File
... The reactivity of alkali metals decreases going down the group. What is the reason for this? The atoms of each element get F larger going down the group. This means that the outer shell gets further away from the nucleus and is shielded by more electron shells. Cl The further the outer shell ...
... The reactivity of alkali metals decreases going down the group. What is the reason for this? The atoms of each element get F larger going down the group. This means that the outer shell gets further away from the nucleus and is shielded by more electron shells. Cl The further the outer shell ...
Unit 4: Chemical Bonding Notes Chemical Bond—a mutual
... Chemical Bond—a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Chemical bonds create more stable arrangements of matter. The goal o ...
... Chemical Bond—a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Chemical bonds create more stable arrangements of matter. The goal o ...
Document
... Covalent compounds are made of molecules, are held together by covalent bonds, share electrons, and are composed of 2 or more non-metals. They also have a lower difference of electronegativity between their atoms. Both types of compounds result from atoms desiring a full octet. ...
... Covalent compounds are made of molecules, are held together by covalent bonds, share electrons, and are composed of 2 or more non-metals. They also have a lower difference of electronegativity between their atoms. Both types of compounds result from atoms desiring a full octet. ...
Period #2 Notes: Electronic Structure of Atoms
... • In this way, materials are like most other physical systems in that they tend to reside at states of minimum potential energy. For a given material system, there usually exists more than one state of minimum potential energy. ...
... • In this way, materials are like most other physical systems in that they tend to reside at states of minimum potential energy. For a given material system, there usually exists more than one state of minimum potential energy. ...
synoptic - chemnotes.org.uk
... nucleus and the outer shell electrons Electronegativity depends on the attraction between the nucleus and the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond Strength of metallic bonding depends on the attraction between the nucleus and the delocalised electrons Across a period, shielding stays the same ...
... nucleus and the outer shell electrons Electronegativity depends on the attraction between the nucleus and the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond Strength of metallic bonding depends on the attraction between the nucleus and the delocalised electrons Across a period, shielding stays the same ...
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... Imagine 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 balloons tied together: ...
... Imagine 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 balloons tied together: ...
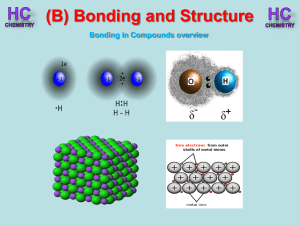
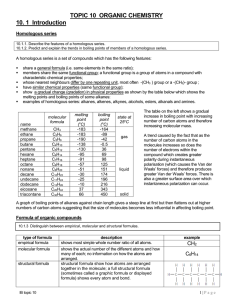
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Silicon, like carbon, can form giant covalent networks. Silicon carbide exist in a similar structure to diamond. Tetrahedral shape ...
... Silicon, like carbon, can form giant covalent networks. Silicon carbide exist in a similar structure to diamond. Tetrahedral shape ...
Intermolecular Attractions
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review 2012-2013 Alchemy Unit
... 17. What are the different functional groups, the smells associated for each, and their common names endings? Functional Group Structure Smell Name endings Ester O=C-O-C Sweet “-ate” Carboxylic Acid O=C-O-H Putrid “-acid” Ketone O=C Minty “-one” Alcohol C-O-H Camphor, Minty, Sweet “-ol” Amine C-N Fi ...
... 17. What are the different functional groups, the smells associated for each, and their common names endings? Functional Group Structure Smell Name endings Ester O=C-O-C Sweet “-ate” Carboxylic Acid O=C-O-H Putrid “-acid” Ketone O=C Minty “-one” Alcohol C-O-H Camphor, Minty, Sweet “-ol” Amine C-N Fi ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exothermic. ...
... unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exothermic. ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs around the central atom can be determined by writing the Lewis structu ...
... atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs around the central atom can be determined by writing the Lewis structu ...
∙ ∙B x
... 28. See the graph with the boiling points of hydrogen halides and state what is exceptional there: ...
... 28. See the graph with the boiling points of hydrogen halides and state what is exceptional there: ...
∙ ∙B x
... 28. See the graph with the boiling points of hydrogen halides and state what is exceptional there: 3. Hydrogen bonding (hydrogen bridges) When a very electronegative element (F, O, N) is bonded to a hydrogen atom, the hydrogen electron is drawn to the more electronegative atom. A hydrogen atom has a ...
... 28. See the graph with the boiling points of hydrogen halides and state what is exceptional there: 3. Hydrogen bonding (hydrogen bridges) When a very electronegative element (F, O, N) is bonded to a hydrogen atom, the hydrogen electron is drawn to the more electronegative atom. A hydrogen atom has a ...
Teknologi Solid State - Universitas Brawijaya
... spacing are possible. The detailed atomic structure is unimportant for these waves and their propagation is governed by the macroscopic elastic properties of the crystal. • We discuss sound waves since they must correspond to the low frequency, long wavelength limit of the more general lattice vibra ...
... spacing are possible. The detailed atomic structure is unimportant for these waves and their propagation is governed by the macroscopic elastic properties of the crystal. • We discuss sound waves since they must correspond to the low frequency, long wavelength limit of the more general lattice vibra ...
Honors Chemistry
... 1. Determine the common ion that each element would form and write its complete electron configuration: a. Rb ...
... 1. Determine the common ion that each element would form and write its complete electron configuration: a. Rb ...
organic chemistry - Peoria Public Schools
... Chemical properties: addition reactions As they are unsaturated alkenes are reactive. The second bond of the double bond is weaker than a single carbon-carbon bond and is broken much easier. It is because of this greater reactivity that alkenes, especially ethene, are important starting materials in ...
... Chemical properties: addition reactions As they are unsaturated alkenes are reactive. The second bond of the double bond is weaker than a single carbon-carbon bond and is broken much easier. It is because of this greater reactivity that alkenes, especially ethene, are important starting materials in ...
Bond
... including its role in nature, depends primarily on its molecular structure, or shape. Molecular shape contributes toward determining a compound’s boiling point, freezing point, viscosity, solubility, types of reactions it can participate in, and a host of other physical and chemical properties. The ...
... including its role in nature, depends primarily on its molecular structure, or shape. Molecular shape contributes toward determining a compound’s boiling point, freezing point, viscosity, solubility, types of reactions it can participate in, and a host of other physical and chemical properties. The ...
Atomic Structure and Crystal Structure File
... Z=p=e=9 n = A – Z = 19 – 9 = 10 • Proton = 9 • Electron = 9 • Neutron = 10 ...
... Z=p=e=9 n = A – Z = 19 – 9 = 10 • Proton = 9 • Electron = 9 • Neutron = 10 ...
Class Notes 2
... – backbone N-H group i+4 forms hydrogen bonding with backbone C = O group i – 3.6 residues per turn (5.4 Å, 1.5 Å per residue) • Variations, with chain more loosely or tightly coiled are possible (i+3 or i+5 instead of i+4) but not often ...
... – backbone N-H group i+4 forms hydrogen bonding with backbone C = O group i – 3.6 residues per turn (5.4 Å, 1.5 Å per residue) • Variations, with chain more loosely or tightly coiled are possible (i+3 or i+5 instead of i+4) but not often ...
Chapter 8 & 9 PowerPoint
... FC = formal charge; G.N. = Group Number #BE = bonding electrons; #LPE = lone pair electrons If Step 4 leads to a positive formal charge on an inner atom beyond the second row, shift electrons to make double or triple bonds to minimize formal charge, even if this gives an inner atom with more than an ...
... FC = formal charge; G.N. = Group Number #BE = bonding electrons; #LPE = lone pair electrons If Step 4 leads to a positive formal charge on an inner atom beyond the second row, shift electrons to make double or triple bonds to minimize formal charge, even if this gives an inner atom with more than an ...
Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
... 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be sure to take ions into account!) 3) Distribute the electrons among the atoms giving octets to all atoms other than H (duet for it). 4) If any atoms lack an octet, form double or triple bonds as necessary. ...
... 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be sure to take ions into account!) 3) Distribute the electrons among the atoms giving octets to all atoms other than H (duet for it). 4) If any atoms lack an octet, form double or triple bonds as necessary. ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
chemia simr01 en - Leszek Niedzicki
... other sources than bonds. It is attracted by free electron pairs of other atoms (oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, etc.) forming weak ‘bonds’ with other molecules or within the same molecule but different atom than bonded one. • These bonds are very weak, but strong with their number. Because of that wate ...
... other sources than bonds. It is attracted by free electron pairs of other atoms (oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, etc.) forming weak ‘bonds’ with other molecules or within the same molecule but different atom than bonded one. • These bonds are very weak, but strong with their number. Because of that wate ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.