Group 2 - UC Davis Canvas
... 107. Both molecules are V shaped, with a lone pair of electrons on the central atom. For O3, the structure is a hybrid of two equivalent structures. In each of these structures, the central atom has a formal charge of +1. The oxygen–oxygen bond order is between 1 and 2. Although many resonance struc ...
... 107. Both molecules are V shaped, with a lone pair of electrons on the central atom. For O3, the structure is a hybrid of two equivalent structures. In each of these structures, the central atom has a formal charge of +1. The oxygen–oxygen bond order is between 1 and 2. Although many resonance struc ...
Chemistry - Napa Valley College
... In 1896, Henri Becquerel placed a rock on unexposed photographic plates inside a drawer. The rock contained uranium. ...
... In 1896, Henri Becquerel placed a rock on unexposed photographic plates inside a drawer. The rock contained uranium. ...
Chapter 10. Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry and
... Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals from p Atomic Orbitals Figure 10.24 - shows interaction to form • σ bonds when atomic orbitals approach end to end • π bonds when atomic orbitals approach side to side ...
... Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals from p Atomic Orbitals Figure 10.24 - shows interaction to form • σ bonds when atomic orbitals approach end to end • π bonds when atomic orbitals approach side to side ...
vsepr_lite_oct_2011 - chemistry11crescentsummer
... understand covalent bonding—polar and non-polar be able to draw Lewis structures for simple molecules and polyatomic ions, including molecules with double and triple bonds Introduction The premise of VSEPR theory: In a molecule or polyatomic ion, pairs of valence electrons on the central atom (c ...
... understand covalent bonding—polar and non-polar be able to draw Lewis structures for simple molecules and polyatomic ions, including molecules with double and triple bonds Introduction The premise of VSEPR theory: In a molecule or polyatomic ion, pairs of valence electrons on the central atom (c ...
Chapters 9 and 10
... Account for the following observations using principles of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding. In each part, your answer must include specific information about both substances. a. The Ca2+ and Cl- ions are isoelectronic, but their radii are not the same. Which ion has the larger radius? Expla ...
... Account for the following observations using principles of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding. In each part, your answer must include specific information about both substances. a. The Ca2+ and Cl- ions are isoelectronic, but their radii are not the same. Which ion has the larger radius? Expla ...
Atomic combinations: Electronegativity and ionic
... book called 'The Nature of the Chemical Bond', which became one of the most in uential chemistry books ever published. For this work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. He also received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962 for his campaign against above-ground nuclear testing. note: ...
... book called 'The Nature of the Chemical Bond', which became one of the most in uential chemistry books ever published. For this work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. He also received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962 for his campaign against above-ground nuclear testing. note: ...
specimen
... Calcium carbonate, CaCO3, reacts with acids such as nitric acid. A student neutralised 2.68 g of CaCO3 with 2.50 mol dm–3 nitric acid, HNO3. The equation for this reaction is shown below. CaCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) ⎯→ Ca(NO3)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) (i) ...
... Calcium carbonate, CaCO3, reacts with acids such as nitric acid. A student neutralised 2.68 g of CaCO3 with 2.50 mol dm–3 nitric acid, HNO3. The equation for this reaction is shown below. CaCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) ⎯→ Ca(NO3)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) (i) ...
Summary from Organic Chemistry Packet:
... • Recognize the terms cis-, trans- isomers – Unsaturated molecules – Orientation around the double bond ...
... • Recognize the terms cis-, trans- isomers – Unsaturated molecules – Orientation around the double bond ...
Inorganic Chemistry 412 / 512
... Note: each acetato ligand is bidentate, with one O atom bonding to each metal ion. (b) Give the electron configuration (filling of σ, π, and δ orbitals) in the cluster. [5 pts] In this case, we have 2 Cr (II) ions, each is d4. The electron configuration is ...
... Note: each acetato ligand is bidentate, with one O atom bonding to each metal ion. (b) Give the electron configuration (filling of σ, π, and δ orbitals) in the cluster. [5 pts] In this case, we have 2 Cr (II) ions, each is d4. The electron configuration is ...
Unit 2 - Biochemistry Notes
... Chemical reactions are the making and breaking of chemical bonds The starting molecules of a chemical reaction are called reactants The final molecules of a chemical reaction are called products ...
... Chemical reactions are the making and breaking of chemical bonds The starting molecules of a chemical reaction are called reactants The final molecules of a chemical reaction are called products ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Carbon forms a variety of strong covalent bonds (共价键) to itself and other atoms. • This allows organic compounds to be structurally diverse. ...
... • Carbon forms a variety of strong covalent bonds (共价键) to itself and other atoms. • This allows organic compounds to be structurally diverse. ...
Organic Chemistry I: Contents
... *Any orbital (molecular or atomic ) can hold a maximium of two electrons, which must be of opposite spin. •The number of MO equal the number of AO used for their formation. •In the filling of MO with e , the lowest- energy orbitals are filled first. . • Sigma bond is formed from sigma MO (orbital th ...
... *Any orbital (molecular or atomic ) can hold a maximium of two electrons, which must be of opposite spin. •The number of MO equal the number of AO used for their formation. •In the filling of MO with e , the lowest- energy orbitals are filled first. . • Sigma bond is formed from sigma MO (orbital th ...
Doping and Crystal Growth Techniques
... Compressive strain if the ionic radius is larger Tensile strain if the ionic radius is smaller ...
... Compressive strain if the ionic radius is larger Tensile strain if the ionic radius is smaller ...
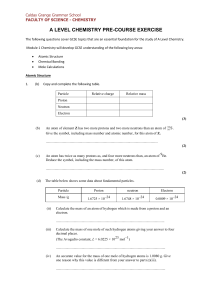
2016 Pre Course CHEMISTRY - Calday Grange Grammar School
... Deduce the type of bonding present in Na2S and that present in CS2 Bonding in Na2S ........................................................................................ Bonding in CS2........................................................................................... ...
... Deduce the type of bonding present in Na2S and that present in CS2 Bonding in Na2S ........................................................................................ Bonding in CS2........................................................................................... ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... Compounds of 3A elements have more covalent character than similar 2A compounds. Aluminum has the physical properties of a metal, but its halides exist as covalent dimers. ...
... Compounds of 3A elements have more covalent character than similar 2A compounds. Aluminum has the physical properties of a metal, but its halides exist as covalent dimers. ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
Density of Electron States and Relaxation Time of Intercalated Layer
... particularly 3d-atoms, allows us to create new materials which can be very important for using in different aspects of applied physics [1]. The structures with alternating semiconducting and magneto-active layers can serve as materials on the base of those ones, can create the spintronics elements, ...
... particularly 3d-atoms, allows us to create new materials which can be very important for using in different aspects of applied physics [1]. The structures with alternating semiconducting and magneto-active layers can serve as materials on the base of those ones, can create the spintronics elements, ...
Chemical Bonds - coellochemistry
... Naming Covalent Compounds For covalent compounds both of the nonmetals must have prefixes assigned to represent the number of atoms The second element has a prefix and has the ending changed to -ide ...
... Naming Covalent Compounds For covalent compounds both of the nonmetals must have prefixes assigned to represent the number of atoms The second element has a prefix and has the ending changed to -ide ...
Introduction to SOLID STATE PHYSICS
... The shape of a molecule influences its ability to form temporary dipoles. Long thin molecules can pack closer to each other than molecules that are more spherical. The bigger the 'surface area' of a molecule, the greater the van der Waal's forces will be and the higher the melting and boiling points ...
... The shape of a molecule influences its ability to form temporary dipoles. Long thin molecules can pack closer to each other than molecules that are more spherical. The bigger the 'surface area' of a molecule, the greater the van der Waal's forces will be and the higher the melting and boiling points ...
Covalent Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
Covalent Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
HOMEWORK 6-1 - losbanosusd.k12.ca.us
... 1. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable than those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
... 1. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable than those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.