Occipital Condyle Fractures - American Journal of Neuroradiology
... AJNR A m J Neurora dio/15: 1309-1315, Aug 1994 ...
... AJNR A m J Neurora dio/15: 1309-1315, Aug 1994 ...
The Human in 3D: Advanced Morphometric Analysis of High
... I would first like to thank my mentor, Dr. Don Hilbelink for his unwavering support and enthusiasm over the past 4 years. You took an anthropologist and helped me become a professional anatomist. I finish this work because of your backing, guidance and friendship. I can’t wait to see what’s next. Ad ...
... I would first like to thank my mentor, Dr. Don Hilbelink for his unwavering support and enthusiasm over the past 4 years. You took an anthropologist and helped me become a professional anatomist. I finish this work because of your backing, guidance and friendship. I can’t wait to see what’s next. Ad ...
Treatment of epistaxis in children - Vula
... While the nose is bleeding, sit the patient upright with the neck flexed and head forward. Pinch the anterior (soft) part of the nose between thumb and index finger for a few minutes to apply pressure to vessels in Little’s area. Apply an ice pack to the forehead, to the bridge of the nose, or place ...
... While the nose is bleeding, sit the patient upright with the neck flexed and head forward. Pinch the anterior (soft) part of the nose between thumb and index finger for a few minutes to apply pressure to vessels in Little’s area. Apply an ice pack to the forehead, to the bridge of the nose, or place ...
Neuro-Anatomy
... The gyri vary in direction and also possess different functional areas e.g, motor, general sensory, visual, olfactory & auditory. The sulci vary in depth, some of them are very shallow, while others are very deep and may indents the walls of the lateral ventricle as the calcarine and collateral sulc ...
... The gyri vary in direction and also possess different functional areas e.g, motor, general sensory, visual, olfactory & auditory. The sulci vary in depth, some of them are very shallow, while others are very deep and may indents the walls of the lateral ventricle as the calcarine and collateral sulc ...
Sphenopalatine artery (SPA) ligation - Vula
... the posterior fontanelle. The fontanelle is a mucosa-covered ‘ostium’ and is located posterior to the uncinate process, under the bullae ethmoidalis and about 1cm anterior to where the middle turbinate attaches to the lateral nasal wall posteriorly. This defect in the bony medial wall of the maxilla ...
... the posterior fontanelle. The fontanelle is a mucosa-covered ‘ostium’ and is located posterior to the uncinate process, under the bullae ethmoidalis and about 1cm anterior to where the middle turbinate attaches to the lateral nasal wall posteriorly. This defect in the bony medial wall of the maxilla ...
The Surgical Anatomy of Six Variations of The Extreme Lateral
... indications for, and surgical anatomy involved in, six variations of ELA. The need for occipito-cervical fusion relative to each option is also discussed. MATERIALS ...
... indications for, and surgical anatomy involved in, six variations of ELA. The need for occipito-cervical fusion relative to each option is also discussed. MATERIALS ...
Injuries of the Head
... Anesthetizing the supraorbital and auriculopalpebral nerves may facilitate the procedure. The reduced fracture is usually stable. Fluorescein dye placed in the conjunctival sac can be used to evaluate the integrity of the lacrimal and nasolacrimal ducts. Discharge of dye from the nasal opening of th ...
... Anesthetizing the supraorbital and auriculopalpebral nerves may facilitate the procedure. The reduced fracture is usually stable. Fluorescein dye placed in the conjunctival sac can be used to evaluate the integrity of the lacrimal and nasolacrimal ducts. Discharge of dye from the nasal opening of th ...
Anatomy Syllabus
... This requires the knowledge of the range of normality and also of normal variants, particularly those that simulate disease or are on the borderlands with disease. 3. Coherent communication with referrers, colleagues, patients and the entire health care team regarding a particular anatomical structu ...
... This requires the knowledge of the range of normality and also of normal variants, particularly those that simulate disease or are on the borderlands with disease. 3. Coherent communication with referrers, colleagues, patients and the entire health care team regarding a particular anatomical structu ...
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
... Each nasal cavity consists of three general regions: nasal vestibule, respiratory and olfactory regions. Each nasal cavity has a floor, roof, medial wall, and lateral wall. The air respired in travels from the nasal cavities into the nasopharnyx (nasal part of the pharynx) then into the laryngeal ca ...
... Each nasal cavity consists of three general regions: nasal vestibule, respiratory and olfactory regions. Each nasal cavity has a floor, roof, medial wall, and lateral wall. The air respired in travels from the nasal cavities into the nasopharnyx (nasal part of the pharynx) then into the laryngeal ca ...
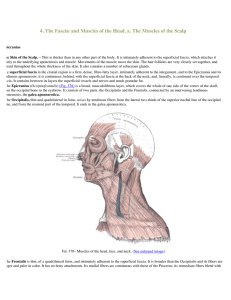
4. The Fascię and Muscles of the Head. a. The Muscles of the Scalp
... The Orbicularis oris (Fig. 381) is not a simple sphincter muscle like the Orbicularis oculi; it consists of numerous strata of muscular fibers surrounding the orifice of the mouth but having different direction. It consists partly of fibers derived from the other facial muscles which are inserted in ...
... The Orbicularis oris (Fig. 381) is not a simple sphincter muscle like the Orbicularis oculi; it consists of numerous strata of muscular fibers surrounding the orifice of the mouth but having different direction. It consists partly of fibers derived from the other facial muscles which are inserted in ...
Facial Nerve - Lightweight OCW University of Palestine
... 1. The posterior auricular nerve. 2. The nerve to: the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and to the stylohyoid muscle. The five terminal branches of the facial nerve: 1. Temporal nerve (from temporofacial branch). 2. Zygomatic nerve (from temporofacial branch). 3. Buccal nerve (from cervicofa ...
... 1. The posterior auricular nerve. 2. The nerve to: the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and to the stylohyoid muscle. The five terminal branches of the facial nerve: 1. Temporal nerve (from temporofacial branch). 2. Zygomatic nerve (from temporofacial branch). 3. Buccal nerve (from cervicofa ...
Respiratory System - Yeditepe University Pharma Anatomy
... Each nasal cavity consists of three general regions: nasal vestibule, respiratory and olfactory regions. Each nasal cavity has a floor, roof, medial wall, and lateral wall. The air respired in travels from the nasal cavities into the nasopharnyx (nasal part of the pharynx) then into the laryngeal ca ...
... Each nasal cavity consists of three general regions: nasal vestibule, respiratory and olfactory regions. Each nasal cavity has a floor, roof, medial wall, and lateral wall. The air respired in travels from the nasal cavities into the nasopharnyx (nasal part of the pharynx) then into the laryngeal ca ...
Morphology of the pectoral girdle in Pomatoschistus lozanoi
... lepidotrichia (Fig. 3A-B, 3D, 7D). In Pomatoschistus lozanoi, only soft, segmented fin rays are present, which are connected to each other by a dermal membrane. The number of pectoral fin rays varies; at least between species. In Pomatoschistus lozanoi, nineteen pectoral fln rays are present. They a ...
... lepidotrichia (Fig. 3A-B, 3D, 7D). In Pomatoschistus lozanoi, only soft, segmented fin rays are present, which are connected to each other by a dermal membrane. The number of pectoral fin rays varies; at least between species. In Pomatoschistus lozanoi, nineteen pectoral fln rays are present. They a ...
frontal sphenoids
... is approximately 8 cm from the nasal spine and at 15⁰ angle with the horizontal plane of nasal cavity ...
... is approximately 8 cm from the nasal spine and at 15⁰ angle with the horizontal plane of nasal cavity ...
Pharynx and soft palate
... Pharynx and soft palate • Pharynx — one of the visceral tubes • — the th common chamber h b off the th respiratory and digestive tracts • located behind the nasal and oral cavities iti • funnel-shaped p in form • 12 cm in length; its greatest width is about b t 5 cm and d narrowestt 1.5 1 5 cm ...
... Pharynx and soft palate • Pharynx — one of the visceral tubes • — the th common chamber h b off the th respiratory and digestive tracts • located behind the nasal and oral cavities iti • funnel-shaped p in form • 12 cm in length; its greatest width is about b t 5 cm and d narrowestt 1.5 1 5 cm ...
CT and Angiography of Primary Extradural Juxtasellar Tumors
... problem because of their location and degree of vascularity. Our two cases were isodense with normal brain before contrast administration and were characterized by their extreme and homogeneous enhancement. No other tumors in our series displaced this degree of enhancement. These tumors tend to disp ...
... problem because of their location and degree of vascularity. Our two cases were isodense with normal brain before contrast administration and were characterized by their extreme and homogeneous enhancement. No other tumors in our series displaced this degree of enhancement. These tumors tend to disp ...
The Arterial Supply of the Dura Mater of the Rhesus
... A study of the dural blood supply i n 20 specimens by dissection, corrosion preparations and cleared specimens indicates that the dural arteries are similar to those of man yet significant differences were noted. The anterior cranial fossa is supplied by small twigs which spread through the dura of ...
... A study of the dural blood supply i n 20 specimens by dissection, corrosion preparations and cleared specimens indicates that the dural arteries are similar to those of man yet significant differences were noted. The anterior cranial fossa is supplied by small twigs which spread through the dura of ...
ZOO 3733C -Human Anatomy Lab Syllabus
... • We are here to help guide you in your learning process but YOU must put the effort in. The material has already been (or is being) lectured in the anatomy lecture class and we briefly mention those at the beginning of each block as well. Therefore, attending the lecture is vital to the lab perform ...
... • We are here to help guide you in your learning process but YOU must put the effort in. The material has already been (or is being) lectured in the anatomy lecture class and we briefly mention those at the beginning of each block as well. Therefore, attending the lecture is vital to the lab perform ...
Abnormality of the Foramen Spinosum due to a Variation in the
... an abnormal shape. The shape is like a channel 5.37 mm in length and 2.36 mm in diameter. In an unusual way, this channel has direct access to the foramen ovale. This abnormality was seen only on the right side and there was no sign of deformation in other skull bones. The diameter of the left foram ...
... an abnormal shape. The shape is like a channel 5.37 mm in length and 2.36 mm in diameter. In an unusual way, this channel has direct access to the foramen ovale. This abnormality was seen only on the right side and there was no sign of deformation in other skull bones. The diameter of the left foram ...
Onc62 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... cerebellopontine angle for about 2.0 cm, accompanied by CN8. It consistently enters internal auditory canal by crossing anterior superior margin of porus acusticus. Vestibulocochlear nerve arises from brain stem slightly posterior to CN7. CN8 remains sheathed in oligodendroglia for approximately 1 ...
... cerebellopontine angle for about 2.0 cm, accompanied by CN8. It consistently enters internal auditory canal by crossing anterior superior margin of porus acusticus. Vestibulocochlear nerve arises from brain stem slightly posterior to CN7. CN8 remains sheathed in oligodendroglia for approximately 1 ...
DIPLOPODIA WITH DOUBLE FIBULA AND AGENESIS OF TIBIA
... at the end of the dissection all soft from the bones revealing that there THE ...
... at the end of the dissection all soft from the bones revealing that there THE ...
Anatomy of the Face
... Buccinator • Buccinator 7th nerve • Accessory muscle of mastication • Outer aspect of maxilla and mandible • Related to molar teeth • Pterygomandibular raphe • Action keeps food out of vestibule • Sucking • Blowing trumpet ...
... Buccinator • Buccinator 7th nerve • Accessory muscle of mastication • Outer aspect of maxilla and mandible • Related to molar teeth • Pterygomandibular raphe • Action keeps food out of vestibule • Sucking • Blowing trumpet ...
Mandibular V
... Buccinator • Buccinator 7th nerve • Accessory muscle of mastication • Outer aspect of maxilla and mandible • Related to molar teeth • Pterygomandibular raphe • Action keeps food out of vestibule • Sucking • Blowing trumpet ...
... Buccinator • Buccinator 7th nerve • Accessory muscle of mastication • Outer aspect of maxilla and mandible • Related to molar teeth • Pterygomandibular raphe • Action keeps food out of vestibule • Sucking • Blowing trumpet ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.