Chapter Outline • Review of Atomic Structure Electrons, protons
... atoms. It is negative if the atoms are bound and positive if they can move away from each other. The interaction energy is the integral of the force over the separation distance, so these two quantities are directly related. The interaction energy is a minimum at the equilibrium position. This value ...
... atoms. It is negative if the atoms are bound and positive if they can move away from each other. The interaction energy is the integral of the force over the separation distance, so these two quantities are directly related. The interaction energy is a minimum at the equilibrium position. This value ...
CHEMICAL BONDING
... • Bond that occurs between molecules containing hydrogen and an atom with a high electronegativity (usually N, O, F, Cl, or S) Hydrogen bonds are strong intermolecular attractions… about 10 x stronger than dipole-dipole attractions ...
... • Bond that occurs between molecules containing hydrogen and an atom with a high electronegativity (usually N, O, F, Cl, or S) Hydrogen bonds are strong intermolecular attractions… about 10 x stronger than dipole-dipole attractions ...
Chapter 8
... • FC = [VE in free atom] - [VE asigned in molecule] • FC is a hypothetical charge for electron loss (+) or gain (-) due to bond formation. • [VE]free = # valence e’s for Group A atoms • [VE] assigned = all lone pair electrons on atom + 1/2 shared electrons ...
... • FC = [VE in free atom] - [VE asigned in molecule] • FC is a hypothetical charge for electron loss (+) or gain (-) due to bond formation. • [VE]free = # valence e’s for Group A atoms • [VE] assigned = all lone pair electrons on atom + 1/2 shared electrons ...
Halogen Bonding in Crystal Engineering
... Because of the similarities involved, the same terminology has also been adapted in halogen bonds. The halogen in D-X acts as the halogen bond donor (electron acceptor). While electron donors such as nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur etc. act as the halogen bond acceptors (Fig. ...
... Because of the similarities involved, the same terminology has also been adapted in halogen bonds. The halogen in D-X acts as the halogen bond donor (electron acceptor). While electron donors such as nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur etc. act as the halogen bond acceptors (Fig. ...
CHEMISTRY 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... 3.) What is the total number of atoms in one molecule of C6Hl2O6? 4.) What types of elements when combined would be most likely to form an ionic compound? 5.) What is the ionic charge on the chromium ion in the ionic compound that has the formula Cr2O3? 6.) In a polyatomic ion the -ite ending indica ...
... 3.) What is the total number of atoms in one molecule of C6Hl2O6? 4.) What types of elements when combined would be most likely to form an ionic compound? 5.) What is the ionic charge on the chromium ion in the ionic compound that has the formula Cr2O3? 6.) In a polyatomic ion the -ite ending indica ...
Here
... c. H = 2.1 and Cl = 3.0 2. Nonpolar a. e- equally shared resulting in a balanced distribution of charge b. e-neg < 0.3 c. H2 C. Basic Definitions 1. Molecule – a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds 2. Chemical Formula – indicates the relative numbers of each kind of atom in a chem ...
... c. H = 2.1 and Cl = 3.0 2. Nonpolar a. e- equally shared resulting in a balanced distribution of charge b. e-neg < 0.3 c. H2 C. Basic Definitions 1. Molecule – a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds 2. Chemical Formula – indicates the relative numbers of each kind of atom in a chem ...
05 Chemistry Basics with Flips 2011
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... In covalently bonded compounds, two or three pairs of electrons can be shared by two atoms. When two pairs are shared the chemical bond is called a double bond. When three pairs are shared it is called a triple bond. Characteristics of Ionic Compounds 1. Crystalline solids made of ions 2. High melti ...
... In covalently bonded compounds, two or three pairs of electrons can be shared by two atoms. When two pairs are shared the chemical bond is called a double bond. When three pairs are shared it is called a triple bond. Characteristics of Ionic Compounds 1. Crystalline solids made of ions 2. High melti ...
Small Business Success on the Web
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... 5. Complete the electron dot structure for each molecule. Each molecule contains only single covalent bonds. ...
... 5. Complete the electron dot structure for each molecule. Each molecule contains only single covalent bonds. ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
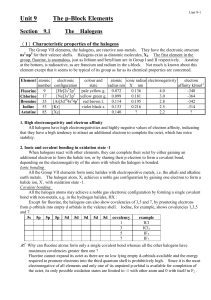
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
File
... Bonding Forces and Energies Inter-atomic spacing is caused by balance between REPULSIVE and ATTRACTIVE forces. Attractive force depends on type of bond trying to form between atoms; Repulsive force occurs when atoms get close together. Net force between atoms is balance of two forces and ...
... Bonding Forces and Energies Inter-atomic spacing is caused by balance between REPULSIVE and ATTRACTIVE forces. Attractive force depends on type of bond trying to form between atoms; Repulsive force occurs when atoms get close together. Net force between atoms is balance of two forces and ...
Ceramic Crystal Structures
... magnesium oxide (used for furnace linings) which is an ionic compound with cubic structure, and silicon carbide, with covalent bonds and a tetrahedral structure similar to that of diamond. Alumina has a close packed hexagonal structure, with a mixture of covalent and ionic bonds, with one-third of t ...
... magnesium oxide (used for furnace linings) which is an ionic compound with cubic structure, and silicon carbide, with covalent bonds and a tetrahedral structure similar to that of diamond. Alumina has a close packed hexagonal structure, with a mixture of covalent and ionic bonds, with one-third of t ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... ______ 4. The B—F bond in BF3 (electronegativity for B is 2.0; electronegativity for F is 4.0) is a. polar covalent. b. nonpolar covalent. c. ionic. d. metallic. ______ 5. The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2p3. How many more electrons does nitrogen need to satisfy the octet rule? a. ...
... ______ 4. The B—F bond in BF3 (electronegativity for B is 2.0; electronegativity for F is 4.0) is a. polar covalent. b. nonpolar covalent. c. ionic. d. metallic. ______ 5. The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2p3. How many more electrons does nitrogen need to satisfy the octet rule? a. ...
Basics of Chemistry
... atom depends on its electron arrangement depends on the number of electrons in its outermost shell, the ...
... atom depends on its electron arrangement depends on the number of electrons in its outermost shell, the ...
Exam 3 Key
... 1. The condition of an atom that has at least one of its electrons in orbitals that do not represent the lowest possible potential energy is called a(n) excited state. 2. A(n) antibonding molecular orbital is formed from out-of-phase interaction of two atomic orbitals. This leads to a decrease in ne ...
... 1. The condition of an atom that has at least one of its electrons in orbitals that do not represent the lowest possible potential energy is called a(n) excited state. 2. A(n) antibonding molecular orbital is formed from out-of-phase interaction of two atomic orbitals. This leads to a decrease in ne ...
Ch. 8 Sections 8.1-8.3 Powerpoint
... •Red indicates the most electron-rich region of the molecule and blue indicates the most electron-poor region. ...
... •Red indicates the most electron-rich region of the molecule and blue indicates the most electron-poor region. ...
Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... [1,2], wood [3,4], organic polymers [5], but to name a few. Their wide range in polarity allows them to be fully miscible with polar substances (water, amides, alcohols, etc.) [6–8], as well as able to dissolve non-polar compounds (aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons) [9]. This fact makes them usefu ...
... [1,2], wood [3,4], organic polymers [5], but to name a few. Their wide range in polarity allows them to be fully miscible with polar substances (water, amides, alcohols, etc.) [6–8], as well as able to dissolve non-polar compounds (aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons) [9]. This fact makes them usefu ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Other types of atomic & molecular interactions – Polar interactions • Attraction between partially charged (polar) molecules and other polar or charged molecules • Similar to ionic bonding ...
... Other types of atomic & molecular interactions – Polar interactions • Attraction between partially charged (polar) molecules and other polar or charged molecules • Similar to ionic bonding ...
Chapter 2 – Chemical Composition of the Body
... • Bonds formed between the hydrogen end (+ charged) of a polar molecule and the – end of any other polar molecule or highly electronegative atom (e.g. P, N, O) are called hydrogen bonds. • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molec ...
... • Bonds formed between the hydrogen end (+ charged) of a polar molecule and the – end of any other polar molecule or highly electronegative atom (e.g. P, N, O) are called hydrogen bonds. • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molec ...
Review Questions
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
cell molecules
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.