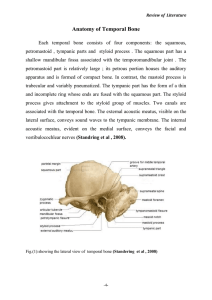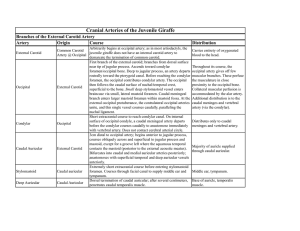
Cranial Arteries of the Juvenile Giraffe
... 3cm distal to occipital artery; begins anterior to jugular process, courses obliquely across and superficial to jugular process and mastoid, except for a groove left where the squamous temporal External Carotid contacts the mastoid (posterior to the external acoustic meatus). Bifurcates into caudal ...
... 3cm distal to occipital artery; begins anterior to jugular process, courses obliquely across and superficial to jugular process and mastoid, except for a groove left where the squamous temporal External Carotid contacts the mastoid (posterior to the external acoustic meatus). Bifurcates into caudal ...
Postilla - Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History
... The description of the braincase of Bienotherium yunnanense Young (1940) is based primarily upon the posterior half of an adult skull which was sectioned serially using the method described by Olson (1944). In addition, several fragmentary specimens of the ear region and part of the braincase were u ...
... The description of the braincase of Bienotherium yunnanense Young (1940) is based primarily upon the posterior half of an adult skull which was sectioned serially using the method described by Olson (1944). In addition, several fragmentary specimens of the ear region and part of the braincase were u ...
Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
... 1. Shift the head end of the supine cadaver on the edge of the dissection table and place a wooden block under the cervicothoracic junction. This will give you a clear space to work on the occipital region as well. 2. Give a median incision ‘A’ from the root of the nose to the external occipital pro ...
... 1. Shift the head end of the supine cadaver on the edge of the dissection table and place a wooden block under the cervicothoracic junction. This will give you a clear space to work on the occipital region as well. 2. Give a median incision ‘A’ from the root of the nose to the external occipital pro ...
Nasal cartilages
... and from the vacuum chamber around them.2-the skeleton of thorax 3-the diaphragm. *Function of the respiratory system: 1-exchange of oxygen. 2-voice producing (a role in which the larynx plays an important part). 3-the respiratory system is also associated with the olfactory system (part nasal mucou ...
... and from the vacuum chamber around them.2-the skeleton of thorax 3-the diaphragm. *Function of the respiratory system: 1-exchange of oxygen. 2-voice producing (a role in which the larynx plays an important part). 3-the respiratory system is also associated with the olfactory system (part nasal mucou ...
suboccipital triangle
... Rectus capitis posterior major Arises by a pointed tendon from the spinous process of the axis, and, becoming broader as it ascends Inserted into the lateral part of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone and the surface of the bone immediately below the line. As the muscles of the two sid ...
... Rectus capitis posterior major Arises by a pointed tendon from the spinous process of the axis, and, becoming broader as it ascends Inserted into the lateral part of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone and the surface of the bone immediately below the line. As the muscles of the two sid ...
Muscles
... The boundaries of the anterior triangle consisted of the following all incorrect except one sentence is correct? A-anterior border of the trapezius muscle. B—anterior border of the sternomastoid muscle. C-upper border of the mandible ;alveolar process .D-inferior belly of omohyoid muscle ...
... The boundaries of the anterior triangle consisted of the following all incorrect except one sentence is correct? A-anterior border of the trapezius muscle. B—anterior border of the sternomastoid muscle. C-upper border of the mandible ;alveolar process .D-inferior belly of omohyoid muscle ...
Septoplasty - Vula - University of Cape Town
... periosteum of the vomer and perichondrium of the quadrangular cartilage due to its origin from the maxillary processes. This has clinical relevance as one has to cut across these fibrous attachments in order to join subperichondrial and subperiosteal dissection planes over the quadrangular cartilage ...
... periosteum of the vomer and perichondrium of the quadrangular cartilage due to its origin from the maxillary processes. This has clinical relevance as one has to cut across these fibrous attachments in order to join subperichondrial and subperiosteal dissection planes over the quadrangular cartilage ...
ARTICULAR SYSTEM
... the contrary, peripheral regions of the mesenchyme, which surround the cavity, condense, giving rise to the fibrous capsule and ligaments of the joint. Cartilaginous epiphyses ossify in such away that a thin layer of articular cartilage remains on their surfaces for life, which provides the smoothne ...
... the contrary, peripheral regions of the mesenchyme, which surround the cavity, condense, giving rise to the fibrous capsule and ligaments of the joint. Cartilaginous epiphyses ossify in such away that a thin layer of articular cartilage remains on their surfaces for life, which provides the smoothne ...
12-Temporal & infratemporal fossa I
... They are derived from mesoderm of 1st branchial arch They originate from temporal or infratemporal fossa They are inserted into ramus of mandible They are supplied, through their deep surfaces by branches of mandibular nerve They act on temporomandibular joint ...
... They are derived from mesoderm of 1st branchial arch They originate from temporal or infratemporal fossa They are inserted into ramus of mandible They are supplied, through their deep surfaces by branches of mandibular nerve They act on temporomandibular joint ...
Amal Ghonemy Metwali Abo Zekry_review
... portion ,both are open separately into the mastoid antrum and may give false impression of reaching the antrum ( Glasscock and Shambaugh,2010). In well pneumatized mastoid process ,this septum is hardly recognizable But if the squamous portion is poorly pneumatized or sclerotic ,there may be great d ...
... portion ,both are open separately into the mastoid antrum and may give false impression of reaching the antrum ( Glasscock and Shambaugh,2010). In well pneumatized mastoid process ,this septum is hardly recognizable But if the squamous portion is poorly pneumatized or sclerotic ,there may be great d ...
Name Period _________ Due date _____________ FROG
... Locate each of the organs below. Fat bodies – spaghetti shaped structures that have a bright orange or yellow color. Fat bodies may need to be removed to see other structures. They are usually located just inside the abdominal wall. Peritoneum – A spider web-like membrane that covers many of the or ...
... Locate each of the organs below. Fat bodies – spaghetti shaped structures that have a bright orange or yellow color. Fat bodies may need to be removed to see other structures. They are usually located just inside the abdominal wall. Peritoneum – A spider web-like membrane that covers many of the or ...
SA04su2a
... Systemic Anatomy Exam II Prepared especially for the trimester one class, summer 2004 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of y ...
... Systemic Anatomy Exam II Prepared especially for the trimester one class, summer 2004 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of y ...
Parotid Gland Dr.
... 4. Superiorly: by the external auditory meatus. 5. Interiorly: separated by the stylomandibular ligament from the submandibular gland. Division: it is divided into 1. superficial lobe 2. deep lobe 3. accessory lobe the superficial and the deep parts connected to each others by an isthmus while the ...
... 4. Superiorly: by the external auditory meatus. 5. Interiorly: separated by the stylomandibular ligament from the submandibular gland. Division: it is divided into 1. superficial lobe 2. deep lobe 3. accessory lobe the superficial and the deep parts connected to each others by an isthmus while the ...
Document
... Visceral Serosa “covering the external surface of the organs within the [ventral] cavity” ...
... Visceral Serosa “covering the external surface of the organs within the [ventral] cavity” ...
Ch. 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
... Four sutures mark the articulations of parietal bones with frontal, occipital, and temporal bones: 1. Coronal suture—between parietal bones and frontal ...
... Four sutures mark the articulations of parietal bones with frontal, occipital, and temporal bones: 1. Coronal suture—between parietal bones and frontal ...
Lacrimal glands
... fossa – passed by maxillary n. and zygomatic br., and vv. to pterygoid venous plexus – Connects orbit with infratemporal fossa – Connects orbit with temporal fossa ...
... fossa – passed by maxillary n. and zygomatic br., and vv. to pterygoid venous plexus – Connects orbit with infratemporal fossa – Connects orbit with temporal fossa ...
The Pterional Port in Dual-Port Endoscopy: A 2D and 3D
... Fig. 3 Right pterional port. (A) The craniectomy is initiated with a burr hole at the intersection of the sphenoparietal and coronal sutures. (B) Increased extradural space is gained with drilling of the lesser wing of the sphenoid. (C) The periorbita is kept intact and serves as a landmark for remo ...
... Fig. 3 Right pterional port. (A) The craniectomy is initiated with a burr hole at the intersection of the sphenoparietal and coronal sutures. (B) Increased extradural space is gained with drilling of the lesser wing of the sphenoid. (C) The periorbita is kept intact and serves as a landmark for remo ...
26-arches+venous&lymphatics2008-05
... walking, overweight or illness, so the weak muscles & ligaments are stretched and pain is produced after walking for a short distance. ...
... walking, overweight or illness, so the weak muscles & ligaments are stretched and pain is produced after walking for a short distance. ...
Pelvic walls
... • Two hip bones, which form the anterior and lateral walls. • Sacrum and coccyx, which form the posterior wall. • These 4 bones are connected by 4 joints and lined by 4 muscles. • The bony pelvis with its joints and muscles form a strong basin-shaped structure (with multiple foramina), • The pelvis ...
... • Two hip bones, which form the anterior and lateral walls. • Sacrum and coccyx, which form the posterior wall. • These 4 bones are connected by 4 joints and lined by 4 muscles. • The bony pelvis with its joints and muscles form a strong basin-shaped structure (with multiple foramina), • The pelvis ...
Knee Nomenclature - One Call Care Management
... ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME - an overuse condition in which inflammation results when a band of a tendon rubs over the outer bone (lateral condyle) of the knee. Although iliotibial band syndrome may be caused by direct injury to the knee, it is most often caused by the stress of long-term overuse, such ...
... ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME - an overuse condition in which inflammation results when a band of a tendon rubs over the outer bone (lateral condyle) of the knee. Although iliotibial band syndrome may be caused by direct injury to the knee, it is most often caused by the stress of long-term overuse, such ...
KUMC 34 Infratemporal Region Student
... Terminal branch of external carotid artery. Divided into three parts by lateral pterygoid muscle: Artery may pass superficial or deep to muscle. ...
... Terminal branch of external carotid artery. Divided into three parts by lateral pterygoid muscle: Artery may pass superficial or deep to muscle. ...
Neonatal Neurosonography – The Premature Infant
... • Use of the posterior fontanelle and posterolateral (mastoid) fontanelle views have aided diagnostic imaging • These techniques place the transducer closer to the subtentorial pathology than does using the anterior fontanelle ...
... • Use of the posterior fontanelle and posterolateral (mastoid) fontanelle views have aided diagnostic imaging • These techniques place the transducer closer to the subtentorial pathology than does using the anterior fontanelle ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.