Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
Electrons - biospaces
... number of orbitals Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... number of orbitals Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
6. NaF
... Rules for Naming Binary Covalent Compounds A binary covalent compound is composed of two different nonmetal elements. For example, a molecule of chlorine trifluoride, ClF3 contains 1 atom of chlorine and 3 atoms of fluorine. Rule 1. The element with the lower group number is written first in the na ...
... Rules for Naming Binary Covalent Compounds A binary covalent compound is composed of two different nonmetal elements. For example, a molecule of chlorine trifluoride, ClF3 contains 1 atom of chlorine and 3 atoms of fluorine. Rule 1. The element with the lower group number is written first in the na ...
Chapter 08
... Lewis Structures and Formal Charge When there is more than one possible structure, the best arrangement is determined by the following guidelines: 1) A Lewis structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferred. 2) Small formal charges are preferred to large formal charges. ...
... Lewis Structures and Formal Charge When there is more than one possible structure, the best arrangement is determined by the following guidelines: 1) A Lewis structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferred. 2) Small formal charges are preferred to large formal charges. ...
Topic 4 Chemistry of the Elements of the Main Group
... electricity. Metals make crystal lattice structures in which electrons can flow freely. Metalloids or semi-metals show intermediate conduction properties (they are semiconductors). Their electronegativity values are close to 2. The valence electrons of metalloids are localised around the nucleus but ...
... electricity. Metals make crystal lattice structures in which electrons can flow freely. Metalloids or semi-metals show intermediate conduction properties (they are semiconductors). Their electronegativity values are close to 2. The valence electrons of metalloids are localised around the nucleus but ...
Isomeric forms of Cu(quinoline-2-carboxylate) O Spectroscopic and magnetic properties H
... The distortion of the CuN2O3 chromophore causes the appearance of an asymmetric band in d-d reflectance spectra, with a maximum at 13 890 cm–1. There is also evidence of a weak, poorly resolved shoulder on the low-frequency side with almost comparable intensity at about 10 200 cm–1, separated by ca. ...
... The distortion of the CuN2O3 chromophore causes the appearance of an asymmetric band in d-d reflectance spectra, with a maximum at 13 890 cm–1. There is also evidence of a weak, poorly resolved shoulder on the low-frequency side with almost comparable intensity at about 10 200 cm–1, separated by ca. ...
Section 4.8: The Structure and Properties of Solids
... 3. (a) Metallic crystals are one of the two solid conductors, and they conduct better than semiconductors. (b) Molecular crystals are held together by intermolecular forces, which are weak compared to the bonding in the other types of crystals, so molecular crystals would melt at a lower temperature ...
... 3. (a) Metallic crystals are one of the two solid conductors, and they conduct better than semiconductors. (b) Molecular crystals are held together by intermolecular forces, which are weak compared to the bonding in the other types of crystals, so molecular crystals would melt at a lower temperature ...
Revision Y12 Chemistry PLC
... Lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs and the bond angles for common examples of each shape including CH4 (109.5°), NH3 (107°) and H2O (104.5°). Electronegativity and bond polarity (i) electronegativity as the ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond; interpretation o ...
... Lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs and the bond angles for common examples of each shape including CH4 (109.5°), NH3 (107°) and H2O (104.5°). Electronegativity and bond polarity (i) electronegativity as the ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond; interpretation o ...
(S-Benzylthiuronium) Chloranilate Supramolecular Crystal Structure
... A novel supramolecular structure, [C8H11N2S]2‚(C6Cl2O4), based on hydrogen bonding of the organic S-benzylthiuronium (SBT) cation and the chloranilate dianion, is presented. Chloranilic acid or 2,5dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, is a strong quinoidal diphenic acid (pK1 ) 1.09 and pK2 ) 2.42 ...
... A novel supramolecular structure, [C8H11N2S]2‚(C6Cl2O4), based on hydrogen bonding of the organic S-benzylthiuronium (SBT) cation and the chloranilate dianion, is presented. Chloranilic acid or 2,5dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, is a strong quinoidal diphenic acid (pK1 ) 1.09 and pK2 ) 2.42 ...
Alcohol responsive 2D coordination network of 3
... One of the most important objectives in the field of coordination networks or metal organic frameworks is the engineering of porous structures with a well defined chemical environment [1–2]. This is however very difficult to achieve in 3D structures due to catenation and interpenetration. Thus in re ...
... One of the most important objectives in the field of coordination networks or metal organic frameworks is the engineering of porous structures with a well defined chemical environment [1–2]. This is however very difficult to achieve in 3D structures due to catenation and interpenetration. Thus in re ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... • Atoms that differ in number of neutrons • Also differ in mass number(since it is p + n) • But all have the same number of protons ...
... • Atoms that differ in number of neutrons • Also differ in mass number(since it is p + n) • But all have the same number of protons ...
Lone pairs
... Occurs when hydrogen is bonded to a highly electronegative element (fluorine, oxygen and nitrogen) – chemistry is FON!!! The hydrogen end of the bond takes on a strong positive charge because of the exposed positive nucleus, while the other element takes on a strong negative charge This positive hyd ...
... Occurs when hydrogen is bonded to a highly electronegative element (fluorine, oxygen and nitrogen) – chemistry is FON!!! The hydrogen end of the bond takes on a strong positive charge because of the exposed positive nucleus, while the other element takes on a strong negative charge This positive hyd ...
IE EA
... f) SF6 Neither; the coordination number of six is rarely exceeded so that this molecule does not act as a Lewis acid and the high electronegativity of fluorine does not allow for it to act as a base. g) PCl5 Acidic; this compound reacts with a wide variety of Lewis bases to form adducts. h) (CH3)3N ...
... f) SF6 Neither; the coordination number of six is rarely exceeded so that this molecule does not act as a Lewis acid and the high electronegativity of fluorine does not allow for it to act as a base. g) PCl5 Acidic; this compound reacts with a wide variety of Lewis bases to form adducts. h) (CH3)3N ...
Ch. 2 Chemistry
... bonding between atoms. • A covalent bond • Is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons ...
... bonding between atoms. • A covalent bond • Is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons ...
ppt Lewis Dot Diagram Rules
... In general when there is a single central atom in the molecule, CH2ClF, SeCl2, O3 (CO2, NH3, PO43-), the central atom is the first atom in the chemical formula. Except when the first atom in the chemical formula is Hydrogen (H) or fluorine (F). In which case the central atom is the second atom in th ...
... In general when there is a single central atom in the molecule, CH2ClF, SeCl2, O3 (CO2, NH3, PO43-), the central atom is the first atom in the chemical formula. Except when the first atom in the chemical formula is Hydrogen (H) or fluorine (F). In which case the central atom is the second atom in th ...
Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... Protons: positively charged (Located in the nucleus) Neutrons: neutrally charged (Located in the nucleus) Electrons: negatively charged (Located around the nucleus) Discovered by ...
... Protons: positively charged (Located in the nucleus) Neutrons: neutrally charged (Located in the nucleus) Electrons: negatively charged (Located around the nucleus) Discovered by ...
CH2 Student Revision Guides pdf
... include induced-dipole - induced-dipole interactions and dipole-dipole interactions. . The electrons within an atom or molecule are in motion and at a given instant they may be so displaced that the effect is to produce an instantaneous dipole. [A dipole in a molecule is a separation of charge so th ...
... include induced-dipole - induced-dipole interactions and dipole-dipole interactions. . The electrons within an atom or molecule are in motion and at a given instant they may be so displaced that the effect is to produce an instantaneous dipole. [A dipole in a molecule is a separation of charge so th ...
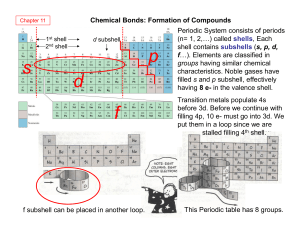
Grade 10 NSC Chemistry Curriculum
... covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simple ionic compounds. Ionic structure as illustrated by sodium chloride • Revise the writing of names when given the form ...
... covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simple ionic compounds. Ionic structure as illustrated by sodium chloride • Revise the writing of names when given the form ...
Elements (NonMetals)
... Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small radius Unique properties of both group 1 and 17 Bond energy 431kJ/mol – very st ...
... Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small radius Unique properties of both group 1 and 17 Bond energy 431kJ/mol – very st ...
Chapter 24. Organic Chemistry
... Example The electron configuration of core electrons of a carbon atom (C) ...
... Example The electron configuration of core electrons of a carbon atom (C) ...
3.091 – Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No
... by electronic rearrangements must be in a lower energy state than the atoms were prior to interaction, prior to bond formation. Since atoms of each of the elements have different electronic structures, the variety of possible chemical bonds (differing from each other in at least some small way) is c ...
... by electronic rearrangements must be in a lower energy state than the atoms were prior to interaction, prior to bond formation. Since atoms of each of the elements have different electronic structures, the variety of possible chemical bonds (differing from each other in at least some small way) is c ...
01 Intro Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
02Ch02chemistry2005
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry
... pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Document
... each multiple bond as a single electron group, because it occupies roughly the same region of space. The number of electron groups around an atom is called the atom’s steric number (SN). Dot structures of formaldehyde and acetylene are arbitrarily shown with angles of 90o. Their true geometry has bo ...
... each multiple bond as a single electron group, because it occupies roughly the same region of space. The number of electron groups around an atom is called the atom’s steric number (SN). Dot structures of formaldehyde and acetylene are arbitrarily shown with angles of 90o. Their true geometry has bo ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.