The Trust Indenture Act of 1939 and Out-of
... debt for equity. And this shift in the company’s capital structure is the key feature. The troubled issuer can stop making bond payments that it cannot afford, and the bondholders are able to trade in bad debt for the chance to profit from the company’s eventual turnaround. But, unlike our example, ...
... debt for equity. And this shift in the company’s capital structure is the key feature. The troubled issuer can stop making bond payments that it cannot afford, and the bondholders are able to trade in bad debt for the chance to profit from the company’s eventual turnaround. But, unlike our example, ...
The Existence of Corporate Bond Clawbacks
... credit quality, issue characteristics, and time trends using a multivariate analysis. Results are robust to several definitions of credit quality. The rest of the paper is structured as follows. We present a simple model for IPOCs in Section 2. Section 3 illustrates a basic numerical analysis of the ...
... credit quality, issue characteristics, and time trends using a multivariate analysis. Results are robust to several definitions of credit quality. The rest of the paper is structured as follows. We present a simple model for IPOCs in Section 2. Section 3 illustrates a basic numerical analysis of the ...
Risk-Adjusted Performance of Private Equity Investments
... arguing that they play an important role in PE transactions that must be priced. They find that, on average, PE investors do not earn positive alphas. Surprisingly, they also find that funds exposed to more idiosyncratic risk earn higher returns than more diversified portfolios. Quigley and Woodward ...
... arguing that they play an important role in PE transactions that must be priced. They find that, on average, PE investors do not earn positive alphas. Surprisingly, they also find that funds exposed to more idiosyncratic risk earn higher returns than more diversified portfolios. Quigley and Woodward ...
DollarsDirect - Treasury.gov.au
... d. Because of the operation of the proposed section 39A, it is not possible for the credit provider to recover the cost of the credit report (or for that matter any other outlay) from the consumer. Therefore, to comply with RG 209, even if the credit provider does nothing externally apart from obtai ...
... d. Because of the operation of the proposed section 39A, it is not possible for the credit provider to recover the cost of the credit report (or for that matter any other outlay) from the consumer. Therefore, to comply with RG 209, even if the credit provider does nothing externally apart from obtai ...
Chapter 11
... means of financing that project, but rather against the weighted average cost of financing all projects for the firm. This principle recognizes that the availability of one source of financing is dependent on other sources. Once a common overall cost is determined, the “colony destroying device” yie ...
... means of financing that project, but rather against the weighted average cost of financing all projects for the firm. This principle recognizes that the availability of one source of financing is dependent on other sources. Once a common overall cost is determined, the “colony destroying device” yie ...
The “Mystery of the Printing Press” Monetary Policy and Self
... their nominal value (see also Hall and Reis 2012). Thus, by purchasing government paper, the central bank e¤ectively swaps default-risky public debt for its own liabilities with a guaranteed face value, subject only to the risk of in‡ation.5 As a result, central bank interventions reduce uncertainty ...
... their nominal value (see also Hall and Reis 2012). Thus, by purchasing government paper, the central bank e¤ectively swaps default-risky public debt for its own liabilities with a guaranteed face value, subject only to the risk of in‡ation.5 As a result, central bank interventions reduce uncertainty ...
An Analysis of the Uniform Consumer Credit Code
... offering, extension, and collection of credit. In effect, the Code integrates into one document virtually all consumer credit regulation and, most importantly, reduces legal impediments restricting competition by applying substantially similar treatment to all creditors and transactions coming withi ...
... offering, extension, and collection of credit. In effect, the Code integrates into one document virtually all consumer credit regulation and, most importantly, reduces legal impediments restricting competition by applying substantially similar treatment to all creditors and transactions coming withi ...
What is a Sustainable Public Debt?∗
... revenue-generating capacity and distortionary effects in the choice of fiscal instruments. The results show that indeed alternative fiscal policy strategies that are equivalent in that they all restore fiscal solvency, have very different effects on welfare and macro aggregates. Moreover, some fisca ...
... revenue-generating capacity and distortionary effects in the choice of fiscal instruments. The results show that indeed alternative fiscal policy strategies that are equivalent in that they all restore fiscal solvency, have very different effects on welfare and macro aggregates. Moreover, some fisca ...
Public Debt and Deficits
... DISCLAIMER This was prepared by Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand with the assistance of Deloitte Access Economics. This publication contains general information only, none of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, its member firms, or their related entities (collectively the “Deloitte Netw ...
... DISCLAIMER This was prepared by Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand with the assistance of Deloitte Access Economics. This publication contains general information only, none of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, its member firms, or their related entities (collectively the “Deloitte Netw ...
Forecasting Financial Statements May05
... the historical relationship. In the example, three years of data were used. However, if a firm's policies or business environment have changed, then perhaps only the last year of data is relevant in predicting the future. On the other hand, if policies and the environment have been stable, then perh ...
... the historical relationship. In the example, three years of data were used. However, if a firm's policies or business environment have changed, then perhaps only the last year of data is relevant in predicting the future. On the other hand, if policies and the environment have been stable, then perh ...
Debt, Equity and Hybrid Decoupling
... morphable (accompanied by the informal ability to acquire voting rights), or both (hidden (morphable) ownership). 3 Hidden (morphable) ownership can be seen as one form of ‘soft parking’ of shares: arranging for shares to be held in friendly hands to avoid regulatory or other burdens of direct owner ...
... morphable (accompanied by the informal ability to acquire voting rights), or both (hidden (morphable) ownership). 3 Hidden (morphable) ownership can be seen as one form of ‘soft parking’ of shares: arranging for shares to be held in friendly hands to avoid regulatory or other burdens of direct owner ...
DOC 477KB - Board of Taxation
... many financial instruments exhibit characteristics of both. As such, the debt and equity divide is not so much a clear delineation but a continuum. Prior to the introduction of Division 974, the tax treatment of interests in an entity was primarily driven by the legal form of the interest, regardles ...
... many financial instruments exhibit characteristics of both. As such, the debt and equity divide is not so much a clear delineation but a continuum. Prior to the introduction of Division 974, the tax treatment of interests in an entity was primarily driven by the legal form of the interest, regardles ...
Optimal Debt and Equity Values in the Presence of Chapter 7 and
... if the firm can avoid liquidation and emerge from bankruptcy. We model this goal by allowing for debt forgiveness once in Chapter 11. Our modeling approach allows us to draw a clear distinction between the notions of bankruptcy and liquidation. Absent the reorganization option, Black and Cox (1976) ...
... if the firm can avoid liquidation and emerge from bankruptcy. We model this goal by allowing for debt forgiveness once in Chapter 11. Our modeling approach allows us to draw a clear distinction between the notions of bankruptcy and liquidation. Absent the reorganization option, Black and Cox (1976) ...
Hedging and Speculating with Interest Rate Swaps
... incentivizes hedging to increase the amount of leverage that firms can sustain (Graham and Rogers (2002)), or because greater debt levels entail larger benefits from successful speculation? Similarly, do high-powered executive compensation contracts motivate more hedging, because managers internaliz ...
... incentivizes hedging to increase the amount of leverage that firms can sustain (Graham and Rogers (2002)), or because greater debt levels entail larger benefits from successful speculation? Similarly, do high-powered executive compensation contracts motivate more hedging, because managers internaliz ...
Bankruptcy Equilibrium: Secured and Unsecured assets
... a loan, the bank usually makes a credit analysis of the individual in order to determine the agent’s ability to repay the debt, and determines a credit limit as the maximum amount of money that the bank should lend the individual [21]. For simplicity, we do not model the way this limit is estimated ...
... a loan, the bank usually makes a credit analysis of the individual in order to determine the agent’s ability to repay the debt, and determines a credit limit as the maximum amount of money that the bank should lend the individual [21]. For simplicity, we do not model the way this limit is estimated ...
reorganizing with Value but Without Profit (or Equity)
... has not been paid the allowed amount of its bankruptcy claim in full.11 Specifically, as it relates to unsecured creditors, this provision mandates that “the holder of any… interest in a debtor may not receive or retain property on account of such an interest unless all creditors have been paid in f ...
... has not been paid the allowed amount of its bankruptcy claim in full.11 Specifically, as it relates to unsecured creditors, this provision mandates that “the holder of any… interest in a debtor may not receive or retain property on account of such an interest unless all creditors have been paid in f ...
Payment, clearing and settlement systems in Brazil
... transfers via TED are settled in real time or “quasi-real time”, depending on whether they are settled via STR or SITRAF (Funds Transfer System), respectively.7 As a general rule, a bank receiving a credit transfer must credit the payee’s account no more than 60 minutes after the interbank settlemen ...
... transfers via TED are settled in real time or “quasi-real time”, depending on whether they are settled via STR or SITRAF (Funds Transfer System), respectively.7 As a general rule, a bank receiving a credit transfer must credit the payee’s account no more than 60 minutes after the interbank settlemen ...
Count the Limbs: Designing Robust Aggregation Clauses in
... possibilities for abuse. The markets might have rebelled. Instead, they yawned. On October 7, barely a month after ICMA launched its new collective action clauses (CACs), Kazakhstan became the first to use them in an English law bond. The issue, Kazakhstan’s first in fourteen years, was oversubscrib ...
... possibilities for abuse. The markets might have rebelled. Instead, they yawned. On October 7, barely a month after ICMA launched its new collective action clauses (CACs), Kazakhstan became the first to use them in an English law bond. The issue, Kazakhstan’s first in fourteen years, was oversubscrib ...
PDF Download
... major creditors in that same month and ceased interest payments on its bonds in early December of 2006. The payment suspension thus occurred just prior to the finalization of its debt exchange in January of 2007, but more than three months after the start of negotiations. In addition, the governmen ...
... major creditors in that same month and ceased interest payments on its bonds in early December of 2006. The payment suspension thus occurred just prior to the finalization of its debt exchange in January of 2007, but more than three months after the start of negotiations. In addition, the governmen ...
Default, rescheduling and inflation : debt crisis in Spain
... the 19th century, restructurings of the external debt were voluntary and agreed upon with foreign investors, while in the 20th Century the prevalence of internal debt allowed governments to both carry out debt restructurings and also use inflation tax. Consequently, in the three first parts of this ...
... the 19th century, restructurings of the external debt were voluntary and agreed upon with foreign investors, while in the 20th Century the prevalence of internal debt allowed governments to both carry out debt restructurings and also use inflation tax. Consequently, in the three first parts of this ...
Threat of entry and debt maturity: evidence from airlines
... How incumbents should accomplish that in practice is, however, unclear. Previous research indicates that leverage ratios are highly persistent (Lemmon, Roberts, and Zender (2008)), while holding excess cash reserves can be significantly expensive (Jensen (1986), Holmström and Tirole (2000)). A grow ...
... How incumbents should accomplish that in practice is, however, unclear. Previous research indicates that leverage ratios are highly persistent (Lemmon, Roberts, and Zender (2008)), while holding excess cash reserves can be significantly expensive (Jensen (1986), Holmström and Tirole (2000)). A grow ...
Monetary and Fiscal Policy with Sovereign Default
... to the Mexican economy which has experienced periods of high inflation and sovereign risk in the recent past. In addition, domestic nominal debt matters for the Mexican government.3 I study the Markov-perfect equilibrium of the public policy problem (see Klein et al., 2008). The government’s decisio ...
... to the Mexican economy which has experienced periods of high inflation and sovereign risk in the recent past. In addition, domestic nominal debt matters for the Mexican government.3 I study the Markov-perfect equilibrium of the public policy problem (see Klein et al., 2008). The government’s decisio ...
Inflating Away the Public Debt? - Centre for Economic Policy Research
... A higher inflation target has some benefits, and one of its most celebrated is to erode the real value of outstanding debt. Across centuries and countries, a common way sovereigns pay for high public debt is by having higher, and sometimes even hyper, inflation. At the same time, higher inflation is ...
... A higher inflation target has some benefits, and one of its most celebrated is to erode the real value of outstanding debt. Across centuries and countries, a common way sovereigns pay for high public debt is by having higher, and sometimes even hyper, inflation. At the same time, higher inflation is ...
forecasting financial statements: proforma analysis
... when the plant and equipment become capacity constrained, these fixed assets may grow at a faster rate than sales since equipment and factories tend to come in “lumpy” amounts. It may be hard to buy 10 percent of a factory when sales increase by 10 percent. Three common ways to describe the historic ...
... when the plant and equipment become capacity constrained, these fixed assets may grow at a faster rate than sales since equipment and factories tend to come in “lumpy” amounts. It may be hard to buy 10 percent of a factory when sales increase by 10 percent. Three common ways to describe the historic ...
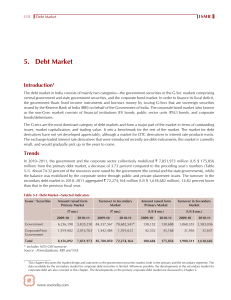
5. Debt Market
... their auction is made by the RBI through a Press Release that would be issued one day prior to the date of auction. The settlement of the auction is on a T+1 basis. Dated Government Securities: Dated government securities are long-term securities that carry a fixed or floating coupon (interest rate), ...
... their auction is made by the RBI through a Press Release that would be issued one day prior to the date of auction. The settlement of the auction is on a T+1 basis. Dated Government Securities: Dated government securities are long-term securities that carry a fixed or floating coupon (interest rate), ...