to adopt one or the other isomer in the context of native protein folds, several r ...
Medical Informatics Group
... intrinsically disordered protein interactions: A focus on BRCA1 • Result: BRCA1 protein functions both individually as well as jointly in protein complexes, and that proteins that form functional complexes with BRCA1 also have separate independent functions ...
... intrinsically disordered protein interactions: A focus on BRCA1 • Result: BRCA1 protein functions both individually as well as jointly in protein complexes, and that proteins that form functional complexes with BRCA1 also have separate independent functions ...
Recombinant Human Glutathione S Transferase theta 1
... Our Abpromise to you: Quality guaranteed and expert technical support Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and S ...
... Our Abpromise to you: Quality guaranteed and expert technical support Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and S ...
From gene to protein 2
... To be able to perform their specific function To assemble correctly with other proteins To bind with small-molecule cofactors that are required for their activity To be appropriately modified by protein kinases or other proteinmodifying enzymes ...
... To be able to perform their specific function To assemble correctly with other proteins To bind with small-molecule cofactors that are required for their activity To be appropriately modified by protein kinases or other proteinmodifying enzymes ...
Soybean Meal - International Feed
... Soybean Meal is the standard to which other protein sources are compared, and is a by-product of soybean oil extraction. Protein, fiber, and fat levels all vary with the process by which the oil is extracted. Soybean Meal is a highly palatable source of protein, and used often as the dominant source ...
... Soybean Meal is the standard to which other protein sources are compared, and is a by-product of soybean oil extraction. Protein, fiber, and fat levels all vary with the process by which the oil is extracted. Soybean Meal is a highly palatable source of protein, and used often as the dominant source ...
Amino acid substitution and protein structure
... Proteins classified as homologs by one tend to be classified as homologs by the other (why?) ...
... Proteins classified as homologs by one tend to be classified as homologs by the other (why?) ...
History and Philosophy of Science
... Sequence assembly systems read the gene sequence of each fragment as text and return the genome. Informatics tools such as ARACHNE and Celera Assembler address the sequencing problem by • finding repeated fragments; • searching for overlapping fragments; • correcting errors; and • joining overlappin ...
... Sequence assembly systems read the gene sequence of each fragment as text and return the genome. Informatics tools such as ARACHNE and Celera Assembler address the sequencing problem by • finding repeated fragments; • searching for overlapping fragments; • correcting errors; and • joining overlappin ...
PBI 3 Student Handout 2
... In this exercise, you are given a model of DNA. This model is a Map which contains the nucleotide sequence of the region of the human genome that contains the β-globin gene. In addition to the nucleotide sequence of both strands of DNA, you will find three possible amino acid sequences encoded in th ...
... In this exercise, you are given a model of DNA. This model is a Map which contains the nucleotide sequence of the region of the human genome that contains the β-globin gene. In addition to the nucleotide sequence of both strands of DNA, you will find three possible amino acid sequences encoded in th ...
ECS 189K - UC Davis
... does that string form a knot? (i.e. if you were to hold the two extremities of the string and pull, would it result in the formation of a knot, or would the string become linear?) Some proteins do form knots, and it remains unclear at this time if these knots play a role in defining the functions of ...
... does that string form a knot? (i.e. if you were to hold the two extremities of the string and pull, would it result in the formation of a knot, or would the string become linear?) Some proteins do form knots, and it remains unclear at this time if these knots play a role in defining the functions of ...
Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Human E. coli
... kingdom. The three known mammalian Hh proteins, Sonic (Shh), Desert (Dhh) and Indian (Ihh), are structurally related, and share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage o ...
... kingdom. The three known mammalian Hh proteins, Sonic (Shh), Desert (Dhh) and Indian (Ihh), are structurally related, and share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage o ...
Biochemistry Topic 1: Chemical nature of enzymes, general
... Coordinate covalent bond Unequal sharing of an electron pair by 2 atoms. The electron pair comes originally just from one atom. ...
... Coordinate covalent bond Unequal sharing of an electron pair by 2 atoms. The electron pair comes originally just from one atom. ...
Full Text
... INTRODUCTION Discrete protein sequence motifs are widely used to describe homology between proteins and establish relationships between well-known and new protein sequences. More specifically, discrete motifs identify amino acids sharing important properties conserved in evolution. Further, they are ...
... INTRODUCTION Discrete protein sequence motifs are widely used to describe homology between proteins and establish relationships between well-known and new protein sequences. More specifically, discrete motifs identify amino acids sharing important properties conserved in evolution. Further, they are ...
Proteiinien rakenne ja laskostuminen
... gives information about the global conformation of a molecule rms distance from each atom of the molecule to their centroid ...
... gives information about the global conformation of a molecule rms distance from each atom of the molecule to their centroid ...
Ch. 5 Pppt
... of organic compounds and hydrolysis in the digestion of organic compounds. How to recognize the 4 biologically important organic compounds (carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) by their structural formulas. The cellular functions of all four organic compounds. The 4 structural levels of proteins ...
... of organic compounds and hydrolysis in the digestion of organic compounds. How to recognize the 4 biologically important organic compounds (carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) by their structural formulas. The cellular functions of all four organic compounds. The 4 structural levels of proteins ...
Episode 24 - The Genetic Code
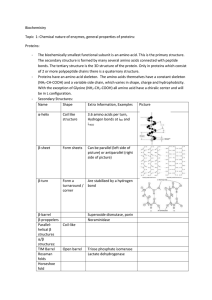
... Primary - the sequence of amino acids in the protein chain Secondary - the formation of - helices or - sheets from the protein chain Tertiary - the folding of protein chains into more compact structures Quatrenary structure - the interactions of polypeptide chains in the protein 4. What is speci ...
... Primary - the sequence of amino acids in the protein chain Secondary - the formation of - helices or - sheets from the protein chain Tertiary - the folding of protein chains into more compact structures Quatrenary structure - the interactions of polypeptide chains in the protein 4. What is speci ...
Phylogenetics and Bioinformatics Questions
... the CytB tree compare to Mr. Ahlander's tree? Why might your molecular phylogeny not perfectly match the standard phylogenetic tree? Every gene sequence has its own evolutionary history. Every animal is made up of a collection of genes representing a collection of molecular evolution. It is best to ...
... the CytB tree compare to Mr. Ahlander's tree? Why might your molecular phylogeny not perfectly match the standard phylogenetic tree? Every gene sequence has its own evolutionary history. Every animal is made up of a collection of genes representing a collection of molecular evolution. It is best to ...
D6- Bulletin Board Powerful Protein
... What are Proteins? • Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Proteins are part of every cell in our bodies, especially muscles, bones, skin, and blood! • Foods that are high in protein are also usually high in B vitamins, Iron, magnesium, zinc, and other vitamins and minerals. ...
... What are Proteins? • Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Proteins are part of every cell in our bodies, especially muscles, bones, skin, and blood! • Foods that are high in protein are also usually high in B vitamins, Iron, magnesium, zinc, and other vitamins and minerals. ...
Flexibility of a polypeptide chain
... phi and psi values actually limit the number of possible structures and it is overcome by interactions that favor the folded form e.g. hydrophobic interactions among apolar side-chains (rather than being exposed to polar water), H-bonding network, S-S bridges, ion pairs, etc. a highly flexible polym ...
... phi and psi values actually limit the number of possible structures and it is overcome by interactions that favor the folded form e.g. hydrophobic interactions among apolar side-chains (rather than being exposed to polar water), H-bonding network, S-S bridges, ion pairs, etc. a highly flexible polym ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.