The Appendicular Skeleton
... Mnemonics can help you remember things through the use of a key word or a key phrase. They can be useful, whether you need to remember the simple facts of which larger bones go where (for the fibula, remember the "fibuLA is LAteral") or for tougher ones (such as the cranial bones, "PEST OF 6", parie ...
... Mnemonics can help you remember things through the use of a key word or a key phrase. They can be useful, whether you need to remember the simple facts of which larger bones go where (for the fibula, remember the "fibuLA is LAteral") or for tougher ones (such as the cranial bones, "PEST OF 6", parie ...
orofacial embryology lecture
... (forms the bridge), the merged medial nasal prominences (form the median ridge and tip of nose), the lateral nasal prominences (form the alae) and the cartilage nasal capsule (forms the septum and the nasal conchae) • the external nasal region develops from the superficial alar field – gives rise to ...
... (forms the bridge), the merged medial nasal prominences (form the median ridge and tip of nose), the lateral nasal prominences (form the alae) and the cartilage nasal capsule (forms the septum and the nasal conchae) • the external nasal region develops from the superficial alar field – gives rise to ...
Cerebral artery - Association of Surgical Technologists
... and makes the brain sensitive to even a few sec onds of reduced vascular flow. Gray matter has a higher oxygen requirement due to the density of synapses rather than the number of neurons. Brain stem circulation The vertebral arteries supply blood to the rostral spinal cord and the caudal medulla (F ...
... and makes the brain sensitive to even a few sec onds of reduced vascular flow. Gray matter has a higher oxygen requirement due to the density of synapses rather than the number of neurons. Brain stem circulation The vertebral arteries supply blood to the rostral spinal cord and the caudal medulla (F ...
5-Cervical Spine2016-12
... All the typical vertebrae have a foramen transversarium and bifid spinous processes. Atypical vertebrae (1,2,7) : 1st (Atlas) : has no body nor spine, has short anterior arch and long posterior arch. 2nd (Axis): has odontoid process (dens). 7th (Cervica Prominens) : has longest not bifid spinous pro ...
... All the typical vertebrae have a foramen transversarium and bifid spinous processes. Atypical vertebrae (1,2,7) : 1st (Atlas) : has no body nor spine, has short anterior arch and long posterior arch. 2nd (Axis): has odontoid process (dens). 7th (Cervica Prominens) : has longest not bifid spinous pro ...
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus (PDF Available)
... Introduction: Frontal sinus is a complex and highly variable structure. These anatomic variations have a tremendous impact on the direction of drainage, efficiency of mucociliary clearance mechanism and frontal recess morphology. CT scans of frontal sinus have conventionally being performed with con ...
... Introduction: Frontal sinus is a complex and highly variable structure. These anatomic variations have a tremendous impact on the direction of drainage, efficiency of mucociliary clearance mechanism and frontal recess morphology. CT scans of frontal sinus have conventionally being performed with con ...
Frontal nerve is branch of which of following
... anterior sinus. Which of the following is anatomically unlikely? A. Erosion into the pulmonary artery B. Involvement of the right coronary artery C. Rupture into the pericardium D. Extension forward to erode the sternum E. Pressure on the recurrent laryngeal nerve causing hoarseness ANSWER: E The es ...
... anterior sinus. Which of the following is anatomically unlikely? A. Erosion into the pulmonary artery B. Involvement of the right coronary artery C. Rupture into the pericardium D. Extension forward to erode the sternum E. Pressure on the recurrent laryngeal nerve causing hoarseness ANSWER: E The es ...
Modified Bristow-Helfet anterior Stabilization
... now exposed using a Rowe pronged retractor or devil's pitchfork; this step must be done under direct vision. A 3.2-mm hole is drilled in the anterior-to-posterior direction of the glenoid neck, parallel but 1 cm medial to the articular surface (Fig. 8-19). Good visualization of the articular surface ...
... now exposed using a Rowe pronged retractor or devil's pitchfork; this step must be done under direct vision. A 3.2-mm hole is drilled in the anterior-to-posterior direction of the glenoid neck, parallel but 1 cm medial to the articular surface (Fig. 8-19). Good visualization of the articular surface ...
Nasal Anatomy and Evaluation
... rest firmly supported by the frontal process of the maxilla to support the bridge of the nose. The lower portion of the nasal pyramid is formed by several major and minor cartilages. The upper lateral cartilage is triangular in shape, extending from the paired nasal bones. The curved lower lateral ca ...
... rest firmly supported by the frontal process of the maxilla to support the bridge of the nose. The lower portion of the nasal pyramid is formed by several major and minor cartilages. The upper lateral cartilage is triangular in shape, extending from the paired nasal bones. The curved lower lateral ca ...
Mastoidectomy and epitympanectomy - Vula
... (removal of incus and malleus head, exenteration of the supralabyrinthine and supratubal cells) and is indicated in poorly pneumatized and ventilated ears with limited access and exposure. It requires skeletonization of the facial nerve along the mastoid segment to lower the posterior canal wall to ...
... (removal of incus and malleus head, exenteration of the supralabyrinthine and supratubal cells) and is indicated in poorly pneumatized and ventilated ears with limited access and exposure. It requires skeletonization of the facial nerve along the mastoid segment to lower the posterior canal wall to ...
Vidian Neurectomy
... strips easily and the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve is identified entering the foramen ovale which lies medial and slightly anterior to foramen spinosum. On stripping the dura from the anteromedial face of petrous bone the greater superficial petrosal nerve can be clearly seen. Without cau ...
... strips easily and the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve is identified entering the foramen ovale which lies medial and slightly anterior to foramen spinosum. On stripping the dura from the anteromedial face of petrous bone the greater superficial petrosal nerve can be clearly seen. Without cau ...
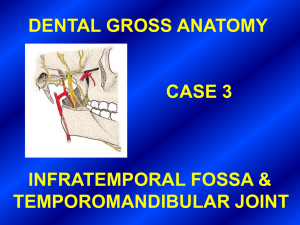
DENTAL GROSS ANATOMY CASE 3 INFRATEMPORAL FOSSA
... After a lengthy hospitalization and numerous surgeries, Ms. Goldsmith was found to have the following neural and neuromuscular disorders: 1. Ipsilateral loss of taste sensations on the anterior part of the tongue. 2. Ipsilateral loss of general sensations on the anterior part of the tongue. 3. When ...
... After a lengthy hospitalization and numerous surgeries, Ms. Goldsmith was found to have the following neural and neuromuscular disorders: 1. Ipsilateral loss of taste sensations on the anterior part of the tongue. 2. Ipsilateral loss of general sensations on the anterior part of the tongue. 3. When ...
pdf
... claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. www.myESR.org ...
... claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. www.myESR.org ...
Basic science
... between the occiput and the atlas is up to 25° of flexion and extension, 5° of lateral bending to each side, and 5° of rotation to each side (Werne 1957; White and Panjabi 1990). The atlantoaxial joint accounts for 50 per cent of overall head–neck rotation or approximately 40° to each side. Addition ...
... between the occiput and the atlas is up to 25° of flexion and extension, 5° of lateral bending to each side, and 5° of rotation to each side (Werne 1957; White and Panjabi 1990). The atlantoaxial joint accounts for 50 per cent of overall head–neck rotation or approximately 40° to each side. Addition ...
Dental Head and Neck Anatomy
... This portion of the base of the skull is composed of parts of the sphenoid, palatine, temporal, vomer, and occipital bones. The lateral and medial pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone project inferiorly; the lateral and medial pterygoid muscles (muscles of mastication) arise from the lateral and me ...
... This portion of the base of the skull is composed of parts of the sphenoid, palatine, temporal, vomer, and occipital bones. The lateral and medial pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone project inferiorly; the lateral and medial pterygoid muscles (muscles of mastication) arise from the lateral and me ...
CLAVICLE
... Mention the bony land marks of bone like borders ,surfaces and land marked used for bond determination. ...
... Mention the bony land marks of bone like borders ,surfaces and land marked used for bond determination. ...
Unit 24: Cranial Cavity and Contents
... The nerve processes passing through the cribriform plate to the nasal mucosa are actually the olfactory nerves for the sense of smell. Elevate the cerebral hemispheres enough to see the optic nerves medial to the anterior clinoid processes. They form the optic chiasma where they appear to join each ...
... The nerve processes passing through the cribriform plate to the nasal mucosa are actually the olfactory nerves for the sense of smell. Elevate the cerebral hemispheres enough to see the optic nerves medial to the anterior clinoid processes. They form the optic chiasma where they appear to join each ...
landmarksforradiology
... film when using the bisecting angle technique with finger retention (The mouth is opened wide, moving the coronoid down and forward). ...
... film when using the bisecting angle technique with finger retention (The mouth is opened wide, moving the coronoid down and forward). ...
THEME 1
... Mastering of each topic in the module by the student can be estimated according to 4 point (traditional) system. Thus all kinds of works stipulated by methodical supply for studying the theme are taken into account. The estimations exposed on a traditional scale are converted in points depending to ...
... Mastering of each topic in the module by the student can be estimated according to 4 point (traditional) system. Thus all kinds of works stipulated by methodical supply for studying the theme are taken into account. The estimations exposed on a traditional scale are converted in points depending to ...
Skeletal system 3
... At birth, fetal skull bones are incomplete and connected by fontanels Fontanels Unossified remnants of fibrous membranes between fetal skull bones ...
... At birth, fetal skull bones are incomplete and connected by fontanels Fontanels Unossified remnants of fibrous membranes between fetal skull bones ...
External ear
... (4) Posterior wall or mastoid wall: Aditus of mastoid antrum: Pyramidal eminence ...
... (4) Posterior wall or mastoid wall: Aditus of mastoid antrum: Pyramidal eminence ...
The Upper Limb
... At birth, fetal skull bones are incomplete and connected by fontanels Fontanels Unossified remnants of fibrous membranes between fetal skull bones ...
... At birth, fetal skull bones are incomplete and connected by fontanels Fontanels Unossified remnants of fibrous membranes between fetal skull bones ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.