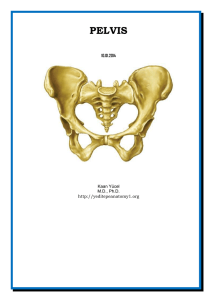
9.Pelvis
... The skin, soft tissues, which cover hipbones, belong to other anatomotopographical regions. The hipbone consists of three bones these are iliac, sciatic, pubic bones and are divided by the cartilage. The neonate may pass through the maternal passages because measures and pelvis configuration may var ...
... The skin, soft tissues, which cover hipbones, belong to other anatomotopographical regions. The hipbone consists of three bones these are iliac, sciatic, pubic bones and are divided by the cartilage. The neonate may pass through the maternal passages because measures and pelvis configuration may var ...
Total maxillectomy and Orbital Exenteration - Vula
... to supply the overlying soft tissues of the face (Figures 12, 14). Sphenopalatine artery (Figure 16): It enters the nasal cavity through the sphenopalatine foramen at the back of the superior meatus. Posterior lateral nasal arteries: They are branches of the sphenopalatine ...
... to supply the overlying soft tissues of the face (Figures 12, 14). Sphenopalatine artery (Figure 16): It enters the nasal cavity through the sphenopalatine foramen at the back of the superior meatus. Posterior lateral nasal arteries: They are branches of the sphenopalatine ...
Rhinology and Facial Plastic Surgery - ReadingSample - Beck-Shop
... etc., can all be evaluated from the frontal view. As with the profile view, the relationships of the columella should also be evaluated from the frontal view when the tip is under consideration. In Caucasian patients, the inferior-most point of the columella usually lies on the same horizontal plane ...
... etc., can all be evaluated from the frontal view. As with the profile view, the relationships of the columella should also be evaluated from the frontal view when the tip is under consideration. In Caucasian patients, the inferior-most point of the columella usually lies on the same horizontal plane ...
PDF file
... semispinalis capitis were examined in 100 formalin-fixed adult cadavers. In addition, the relative position of the nerve on a horizontal line between the external occipital protuberance and the mastoid process, as well as between the mastoid processes was measured. The greater occipital nerve was fo ...
... semispinalis capitis were examined in 100 formalin-fixed adult cadavers. In addition, the relative position of the nerve on a horizontal line between the external occipital protuberance and the mastoid process, as well as between the mastoid processes was measured. The greater occipital nerve was fo ...
Facial Nerve
... - Nerve lies 6-8mm deep to this suture line (Most Constant landmark) Posterior Belly of digastric tendon - trace posterior belly of digastric till Digastric groove (its attachment) and nerve is found to lie between it styloid process. Styloid process - Lateral to it at skull base Tracing terminal br ...
... - Nerve lies 6-8mm deep to this suture line (Most Constant landmark) Posterior Belly of digastric tendon - trace posterior belly of digastric till Digastric groove (its attachment) and nerve is found to lie between it styloid process. Styloid process - Lateral to it at skull base Tracing terminal br ...
Paranasal Sinus Anatomy and Function January 2002
... The complexity of the paranasal sinuses anatomy, as well as their many functions make the sinuses an interesting and rewarding topic of study. There are a total of four paired sinuses. They include the frontal, ethmoid, maxillary and sphenoid sinuses. These sinuses are essentially mucosa-lined airsp ...
... The complexity of the paranasal sinuses anatomy, as well as their many functions make the sinuses an interesting and rewarding topic of study. There are a total of four paired sinuses. They include the frontal, ethmoid, maxillary and sphenoid sinuses. These sinuses are essentially mucosa-lined airsp ...
Chapter 8
... equalize pressure between the vertebrae during body movement. As each disk is slightly flexible, the combined movements of many of the joints in the vertebral column allow the back to bend forward, to the side, or to twist. 8.3 General Structure of a Synovial Joint 8. Draw the general structure of a ...
... equalize pressure between the vertebrae during body movement. As each disk is slightly flexible, the combined movements of many of the joints in the vertebral column allow the back to bend forward, to the side, or to twist. 8.3 General Structure of a Synovial Joint 8. Draw the general structure of a ...
OSU Anatomy Outline
... Module Three: Ligaments Of The Foot ...............................................................23 Lesson One: Basic Terminology......................................................................23 Ligaments and Tendons, What's the difference? .....................................23 Ligaments ...
... Module Three: Ligaments Of The Foot ...............................................................23 Lesson One: Basic Terminology......................................................................23 Ligaments and Tendons, What's the difference? .....................................23 Ligaments ...
Anatomical Considerations of the Endonasal Transsphenoidal
... these layers form the dura mater that covers the sphenoid planum and the anterior cranial fossa. Posteriorly, they are continuous with the dura mater covering dorsum sellae and clivus. The superficial or meningeal layer is continuous laterally with the superficial layer of the roof and lateral wall ...
... these layers form the dura mater that covers the sphenoid planum and the anterior cranial fossa. Posteriorly, they are continuous with the dura mater covering dorsum sellae and clivus. The superficial or meningeal layer is continuous laterally with the superficial layer of the roof and lateral wall ...
Bones of the Back Region - Listed in Superior to Inferior Order
... the fifth lumbar vertebra through an intervertebral disk ...
... the fifth lumbar vertebra through an intervertebral disk ...
proptosis - Otolaryngology online
... Entire venous system is devoid of valves – hence two way communication between orbit and sinuses is a reality Superior opthalmic vein connects facial vein to cavernous sinus – causing spread of infections from face to cavernous sinus ...
... Entire venous system is devoid of valves – hence two way communication between orbit and sinuses is a reality Superior opthalmic vein connects facial vein to cavernous sinus – causing spread of infections from face to cavernous sinus ...
First Part of the Subclavian Artery
... The emissary veins are valve-less veins that pass through the skull bones. They connect the veins of the scalp to the venous sinuses (and are an important route for the spread of infection). ...
... The emissary veins are valve-less veins that pass through the skull bones. They connect the veins of the scalp to the venous sinuses (and are an important route for the spread of infection). ...
Identification of greater occipital nerve landmarks for the treatment of
... as it passes through these aponeuroses, causing symptoms of occipital neuralgia. The aim of this study was to identify topographic landmarks for accurate identification of GON, which might facilitate its anaesthetic blockade. The course and distribution of GON and its relation to the aponeuroses of ...
... as it passes through these aponeuroses, causing symptoms of occipital neuralgia. The aim of this study was to identify topographic landmarks for accurate identification of GON, which might facilitate its anaesthetic blockade. The course and distribution of GON and its relation to the aponeuroses of ...
Tendons, Ligaments, Joints
... Stretching exercises increase the length and flexibility of the muscles, allowing the joint to move farther than before. The ligaments themselves are not stretched, as they provide the support for the joint. If ligaments are stretched, either by injury, excess strain on a joint, or by improper stret ...
... Stretching exercises increase the length and flexibility of the muscles, allowing the joint to move farther than before. The ligaments themselves are not stretched, as they provide the support for the joint. If ligaments are stretched, either by injury, excess strain on a joint, or by improper stret ...
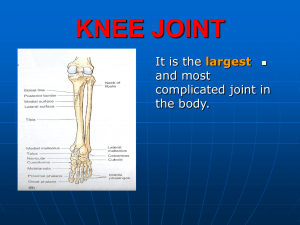
21-KNEE JOINT
... injured especially in footballers and cricketers. The medial is torn three times more often than the lateral. The injury is produced by the rotation of the femur on the tibia or the reverse with the knee joint partially flexed and carries the weight of the body. ...
... injured especially in footballers and cricketers. The medial is torn three times more often than the lateral. The injury is produced by the rotation of the femur on the tibia or the reverse with the knee joint partially flexed and carries the weight of the body. ...
Intratemporal Facial Nerve Surgery
... The final layer of bone over the nerve should be removed by blunt elevators specially designed for this purpose. These instruments are thin but strong enough to remove a thin layer of bone. Stapes curettes are usually too large and can cause compression injury to the nerve. If a neurolysis is to be ...
... The final layer of bone over the nerve should be removed by blunt elevators specially designed for this purpose. These instruments are thin but strong enough to remove a thin layer of bone. Stapes curettes are usually too large and can cause compression injury to the nerve. If a neurolysis is to be ...
functional anatomy of the mammal
... The presentation is designed to integrate a rtJ- ther specific laboratory study of the cat with text material of a more gerleral character with emphasis on man. As far as possible, descriptive avatomy has been treated with special reference to the functional organization of the parts and their inter ...
... The presentation is designed to integrate a rtJ- ther specific laboratory study of the cat with text material of a more gerleral character with emphasis on man. As far as possible, descriptive avatomy has been treated with special reference to the functional organization of the parts and their inter ...
Нейроанатомия
... The thalami form the majority of the lateral walls of the third ventricle. In 70–80% of people there is a midline interthalamic adhesion known as the massa intermedia. It is made up of nerve cell bodies and a few nerve fibres. The exact function of this adhesion is not known and its absence does not ...
... The thalami form the majority of the lateral walls of the third ventricle. In 70–80% of people there is a midline interthalamic adhesion known as the massa intermedia. It is made up of nerve cell bodies and a few nerve fibres. The exact function of this adhesion is not known and its absence does not ...
Otolaryngology -- Head and Neck Surgery
... The EAC of the young child is quite different (Figure 2). At birth, the cartilaginous canal sits directly against the tympanic ring. Thus, the tympanic membrane comes immediately into view on entering the cartilaginous canal with an endoscope. In the first 5 years of life, ossification and growth of ...
... The EAC of the young child is quite different (Figure 2). At birth, the cartilaginous canal sits directly against the tympanic ring. Thus, the tympanic membrane comes immediately into view on entering the cartilaginous canal with an endoscope. In the first 5 years of life, ossification and growth of ...
Parotid duct
... Frey's syndrome is an interesting complication • that sometimes develops after penetrating wounds of the parotid gland. When the patient eats, beads of perspiration appear on the skin covering the parotid. This condition is caused by damage to the auriculotemporal and great auricular nerves. During ...
... Frey's syndrome is an interesting complication • that sometimes develops after penetrating wounds of the parotid gland. When the patient eats, beads of perspiration appear on the skin covering the parotid. This condition is caused by damage to the auriculotemporal and great auricular nerves. During ...
Vertebrobasilar junction aneurysm: surgical treatment via far lateral
... Exposure of the extradural VA: Exposure and control of the extradural VA is important and was achieved by identifying its extradural course from the foramen transversarium of C-2 to the occiput. The ventral ramus of the C-2 nerve root, which was found between the laminae of C-1 and C-2, was traced l ...
... Exposure of the extradural VA: Exposure and control of the extradural VA is important and was achieved by identifying its extradural course from the foramen transversarium of C-2 to the occiput. The ventral ramus of the C-2 nerve root, which was found between the laminae of C-1 and C-2, was traced l ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Pelvis pelvıs 10.01.2014
... The ischium has a body and ramus. The body of the ischium helps form the acetabulum and the ramus of the ischium forms part of the obturator foramen. The large posteroinferior protuberance of the ischium is the ischial tuberosity. The small pointed posteromedial projection near the junction of the r ...
... The ischium has a body and ramus. The body of the ischium helps form the acetabulum and the ramus of the ischium forms part of the obturator foramen. The large posteroinferior protuberance of the ischium is the ischial tuberosity. The small pointed posteromedial projection near the junction of the r ...
Biology 231 - Request a Spot account
... functions: squamous cells, cuboidal cells, columnar cells 6. For each epithelial tissue type, in the left hand column below its name, draw a brief sketch of its appearance and write a short phrase reminding you of what it looks like. For example, underneath a sketch of simple squamous epithelium wri ...
... functions: squamous cells, cuboidal cells, columnar cells 6. For each epithelial tissue type, in the left hand column below its name, draw a brief sketch of its appearance and write a short phrase reminding you of what it looks like. For example, underneath a sketch of simple squamous epithelium wri ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.