Foot, Ankle, Lower leg - James Island Charter High School
... – Proximal attachment – posterior surface of medial and lateral condyles of femur – Distal attachment – posterior surface of the calcaneus – Action – plantar flexion of the ankle and flexion of the knee ...
... – Proximal attachment – posterior surface of medial and lateral condyles of femur – Distal attachment – posterior surface of the calcaneus – Action – plantar flexion of the ankle and flexion of the knee ...
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
... • CT and MRI may show – Enlarged superior ophthalmic vein – Enlarged muscles – Enlarged cavernous sinus with a convex shape to the lateral wall ...
... • CT and MRI may show – Enlarged superior ophthalmic vein – Enlarged muscles – Enlarged cavernous sinus with a convex shape to the lateral wall ...
Access to Parapharyngeal Space - Vula
... digastric. The submandibular gland is mobilised with gentle finger dissection in a posterior-to-anterior direction leaving the thin fascial layer over the ranine veins and the hypoglossal nerve intact (Figure 12). Additional mobility of the SSG may be achieved (if required) by dividing the facial ar ...
... digastric. The submandibular gland is mobilised with gentle finger dissection in a posterior-to-anterior direction leaving the thin fascial layer over the ranine veins and the hypoglossal nerve intact (Figure 12). Additional mobility of the SSG may be achieved (if required) by dividing the facial ar ...
Chapter 24 - respiratory
... II. Upper Respiratory System A. Nasal cavity 1. superior, middle, inferior nasal conchae: for air turbulence & increase surface area for warming & humidifying. 2. superior, middle, inferior meatus: spaces between conchae 3. nasal septum (made from ethmoid & vomer bones) 4. eustacian tube opening B. ...
... II. Upper Respiratory System A. Nasal cavity 1. superior, middle, inferior nasal conchae: for air turbulence & increase surface area for warming & humidifying. 2. superior, middle, inferior meatus: spaces between conchae 3. nasal septum (made from ethmoid & vomer bones) 4. eustacian tube opening B. ...
Introduction
... dissection only General introduction of Lower Limb//535 Functions/537 Support the body weight/537 ...
... dissection only General introduction of Lower Limb//535 Functions/537 Support the body weight/537 ...
Melissa`s Dissector bold terms Unit 2
... Posterior mediastinum: posterior to pericardium and anterior to bodies of T5 to T12; contains structures that pass between neck, thorax, and abdomen Four parts of mediastinum Mediastinal pleura—N230, 231 Pericardium Root of the lung Esophagus (right side) Thoracic aorta (left side) Costal pleura (on ...
... Posterior mediastinum: posterior to pericardium and anterior to bodies of T5 to T12; contains structures that pass between neck, thorax, and abdomen Four parts of mediastinum Mediastinal pleura—N230, 231 Pericardium Root of the lung Esophagus (right side) Thoracic aorta (left side) Costal pleura (on ...
Document
... The cavernous sinuses are found on either side of the body of the sphenoid bone in middle cranial fossae. They receive blood from the sphenoparietal sinuses which are located underneath the free edges of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. Blood also drains into the cavernous sinuses via the supe ...
... The cavernous sinuses are found on either side of the body of the sphenoid bone in middle cranial fossae. They receive blood from the sphenoparietal sinuses which are located underneath the free edges of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. Blood also drains into the cavernous sinuses via the supe ...
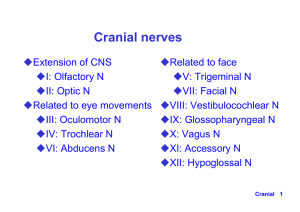
Cranial nerve
... http://www.thesun.co.uk/sol/homepage/news/4311689/Boy-shot-in-face-is-robbed-of-his-smile-TeenagerJordan-Winstanley-was-hit-with-an-air-gun-pellet-shot-by-a-mystery-sniper-hiding-in-bushes.html ...
... http://www.thesun.co.uk/sol/homepage/news/4311689/Boy-shot-in-face-is-robbed-of-his-smile-TeenagerJordan-Winstanley-was-hit-with-an-air-gun-pellet-shot-by-a-mystery-sniper-hiding-in-bushes.html ...
TEST 2 DREAM SHEET
... TEST 2 DREAM SHEET Amphiarthrosis- secondary cartilaginous joint; slightly moveable; symphisis pubis, intervertebral joints Primary cartilaginous joints are immovable joints (synchondrosis) that ossify with age and are bone-cartilage-bone (epiphyseal plates). Secondary cartilaginous joints are bonec ...
... TEST 2 DREAM SHEET Amphiarthrosis- secondary cartilaginous joint; slightly moveable; symphisis pubis, intervertebral joints Primary cartilaginous joints are immovable joints (synchondrosis) that ossify with age and are bone-cartilage-bone (epiphyseal plates). Secondary cartilaginous joints are bonec ...
Morphometric Analysis of the Occipital Condyle and Its Surgical
... transcondylar approach, the complete transcondylar approach, the extreme-lateral transjugular approach and the transtubercular approach. Majority of these approaches demand resection of the OC partially or completely. The dimensions and orientation of the OC may influence the surgical approach to th ...
... transcondylar approach, the complete transcondylar approach, the extreme-lateral transjugular approach and the transtubercular approach. Majority of these approaches demand resection of the OC partially or completely. The dimensions and orientation of the OC may influence the surgical approach to th ...
obstetric anatomy midw 201
... • The Cocyx (Tail): This is four tiny fused vertebrae. It is also triangular in shape. The base articulates superiorly with the inferior aspect of the 5th sacral vertebra. It serves as an attachment for muscles and ligaments. • Obstetric importance: In the female, during the second stage of labour, ...
... • The Cocyx (Tail): This is four tiny fused vertebrae. It is also triangular in shape. The base articulates superiorly with the inferior aspect of the 5th sacral vertebra. It serves as an attachment for muscles and ligaments. • Obstetric importance: In the female, during the second stage of labour, ...
CNS-2 Cerebral hemisphere 1. to know a septum of the
... At the end of the class a student should participate in the credit consisting of 6 MCQ and 4 pins in order to confirm the presence at the class and collect the points if successful. EXAMPLE QUESTIONS (choose one correct answer): ...
... At the end of the class a student should participate in the credit consisting of 6 MCQ and 4 pins in order to confirm the presence at the class and collect the points if successful. EXAMPLE QUESTIONS (choose one correct answer): ...
A Case of Large Foramen Magnum Schwannoma
... ll cranial nerves, with the exception of the cranial nerve I, II possessing myelinated sheaths, have the potential for developing associated intracranial schwannomas21). The vestibular division of the cranial nerve VIII is the most commonly affected. Trigeminal nerve schwannomas are the most common ...
... ll cranial nerves, with the exception of the cranial nerve I, II possessing myelinated sheaths, have the potential for developing associated intracranial schwannomas21). The vestibular division of the cranial nerve VIII is the most commonly affected. Trigeminal nerve schwannomas are the most common ...
View PDF - OMICS International
... covered by deep fascia which arises from the superior temporal ridge of the skull and passes downwards on the surface of the superficial fibres of the muscle to the coronoid process of the mandible. The main (deep) part of the temporal muscle is below the superficial temporal muscle and arises from ...
... covered by deep fascia which arises from the superior temporal ridge of the skull and passes downwards on the surface of the superficial fibres of the muscle to the coronoid process of the mandible. The main (deep) part of the temporal muscle is below the superficial temporal muscle and arises from ...
CHAPTER 7 “The Axial Skeleton #2” Course objectives: Define and
... costal cartilage. - are called vertebrosternal ribs. 2. false ribs – the remaining five pairs of ribs. There are two types of false ribs. vertebrochondral ribs -- rib pairs #8, #9, and #10 are connected by a single band of costal cartilage to the inferior portion of the sternum. Unlike the first s ...
... costal cartilage. - are called vertebrosternal ribs. 2. false ribs – the remaining five pairs of ribs. There are two types of false ribs. vertebrochondral ribs -- rib pairs #8, #9, and #10 are connected by a single band of costal cartilage to the inferior portion of the sternum. Unlike the first s ...
Kaan Yücel MD, Ph.D.
... Diagonal conjugate (from inferior pubic lig. to promontory) Measured by palpating sacral promontory with the tip of the middle finger, using the other hand to mark the level of the inferior margin of the pubic symphysis on the examining hand. After the examining hand is withdrawn, the distance betw ...
... Diagonal conjugate (from inferior pubic lig. to promontory) Measured by palpating sacral promontory with the tip of the middle finger, using the other hand to mark the level of the inferior margin of the pubic symphysis on the examining hand. After the examining hand is withdrawn, the distance betw ...
MIDDLE MENINGEAL ARTERY Is typically the 3 rd
... in outside of cranium to veins inside the cranium. There are also emissary veins passing through the foramen ovale,jugular foramen,foramen lacerum Because the emissary veins are valveless they are an important part in selective brain cooling bidirectional flow of cooler blood from evaporatIng surfac ...
... in outside of cranium to veins inside the cranium. There are also emissary veins passing through the foramen ovale,jugular foramen,foramen lacerum Because the emissary veins are valveless they are an important part in selective brain cooling bidirectional flow of cooler blood from evaporatIng surfac ...
The relationship between the carotid canal and mandibular condyle
... artery transection and thrombosis to embolism of distal communicating segments. Hence, knowing the relationship of these important structures is of utmost importance for skull base surgeons. In addition, the necessity for this knowledge is critical for clinicians to be able to understand the mechani ...
... artery transection and thrombosis to embolism of distal communicating segments. Hence, knowing the relationship of these important structures is of utmost importance for skull base surgeons. In addition, the necessity for this knowledge is critical for clinicians to be able to understand the mechani ...
Spring 03
... Prepared especially for the trimester one class, Spring 2003 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of your questions (unless you ...
... Prepared especially for the trimester one class, Spring 2003 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of your questions (unless you ...
paleontological contributions - KU ScholarWorks
... Mosasaurs differ from varanids in that near the mid-line the supraoccipital abuts on the parietal, but ventrolaterally, the supraoccipital sends a flat process internal to the descending process of the parietal. The alar process of the prootic, which has a flat process internal to the descending win ...
... Mosasaurs differ from varanids in that near the mid-line the supraoccipital abuts on the parietal, but ventrolaterally, the supraoccipital sends a flat process internal to the descending process of the parietal. The alar process of the prootic, which has a flat process internal to the descending win ...
Superficial muscles of neck Platysma Attaches from inferior border of
... Attaches from inferior border of mandible to fascia covering superior parts of pec major and deltoid muscles Innervated by cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII) Draws corners of mouth inferiorly and widens it as in expressions of sadness and fright; draws skin of neck superiorly when teeth ...
... Attaches from inferior border of mandible to fascia covering superior parts of pec major and deltoid muscles Innervated by cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII) Draws corners of mouth inferiorly and widens it as in expressions of sadness and fright; draws skin of neck superiorly when teeth ...
Joints of the Skeletal System - Bio-Guru
... Exist between flat bones of the skull only – joined by a thin layer of dense connective tissue Starts out as a fontanel – wide membranes of dense connective tissue between the skull bones, and allows compression of skull during childbirth, as well as room for growth Fontanels are replaced by sutures ...
... Exist between flat bones of the skull only – joined by a thin layer of dense connective tissue Starts out as a fontanel – wide membranes of dense connective tissue between the skull bones, and allows compression of skull during childbirth, as well as room for growth Fontanels are replaced by sutures ...
Superior view— Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with
... Superior view— Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It also has muscle attachments. In spite of the fact that it is not attached to the skull, it is co ...
... Superior view— Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It also has muscle attachments. In spite of the fact that it is not attached to the skull, it is co ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.