ICD-10-PCS
... The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain (the medulla oblongata specifically). The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system. The spinal cord begins at the Occipital bone and extends down to the space betw ...
... The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain (the medulla oblongata specifically). The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system. The spinal cord begins at the Occipital bone and extends down to the space betw ...
The utility of the temporalis muscle flap for oropharyngeal, base of
... Four patients had received preoperative chemotherapy, and 3 patients received postoperative chemotherapy. All 24 patients received an average of 30 grams (range, 10100 g) of hydroxyapatite cement for the temporal fossa cranioplasty as part of their primary reconstructive procedure. We employed a spl ...
... Four patients had received preoperative chemotherapy, and 3 patients received postoperative chemotherapy. All 24 patients received an average of 30 grams (range, 10100 g) of hydroxyapatite cement for the temporal fossa cranioplasty as part of their primary reconstructive procedure. We employed a spl ...
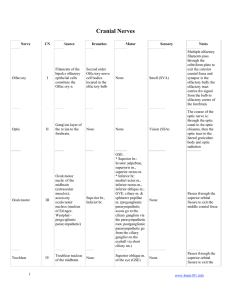
Cranial Nerves Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain
... Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear ...
... Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear ...
CLINICAL IMpORtANCE OF thE MIDDLE MENINgEAL ARtERy
... Meningeal vessels closely adhere to the internal aspect of bony vault of the skull and in case of their fracture can be damaged causing epidural hematoma even until 85% of cases [16]. Patients with cranial fractures affecting the meningeal vessels are more commonly subjected to epidural hematomas an ...
... Meningeal vessels closely adhere to the internal aspect of bony vault of the skull and in case of their fracture can be damaged causing epidural hematoma even until 85% of cases [16]. Patients with cranial fractures affecting the meningeal vessels are more commonly subjected to epidural hematomas an ...
Document
... back (deviation to left or right),crooked or curved back (appears between ages of 10-15). Very dangerous condition, surgeons have difficulty in repairing this condition; because the intervertebral discs are more compressed at one side than the other, so they have to replace many discs. Lordosis ...
... back (deviation to left or right),crooked or curved back (appears between ages of 10-15). Very dangerous condition, surgeons have difficulty in repairing this condition; because the intervertebral discs are more compressed at one side than the other, so they have to replace many discs. Lordosis ...
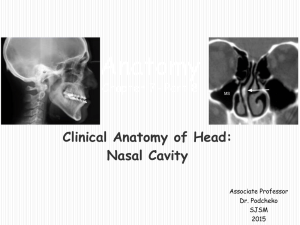
Clinical Anatomy of Nasal Cavity and Olfaction
... bones are common facial fractures in automobile accidents and sports (unless face guards are worn). •Fractures usually result in deformation of the nose, particularly when a lateral force is applied by someone's elbow, for example. •Epistaxis (nosebleed) usually occurs. •In severe fractures, disrupt ...
... bones are common facial fractures in automobile accidents and sports (unless face guards are worn). •Fractures usually result in deformation of the nose, particularly when a lateral force is applied by someone's elbow, for example. •Epistaxis (nosebleed) usually occurs. •In severe fractures, disrupt ...
CLAVICLE
... The clavicle is the first bone to begin the process of ossification during development of the embryo, during the 5th and 6th weeks of gestation. It is one of the last bones to finish ossification, at about 21-25 years of age. It forms by intramembranous ossification It consists of a mass of ...
... The clavicle is the first bone to begin the process of ossification during development of the embryo, during the 5th and 6th weeks of gestation. It is one of the last bones to finish ossification, at about 21-25 years of age. It forms by intramembranous ossification It consists of a mass of ...
The Knee
... general stability during weight bearing activities. The ACL provides the tibia with stabilization to prevent excessive internal rotation and serves as a secondary stabilizer when the collateral ligaments become ...
... general stability during weight bearing activities. The ACL provides the tibia with stabilization to prevent excessive internal rotation and serves as a secondary stabilizer when the collateral ligaments become ...
2. Discuss the anatomy of the SMAS, platysma and the
... transverse facial a, and infra orbital artery- these vessels anastamose together to form a subdermal plexus. The subcutaneous flap is supplied mainly by musculocutaneous perforators as they emerge from 3 main arterial trunks: the facial, superficial temporal, and ophthalmic arteries. Most blood flow ...
... transverse facial a, and infra orbital artery- these vessels anastamose together to form a subdermal plexus. The subcutaneous flap is supplied mainly by musculocutaneous perforators as they emerge from 3 main arterial trunks: the facial, superficial temporal, and ophthalmic arteries. Most blood flow ...
Access to Parapharyngeal Space - Vula
... ACCESS TO THE PARAPHARYNGEAL SPACE The parapharyngeal space (PPS) extends from the skull base above, to the hyoid bone below, and contains fat, the carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and the lower cranial nerves and sympathetic nerve. Surgical resection of tumours of the PPS requires a good unde ...
... ACCESS TO THE PARAPHARYNGEAL SPACE The parapharyngeal space (PPS) extends from the skull base above, to the hyoid bone below, and contains fat, the carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and the lower cranial nerves and sympathetic nerve. Surgical resection of tumours of the PPS requires a good unde ...
The Maxillary nerve HO
... After the Maxillary nerve has given off its Posterior Superior Alveolar and Zygomatic branches, it continues into the infraorbital groove as the Infraorbital nerve. Like the Infraorbital artery, the nerve gives off a Middle Superior Alveolar branch for the premolar teeth, and an Anterior Superior Al ...
... After the Maxillary nerve has given off its Posterior Superior Alveolar and Zygomatic branches, it continues into the infraorbital groove as the Infraorbital nerve. Like the Infraorbital artery, the nerve gives off a Middle Superior Alveolar branch for the premolar teeth, and an Anterior Superior Al ...
A study of the anterior ethmoidal artery and a new classification of
... adjusted in such a way that the hard palate was parallel to the floor, while the sagittal plane was perpendicular to the floor. All CT images had been ordered for sinonasal, otologic or maxillofacial inquiries between January 2014 and January 2015. Patients with nasal polyposis or sinus anomalies an ...
... adjusted in such a way that the hard palate was parallel to the floor, while the sagittal plane was perpendicular to the floor. All CT images had been ordered for sinonasal, otologic or maxillofacial inquiries between January 2014 and January 2015. Patients with nasal polyposis or sinus anomalies an ...
Anatomy of the Face and Neck
... of the mental foramen, where fibers of depressor anguli oris cover it. It passes upward and medially to insert into the skin and mucosa of the lower lip and into fibers of orbicularis oris. Mentalis arises from the incisive fossa of the mandible and descends to insert into the dermis of the chin. Co ...
... of the mental foramen, where fibers of depressor anguli oris cover it. It passes upward and medially to insert into the skin and mucosa of the lower lip and into fibers of orbicularis oris. Mentalis arises from the incisive fossa of the mandible and descends to insert into the dermis of the chin. Co ...
Medical Nutrient Foramina of the Dry Human Clavicle and Their
... vessels .Knudsen et al. stated that the clavicle gets nourishment through the suprascapular, thoracoacromial and internal thoracic arteries. According to them the clavicle is supplied by periosteal arteries and not by the nutrient artery.The absence of nutrient artery to the clavicle explained by th ...
... vessels .Knudsen et al. stated that the clavicle gets nourishment through the suprascapular, thoracoacromial and internal thoracic arteries. According to them the clavicle is supplied by periosteal arteries and not by the nutrient artery.The absence of nutrient artery to the clavicle explained by th ...
The complications of sinusitis BH Pickard
... The roots of the upper teeth, particularly the second premolar and first molar may lie in close proximity to a well-formed maxillary sinus. The tooth roots which project into the antrum are then covered by a thin layer of bone resembling the fingers of a glove. Extraction of one such tooth, even wit ...
... The roots of the upper teeth, particularly the second premolar and first molar may lie in close proximity to a well-formed maxillary sinus. The tooth roots which project into the antrum are then covered by a thin layer of bone resembling the fingers of a glove. Extraction of one such tooth, even wit ...
Feeding Mechanism in the Rattlesnake Crotalus durissus
... some new interpretations of the jaw apparatus of the rattlesnake, Crotalus durissus. 2. Materials and Methods Two Crotalus durzssus ruruzma Hoge, approximately 1 meter in overall length, were used in the experiments. They were fed with mice 25-30 grams. For the radiography experiments, the snakes we ...
... some new interpretations of the jaw apparatus of the rattlesnake, Crotalus durissus. 2. Materials and Methods Two Crotalus durzssus ruruzma Hoge, approximately 1 meter in overall length, were used in the experiments. They were fed with mice 25-30 grams. For the radiography experiments, the snakes we ...
Anatomy of the Temporal Bone
... number of spaces, the mastoid cells, which exhibit the greatest possible variety as to their size and number. At the upper and front part of the process they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequentl ...
... number of spaces, the mastoid cells, which exhibit the greatest possible variety as to their size and number. At the upper and front part of the process they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequentl ...
Aspiration Techniques
... Actual insertion point may vary based on a individual patient's anatomy Conlideniial. Intended solely lor Blome! Biologics Distributors and Sal.. Representatives ...
... Actual insertion point may vary based on a individual patient's anatomy Conlideniial. Intended solely lor Blome! Biologics Distributors and Sal.. Representatives ...
Welcome to Anatomy!
... week, extends posteriorly and is completed by 12th week Bone develops in the anterior part to form the hard palate. The posterior part develops as muscular soft palate ...
... week, extends posteriorly and is completed by 12th week Bone develops in the anterior part to form the hard palate. The posterior part develops as muscular soft palate ...
Pharynx and soft palate
... from the lower part of the torus to palatopharyngeus pharyngeal recess: a slit-like recess behind the salpingopharyngeal fold pharyngeal tonsil: a collection of lymphatic tissue lying on the roof of the pharynx; enlarged→ adenoids ...
... from the lower part of the torus to palatopharyngeus pharyngeal recess: a slit-like recess behind the salpingopharyngeal fold pharyngeal tonsil: a collection of lymphatic tissue lying on the roof of the pharynx; enlarged→ adenoids ...
File - Jamison Spencer, DMD, MS
... centric relation \se˘n′tri˘k ri˘-lā′shun\ 1: the maxillomandibular relationship in which the condyles articulate with the thinnest avascular portion of their respective disks with the complex in the anterior-superior position against the shapes of the articular eminencies. This position is independ ...
... centric relation \se˘n′tri˘k ri˘-lā′shun\ 1: the maxillomandibular relationship in which the condyles articulate with the thinnest avascular portion of their respective disks with the complex in the anterior-superior position against the shapes of the articular eminencies. This position is independ ...
sample - Create Training
... well as a review for the practicing clinician. The head and neck comprise the foundation for dental anatomical study. The many small, inter-related structures are not easily observable, which makes head and neck anatomy one of the most difficult disciplines for students to master. This second editio ...
... well as a review for the practicing clinician. The head and neck comprise the foundation for dental anatomical study. The many small, inter-related structures are not easily observable, which makes head and neck anatomy one of the most difficult disciplines for students to master. This second editio ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.