Chapter 2 BIO 100 Chemistry
... 1) Hydrogen 2) Ionic (weak in water) 3)Van der Waals Because these bonds are transient and easily broken, they can be used for: 1) Cell Signaling 2) Linking Molecules Together 3) 3D shape ...
... 1) Hydrogen 2) Ionic (weak in water) 3)Van der Waals Because these bonds are transient and easily broken, they can be used for: 1) Cell Signaling 2) Linking Molecules Together 3) 3D shape ...
www.theallpapers.com
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
Odd Number of Electrons
... 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend to be chemically unreactive. 5. Units are measured in kJ/mo1 6. A mol is a che ...
... 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend to be chemically unreactive. 5. Units are measured in kJ/mo1 6. A mol is a che ...
Honors Unit 5 Practice Test
... a. increase their potential energy, thus creating less-stable arrangements of matter. b. decrease their potential energy, thus creating less-stable arrangements of matter. c. increase their potential energy, thus creating more-stable arrangements of matter. d. decrease their potential energy, thus c ...
... a. increase their potential energy, thus creating less-stable arrangements of matter. b. decrease their potential energy, thus creating less-stable arrangements of matter. c. increase their potential energy, thus creating more-stable arrangements of matter. d. decrease their potential energy, thus c ...
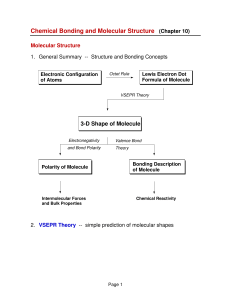
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
... between a pair of atoms, the shorter the bond. This implies that atoms are held together more tightly when there are multiple bonds, so there is a relation between bond order and the energy required to separate them. Calculating reaction energies from bond energies: Bonds in reactants are broken whi ...
... between a pair of atoms, the shorter the bond. This implies that atoms are held together more tightly when there are multiple bonds, so there is a relation between bond order and the energy required to separate them. Calculating reaction energies from bond energies: Bonds in reactants are broken whi ...
video slide
... Around 25 elements are essential to life C, H, O, and N -- 96% of living matter Ca, P, K, and S -- most of the rest Trace elements -- required by an organism in ...
... Around 25 elements are essential to life C, H, O, and N -- 96% of living matter Ca, P, K, and S -- most of the rest Trace elements -- required by an organism in ...
Covalent Bonds - WordPress.com
... • A molecule’s shape is usually very important to its function • A molecule’s shape is determined by the positions of its atoms’ valence orbitals • Biological molecules recognize and interact with each other with a specificity based on ...
... • A molecule’s shape is usually very important to its function • A molecule’s shape is determined by the positions of its atoms’ valence orbitals • Biological molecules recognize and interact with each other with a specificity based on ...
Chemical Bonding I
... 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be sure to take ions into account!) 3) Distribute the electrons among the atoms giving octets to all atoms ...
... 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be sure to take ions into account!) 3) Distribute the electrons among the atoms giving octets to all atoms ...
Medical Physics and Statistics
... which the public is manipulated by vague references to science in generating environmental concern. He prepared a proposal for banning the use of the chemical ...
... which the public is manipulated by vague references to science in generating environmental concern. He prepared a proposal for banning the use of the chemical ...
1 Chemistry 400: General Chemistry Name: Miller Fall 2015 Final
... involved and their percents of ionization. (8 points) ...
... involved and their percents of ionization. (8 points) ...
ch14
... Compounds of 3A elements have more covalent character than similar 2A compounds. Aluminum has the physical properties of a metal, but its halides exist as covalent dimers. ...
... Compounds of 3A elements have more covalent character than similar 2A compounds. Aluminum has the physical properties of a metal, but its halides exist as covalent dimers. ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... (a) Size of cation is always smaller than the parent atom. (b) Ionization enthalpy of nitrogen is greater than that of oxygen. (c) Electron gain enthalpies of beryllium and magnesium are positive. ...
... (a) Size of cation is always smaller than the parent atom. (b) Ionization enthalpy of nitrogen is greater than that of oxygen. (c) Electron gain enthalpies of beryllium and magnesium are positive. ...
Chem Bonding Notes
... 9. Metallic bonding occurs between atoms of (1) sulfur (3) fluorine (2) copper (4) carbon 10. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are (1) transferred from one atom to another (2) captured by the nucleus (3) mobile within a metal (4) shared between two atoms ...
... 9. Metallic bonding occurs between atoms of (1) sulfur (3) fluorine (2) copper (4) carbon 10. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are (1) transferred from one atom to another (2) captured by the nucleus (3) mobile within a metal (4) shared between two atoms ...
bonding and geometry
... Very rare Tend to form harmful molecules Occurs when both of the bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond come from only ONE of the atoms Example: CO ...
... Very rare Tend to form harmful molecules Occurs when both of the bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond come from only ONE of the atoms Example: CO ...
atoms-chemical
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... • Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their electron configurations are especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharin ...
... • Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their electron configurations are especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharin ...
Bonding
... b.On the basis of the Lewis structures drawn in part (a), answer the following questions about the particular species indicated. i. What is the Cl-Ge-Cl bond angle in GeCl4? ...
... b.On the basis of the Lewis structures drawn in part (a), answer the following questions about the particular species indicated. i. What is the Cl-Ge-Cl bond angle in GeCl4? ...
download
... electrical charge of the molecule. Take water as an example. Research has determined the hydrogen atoms are bonded to the oxygen atoms at an angle of 104.5°. This angle produces a positive polarity at the hydrogen-rich end of the molecule and a negative polarity at the other end. A result of this ch ...
... electrical charge of the molecule. Take water as an example. Research has determined the hydrogen atoms are bonded to the oxygen atoms at an angle of 104.5°. This angle produces a positive polarity at the hydrogen-rich end of the molecule and a negative polarity at the other end. A result of this ch ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... Intermolecular bonds are also called as weak interactions, since their strength is much less as compared to intra molecular bonds, such as ionic, covalent, metallic and covalent network bonds. ...
... Intermolecular bonds are also called as weak interactions, since their strength is much less as compared to intra molecular bonds, such as ionic, covalent, metallic and covalent network bonds. ...
Chem MCQ for Class-9th
... 1. The atomic radii of the elements in Periodic Table: a. Incrase from left to right ina period b. Increase from top to bottom in group c. Do not change from left to right in a period d. Decrease from top to bottom in a group 2. The amount of energy given out when an electron is added to an atom is ...
... 1. The atomic radii of the elements in Periodic Table: a. Incrase from left to right ina period b. Increase from top to bottom in group c. Do not change from left to right in a period d. Decrease from top to bottom in a group 2. The amount of energy given out when an electron is added to an atom is ...
Elements, basic principles, periodic table
... - ion is larger than the neutral atom Ions behave the same as atoms across the periodic table (row vs column Importance of the radius: molecules can only “fit” certain sizes ...
... - ion is larger than the neutral atom Ions behave the same as atoms across the periodic table (row vs column Importance of the radius: molecules can only “fit” certain sizes ...
12-3: Lewis Structures
... around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so it is like helium Draw the Lewis structures for: H Ca N F ...
... around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so it is like helium Draw the Lewis structures for: H Ca N F ...
Stoichiometry Mole Concept Balancing Chemical Equations
... All such compounds involve the transfer of one or two electrons from the metal atom to the nonmetal atom to form positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). ...
... All such compounds involve the transfer of one or two electrons from the metal atom to the nonmetal atom to form positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). ...
3-D Shape of Molecule
... e- pair bonds between two atoms using overlap of atomic orbitals on two atoms Molecular Orbital Theory (more general but "complex") all e-'s in molecule fill up a set of molecular orbitals that are made up of linear combinations of atomic orbitals on two or more atoms MO's can be: ...
... e- pair bonds between two atoms using overlap of atomic orbitals on two atoms Molecular Orbital Theory (more general but "complex") all e-'s in molecule fill up a set of molecular orbitals that are made up of linear combinations of atomic orbitals on two or more atoms MO's can be: ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.