Homework 1 - Devin Gatherwright IET 307 Portfolio
... the electron. Some characteristics of covalent bonding are as follows: covalent bonding is that they can either be a very strong bond (such as a diamond,) or a very weak bond (such as barium.) Also, covalent bonds, like ionic bonds, are good insulators of heat and electricity. 4. What is Van der Waa ...
... the electron. Some characteristics of covalent bonding are as follows: covalent bonding is that they can either be a very strong bond (such as a diamond,) or a very weak bond (such as barium.) Also, covalent bonds, like ionic bonds, are good insulators of heat and electricity. 4. What is Van der Waa ...
Small molecule Crystallography at the Indian Institute of Science
... solids, charge density analysis, crystal engineering and supramolecular chemistry iinvolving fluorine, materials design using novel organometallic framework. The Bruker AXS SMART APEX system is the most recent member of the SMART CCD product line of instrumentation for single crystal X-ray diffracti ...
... solids, charge density analysis, crystal engineering and supramolecular chemistry iinvolving fluorine, materials design using novel organometallic framework. The Bruker AXS SMART APEX system is the most recent member of the SMART CCD product line of instrumentation for single crystal X-ray diffracti ...
Small molecule Crystallography at the Indian Institute of Science
... structure determination of inorganic systems ranging from metal hydrides, Cu I and Cu II complexes, Calixarenes and Phosphazenes and related metal complexes, organic frameworks depicting biological activity like for example Otteliones (anti-tuberculosis), antibiotic diterpene Guanacastpene A and fra ...
... structure determination of inorganic systems ranging from metal hydrides, Cu I and Cu II complexes, Calixarenes and Phosphazenes and related metal complexes, organic frameworks depicting biological activity like for example Otteliones (anti-tuberculosis), antibiotic diterpene Guanacastpene A and fra ...
Chapter 5
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
Review for second exam:
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
Bonding. A. Ionic bonds form when anions and cations arise
... 1. The oxidation number of any element in its free (or uncombined) state is 0. 2. The oxidation number of any ion is the charge of the ion. 3. The oxidation number of any family IA metal is +1. 4. The oxidation number of any family IIA metal is +2. 5. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (except a ...
... 1. The oxidation number of any element in its free (or uncombined) state is 0. 2. The oxidation number of any ion is the charge of the ion. 3. The oxidation number of any family IA metal is +1. 4. The oxidation number of any family IIA metal is +2. 5. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (except a ...
Microsoft Word
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
Chapter 9 Notes - UIC Department of Chemistry
... Ionic compounds contain both a cation and an anion held together by strong electrostatic forces (originating in their charges.) Lewis structures for ionic compounds are written by putting two Lewis ionic symbols together. F− Lewis structures for ions: Mg2+ Ionic compounds-put the ions together as in ...
... Ionic compounds contain both a cation and an anion held together by strong electrostatic forces (originating in their charges.) Lewis structures for ionic compounds are written by putting two Lewis ionic symbols together. F− Lewis structures for ions: Mg2+ Ionic compounds-put the ions together as in ...
halogen compounds organic chemistry
... the C-Cl bond in aryl halides is less polar than in alkyl halides. This is supported by the fact that the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is 1.73 D while the dipole moment of chloroethane is 2.05 D. Lesser the polarity of C-Cl bond, lesser is the reactivity. Thus, haloarenes are less reactive towards ...
... the C-Cl bond in aryl halides is less polar than in alkyl halides. This is supported by the fact that the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is 1.73 D while the dipole moment of chloroethane is 2.05 D. Lesser the polarity of C-Cl bond, lesser is the reactivity. Thus, haloarenes are less reactive towards ...
Ceramics Ceramics are inorganic and nonmetallic materials
... Because ceramics are composed of at least two elements, and often more, their crystal structures are generally more complex than those for metals Crystal Structures For those ceramic materials for which the atomic bonding is predominantly ionic, the crystal structures may be thought of as being comp ...
... Because ceramics are composed of at least two elements, and often more, their crystal structures are generally more complex than those for metals Crystal Structures For those ceramic materials for which the atomic bonding is predominantly ionic, the crystal structures may be thought of as being comp ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding
... Atoms tend to gain, lose or share e- to get to the nearest noble gas configuration Noble gases: all (except He) have s2p6 valence shells (8 e-) ...
... Atoms tend to gain, lose or share e- to get to the nearest noble gas configuration Noble gases: all (except He) have s2p6 valence shells (8 e-) ...
Type of Bonding
... • coulombic in origin, occurs between oppositely charged species • electron transfer from one atom to another • force between an ion and a dipole or two dipoles where the (+) charge attracts the (-) charge (purely electrostatic) • H-bonding : a special type of dipole-dipole interaction that results ...
... • coulombic in origin, occurs between oppositely charged species • electron transfer from one atom to another • force between an ion and a dipole or two dipoles where the (+) charge attracts the (-) charge (purely electrostatic) • H-bonding : a special type of dipole-dipole interaction that results ...
Worksheet 20.2
... 1- Atoms can achieve a noble gas structure by gaining, losing or sharing electrons with other atoms. 2- The rule states that, except for hydrogen , an atom combines with other atoms to form bonds in order to have 8 electrons in its valence energy level ( like noble gases). Lewis dot symbols are repr ...
... 1- Atoms can achieve a noble gas structure by gaining, losing or sharing electrons with other atoms. 2- The rule states that, except for hydrogen , an atom combines with other atoms to form bonds in order to have 8 electrons in its valence energy level ( like noble gases). Lewis dot symbols are repr ...
Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
PSI AP Chemistry Name Unit 4: Chemical Bonding MC Review Part
... (C) Bond length and bond strength are not related. (D) The relationship between bond length and bond strength depends on other factors. 13. Of the bonds C–C, C=C, and C≡C, the C–C bond is __________. (A) strongest/shortest (B) strongest/longest (C) weakest/longest (D) weakest/shortest (E) intermedia ...
... (C) Bond length and bond strength are not related. (D) The relationship between bond length and bond strength depends on other factors. 13. Of the bonds C–C, C=C, and C≡C, the C–C bond is __________. (A) strongest/shortest (B) strongest/longest (C) weakest/longest (D) weakest/shortest (E) intermedia ...
Chemistry 212 Name:
... Na2S(aq) + 2 HCl(aq) → 2 NaCl(aq) + H2S(g) 5. Discuss the halogens. (5 points) Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms re ...
... Na2S(aq) + 2 HCl(aq) → 2 NaCl(aq) + H2S(g) 5. Discuss the halogens. (5 points) Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms re ...
Chapter 4 REVIEW
... Chapter 4 REVIEW 1. Draw Lewis symbols for atoms of the following elements and predict their bonding capacity: (a) calcium (d) silicon (b) chlorine (e) sulfur (c) phosphorus ...
... Chapter 4 REVIEW 1. Draw Lewis symbols for atoms of the following elements and predict their bonding capacity: (a) calcium (d) silicon (b) chlorine (e) sulfur (c) phosphorus ...
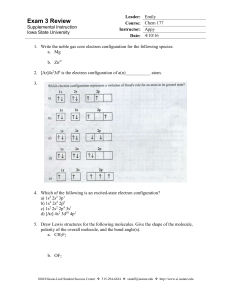
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 1. What is atomic number? 2. How does increasing the atomic number affect the identity of an atom? 3. What is atomic mass? What two subatomic particles make up the majority of an atom’s mass? 4. Describe the gold foil experiment. What was the important discovery in that experiment? 5. Where are the ...
... 1. What is atomic number? 2. How does increasing the atomic number affect the identity of an atom? 3. What is atomic mass? What two subatomic particles make up the majority of an atom’s mass? 4. Describe the gold foil experiment. What was the important discovery in that experiment? 5. Where are the ...
lecture 6
... with only a small amount of cubic ice Ic Ice rules: two H atoms near each O atom, one H atom on each O …O bond, H-O-H angle little less than the tetrahedral angle (109.47°), at about 107°. Cohesive energy 0.58eV; lattice constant 2.75Å ...
... with only a small amount of cubic ice Ic Ice rules: two H atoms near each O atom, one H atom on each O …O bond, H-O-H angle little less than the tetrahedral angle (109.47°), at about 107°. Cohesive energy 0.58eV; lattice constant 2.75Å ...
Bonding Challenge
... 2) Put each of the following series in order of increasing size: a) Al3+, N3-, O2-, Ar, Li+ b) K, Na, Sr, Na+, P33) Put the following in order of increasing C-C bond length: C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 4) Put the following in order of increasing C-C bond strength: C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 5) Using princi ...
... 2) Put each of the following series in order of increasing size: a) Al3+, N3-, O2-, Ar, Li+ b) K, Na, Sr, Na+, P33) Put the following in order of increasing C-C bond length: C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 4) Put the following in order of increasing C-C bond strength: C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 5) Using princi ...
Chemistry: The Basics
... – Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. – Actual mass = 1.67 x 10-24 grams – No charge ...
... – Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. – Actual mass = 1.67 x 10-24 grams – No charge ...
Chemistry I Honors
... The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal energies Hybrid orbitals - equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom ...
... The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal energies Hybrid orbitals - equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.