Chapter 8: Joints of the Skeletal System
... parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth, and enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions. C. Three general groups of joints classified structurally by the type of tissue that binds the bones together are: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial. D. Joints can als ...
... parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth, and enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions. C. Three general groups of joints classified structurally by the type of tissue that binds the bones together are: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial. D. Joints can als ...
BONY PELVIS
... a sacrum and a coccyx, which are part of the vertebral column and form the back wall. The pelvis is divided into two parts by the pelvic brim. Above the brim is the false pelvis, which forms part of the abdominal cavity. Below the brim is the true pelvis. The pelvic brim is formed by: The sacral pro ...
... a sacrum and a coccyx, which are part of the vertebral column and form the back wall. The pelvis is divided into two parts by the pelvic brim. Above the brim is the false pelvis, which forms part of the abdominal cavity. Below the brim is the true pelvis. The pelvic brim is formed by: The sacral pro ...
pdf
... centres that appear around the time of puberty and fuse at approximately 22 years of age. Failure of fusion at any of these centres results in formation of the os acromiale variant. Fig. 14 on page 15 ...
... centres that appear around the time of puberty and fuse at approximately 22 years of age. Failure of fusion at any of these centres results in formation of the os acromiale variant. Fig. 14 on page 15 ...
Rounded Rectangles - Otolaryngology online
... frontal recess superiorly Upward migration of anterior ethmoid air cells Penetration via inferior aspect of frontal bone between the two tables ...
... frontal recess superiorly Upward migration of anterior ethmoid air cells Penetration via inferior aspect of frontal bone between the two tables ...
Chapter 7
... called the median sacral crest – Joined to the coxae of the pelvis at its auricular surfaces by fibrocartilage of the sacroiliac joints – The upper anterior margin of the sacrum (or the first sacral vertebra) is called the sacral promontory – Posterior sacral foramina are located to the sides of the ...
... called the median sacral crest – Joined to the coxae of the pelvis at its auricular surfaces by fibrocartilage of the sacroiliac joints – The upper anterior margin of the sacrum (or the first sacral vertebra) is called the sacral promontory – Posterior sacral foramina are located to the sides of the ...
Ch 9 Joints
... – nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste – makes movement of synovial joints almost friction free • joint (articular) capsule – connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid – outer fibrous capsule – continuous with periosteum of adjoining bones – inner synovial membrane ...
... – nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste – makes movement of synovial joints almost friction free • joint (articular) capsule – connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid – outer fibrous capsule – continuous with periosteum of adjoining bones – inner synovial membrane ...
Ch 9 Joints
... – nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste – makes movement of synovial joints almost friction free • joint (articular) capsule – connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid – outer fibrous capsule – continuous with periosteum of adjoining bones – inner synovial membrane ...
... – nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste – makes movement of synovial joints almost friction free • joint (articular) capsule – connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid – outer fibrous capsule – continuous with periosteum of adjoining bones – inner synovial membrane ...
calcaneal autografts: indications, technique, and complications
... of the graft. A sagittal saw is then used to cut the anterior, posterior, and inferior borders of the graft, respectively. A line can be drawn on the saw to ensure the proper depth is obtained. For example, if the graft should be 1 cm in height, then this length is marked on the saw blade (Figure 8) ...
... of the graft. A sagittal saw is then used to cut the anterior, posterior, and inferior borders of the graft, respectively. A line can be drawn on the saw to ensure the proper depth is obtained. For example, if the graft should be 1 cm in height, then this length is marked on the saw blade (Figure 8) ...
(FOR QUESTIONS 1-5, SEE PICTURES AT THE END OF THIS
... b. Posterior talofibular ligament c. Calcaneofibular ligament d. Anterior talofibular ligament Fill in the blank: the _______ bone is _______ to the ________ bone. a. 1st metatarsal; medial; 5th metatarsal b. 2nd metatarsal; medial; 1st metatarsal c. Tibia; lateral; fibula d. Calcaneus; lateral; cun ...
... b. Posterior talofibular ligament c. Calcaneofibular ligament d. Anterior talofibular ligament Fill in the blank: the _______ bone is _______ to the ________ bone. a. 1st metatarsal; medial; 5th metatarsal b. 2nd metatarsal; medial; 1st metatarsal c. Tibia; lateral; fibula d. Calcaneus; lateral; cun ...
Temporalis muscle flap - Vula
... the coronoid process of the mandible may be osteotomised to permit passage of the flap. The zygomatic bone can be kept in saline and plated/wired back later in the procedure. The coronoid osteotomy is done either from above via the temporal fossa, or via the mouth. Great care has to be taken not to ...
... the coronoid process of the mandible may be osteotomised to permit passage of the flap. The zygomatic bone can be kept in saline and plated/wired back later in the procedure. The coronoid osteotomy is done either from above via the temporal fossa, or via the mouth. Great care has to be taken not to ...
Anatomical study of endoscope assisted far lateral keyhole
... the problem of depth deficiency from an endoscopic image. It also overcomes some of the disadvantages of the angled endoscope like the inability to see straight ahead, resulting in possible injury to adjacent structures[20,21]. In addition, neuronavigation can be used before surgery to determine the ...
... the problem of depth deficiency from an endoscopic image. It also overcomes some of the disadvantages of the angled endoscope like the inability to see straight ahead, resulting in possible injury to adjacent structures[20,21]. In addition, neuronavigation can be used before surgery to determine the ...
pharynx
... 7. The middle constrictor muscle: a. Lies inner to the superior constrictor. b. Attached anteriorly to the pharyngeal raphe. c. The internal laryngeal nerve is between it and the inferior constrictor. d. The stylopharyngeus muscle passes between it and the superior constrictor. e. Propels the ...
... 7. The middle constrictor muscle: a. Lies inner to the superior constrictor. b. Attached anteriorly to the pharyngeal raphe. c. The internal laryngeal nerve is between it and the inferior constrictor. d. The stylopharyngeus muscle passes between it and the superior constrictor. e. Propels the ...
Sheet 3
... here that the posterior ethmoidal nerve did not go with the corresponding artery to the lateral wall Sphenopalatine nerve branch of the maxillary nerve will go through the sphenopalatine foramen to the nasal cavity and also as the artery will give long and short , so the short will go posterior supe ...
... here that the posterior ethmoidal nerve did not go with the corresponding artery to the lateral wall Sphenopalatine nerve branch of the maxillary nerve will go through the sphenopalatine foramen to the nasal cavity and also as the artery will give long and short , so the short will go posterior supe ...
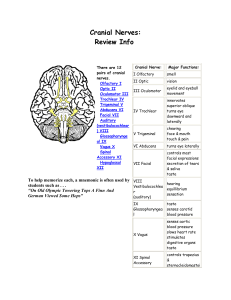
Cranial Nerves: Review Info
... Or go to cranial foramina Quizzer. . .identify structures passing through major cranial formamina Try These Links For Other Info & Images... Cranial Nerve Dissection ...several views of cranial nerves in cadaver brain. Cranial Nerve Pathways ...very good views of cranial nerve pathways in skull Yale ...
... Or go to cranial foramina Quizzer. . .identify structures passing through major cranial formamina Try These Links For Other Info & Images... Cranial Nerve Dissection ...several views of cranial nerves in cadaver brain. Cranial Nerve Pathways ...very good views of cranial nerve pathways in skull Yale ...
The Nasal Cavity
... Lower posterior part by the long sphenopalatine nerve Upper anterior part by the septal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve. Blood supply by the long sphenopalatine artery. ...
... Lower posterior part by the long sphenopalatine nerve Upper anterior part by the septal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve. Blood supply by the long sphenopalatine artery. ...
The Nasal Cavity
... Lower posterior part by the long sphenopalatine nerve Upper anterior part by the septal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve. Blood supply by the long sphenopalatine artery. ...
... Lower posterior part by the long sphenopalatine nerve Upper anterior part by the septal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve. Blood supply by the long sphenopalatine artery. ...
1 Chapter 5: Anatomy of the nose and paranasal sinuses P. H. Rhys
... The palate and nasal septum By the time the embryo is 13.5 mm, the primitive palate is beginning to form by fusion of the maxillary processes with the caudal end of the frontonasal process. Behind this are the openings of the primitive posterior nares, and in the midline the rudiment of the nasal s ...
... The palate and nasal septum By the time the embryo is 13.5 mm, the primitive palate is beginning to form by fusion of the maxillary processes with the caudal end of the frontonasal process. Behind this are the openings of the primitive posterior nares, and in the midline the rudiment of the nasal s ...
[edit]Pelvic cavity - Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences
... The muscles of the hip are divided into a dorsal and a ventral group. The dorsal hip muscles are either inserted into the region of the lesser trochanter(anterior or inner group) or the greater trochanter (posterior or outer group). Anteriorly, the psoas major (and occasionally psoas minor) originat ...
... The muscles of the hip are divided into a dorsal and a ventral group. The dorsal hip muscles are either inserted into the region of the lesser trochanter(anterior or inner group) or the greater trochanter (posterior or outer group). Anteriorly, the psoas major (and occasionally psoas minor) originat ...
Talocrural Joint - Jonathan Jordan Fitness
... The ankle is required for running, walking, squatting, lunging, climbing, etc. The ankle provides key proprioceptive input to the brain Even without a traumatic injury poor ankle mobility can affect other joints Personal experience with PT and rehab of my issue Overhead squatting demonstration ...
... The ankle is required for running, walking, squatting, lunging, climbing, etc. The ankle provides key proprioceptive input to the brain Even without a traumatic injury poor ankle mobility can affect other joints Personal experience with PT and rehab of my issue Overhead squatting demonstration ...
Bones Muscles Ligaments Nerve supply Synovial flexor sheaths
... Lumbricals and opponens Abductor pollicis brevis ...
... Lumbricals and opponens Abductor pollicis brevis ...
1 | Page
... Why we have shallower false pelvis in females? Because it’s oriented more horizontal of iliac bone Why its more tapered in males ? the sacrum more anteriorly and the ischial tuberosities become more inverted. In females the tuberosities are more everted and the sacrum is flatter. What makes th ...
... Why we have shallower false pelvis in females? Because it’s oriented more horizontal of iliac bone Why its more tapered in males ? the sacrum more anteriorly and the ischial tuberosities become more inverted. In females the tuberosities are more everted and the sacrum is flatter. What makes th ...
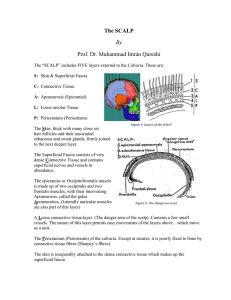
The SCALP
... they pierce the frontalis muscle to enter the dense connective tissue. Infections in the dense connective tissue elicit much pain because this tissue resists swelling and thus exerts pressure on the nerves lying within it. Arterial Supply of the SCALP Each side of the scalp receives FIVE arteries: ...
... they pierce the frontalis muscle to enter the dense connective tissue. Infections in the dense connective tissue elicit much pain because this tissue resists swelling and thus exerts pressure on the nerves lying within it. Arterial Supply of the SCALP Each side of the scalp receives FIVE arteries: ...
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of oral Cavity
... The horizontal plates of the palatine bone articulates with the posterior rough border of horizontal palatal process of maxilla. The posterior border of horizontal plates of the palatine bone unite at midline to form a sharp line,the posterior nasal spine. The posterior margins of hard palate serve ...
... The horizontal plates of the palatine bone articulates with the posterior rough border of horizontal palatal process of maxilla. The posterior border of horizontal plates of the palatine bone unite at midline to form a sharp line,the posterior nasal spine. The posterior margins of hard palate serve ...
Spine thorax - Sinoe Medical Association TM
... fibrous cartilage that act as shock absorbers and allow the back to move. As a person ages, these discs compress and shrink, resulting in a distinct loss of height (generally between 0.5 and 2.0cm) between the ages of 50 and 55. When looked at from the side, the spine forms four curves. • These curv ...
... fibrous cartilage that act as shock absorbers and allow the back to move. As a person ages, these discs compress and shrink, resulting in a distinct loss of height (generally between 0.5 and 2.0cm) between the ages of 50 and 55. When looked at from the side, the spine forms four curves. • These curv ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.















![[edit]Pelvic cavity - Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000164092_1-0bf08b2d7896fb51bd702acf95617848-300x300.png)