Science 10 - SharpSchool
... 1. metals are good conductors, strong, malleable (pound into thin sheet), ductile (can draw into a wire, bendable), have high luster; are found on left side of stair case 2. non metals are poor conductors, non-lustrous, weak, etc…opposite properties to metals; found on right side of ...
... 1. metals are good conductors, strong, malleable (pound into thin sheet), ductile (can draw into a wire, bendable), have high luster; are found on left side of stair case 2. non metals are poor conductors, non-lustrous, weak, etc…opposite properties to metals; found on right side of ...
Synthesis of monoselenanedisulfanediphosphonate by the reaction
... (10 mmol) of ascorbic acid in 75 ml of water; then a solution of potassium dihydrogenmonothiophosphate, KH2PO3S, prepared by dissolution of 3.04 g (20 mmol) of KH2PO3S in 75 ml of water was added into it. The solution (2) was slowly added to the solution (1), and a clear yellowish-green solution of ...
... (10 mmol) of ascorbic acid in 75 ml of water; then a solution of potassium dihydrogenmonothiophosphate, KH2PO3S, prepared by dissolution of 3.04 g (20 mmol) of KH2PO3S in 75 ml of water was added into it. The solution (2) was slowly added to the solution (1), and a clear yellowish-green solution of ...
Chapter 7: Recent advances in enzyme technology
... initially formed. Under normal physiological conditions, hydrolytic enzymes catalyse the degradation of polymers; i.e. hydrolases are transferases normally transferring a moiety to the acceptor, water. Water is normally present in a vast molar excess over other potential acceptor molecules so no rea ...
... initially formed. Under normal physiological conditions, hydrolytic enzymes catalyse the degradation of polymers; i.e. hydrolases are transferases normally transferring a moiety to the acceptor, water. Water is normally present in a vast molar excess over other potential acceptor molecules so no rea ...
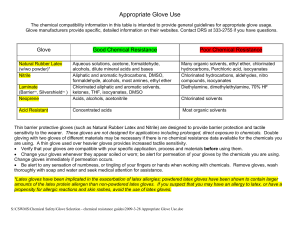
Appropriate Glove Use
... Appropriate Glove Use The chemical compatibility information in this table is intended to provide general guidelines for appropriate glove usage. Glove manufacturers provide specific, detailed information on their websites. Contact DRS at 333-2755 if you have questions. ...
... Appropriate Glove Use The chemical compatibility information in this table is intended to provide general guidelines for appropriate glove usage. Glove manufacturers provide specific, detailed information on their websites. Contact DRS at 333-2755 if you have questions. ...
Minimum electrophilicity principle in Lewis acid–base complexes of
... The acid and base are among the most widely used concepts in chemistry and are almost as old as chemistry itself. Although there are different definitions for these concepts [1], but all of the current definitions are compatible with each other. Perhaps the most widely used of these definitions is Lewi ...
... The acid and base are among the most widely used concepts in chemistry and are almost as old as chemistry itself. Although there are different definitions for these concepts [1], but all of the current definitions are compatible with each other. Perhaps the most widely used of these definitions is Lewi ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Give the student the formula of barium hydroxide and sulfuric acid and ask them to predict the product of the reaction. 2. To a 250-mL beaker add 30 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid. 3. To the beaker add 50 mL of water and 2 drops of phenolphthalein. 4. Ask the student for their opinion as why the water ...
... 1. Give the student the formula of barium hydroxide and sulfuric acid and ask them to predict the product of the reaction. 2. To a 250-mL beaker add 30 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid. 3. To the beaker add 50 mL of water and 2 drops of phenolphthalein. 4. Ask the student for their opinion as why the water ...
Chemistry
... point and depression in freezing point, SI units for Kb, Kf , osmosis – osmotic pressure, isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic solutions, reverse osmosis – application in desalination of water. Numerical problems on determination of molar mass using colligative properties. Abnormal molar mass, van’t Hoff ...
... point and depression in freezing point, SI units for Kb, Kf , osmosis – osmotic pressure, isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic solutions, reverse osmosis – application in desalination of water. Numerical problems on determination of molar mass using colligative properties. Abnormal molar mass, van’t Hoff ...
Chapter 2
... • In this series of elements, the mass number (A) varies but the atomic number (Z) is constant. • This means that we are looking at a series of isotopes. ...
... • In this series of elements, the mass number (A) varies but the atomic number (Z) is constant. • This means that we are looking at a series of isotopes. ...
CHAPTER 1 Differentiate b/w Mendeleev`s periodic law and modern
... Why atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group? Ans.The increasing number of shells and increasing. shielding effect increase the atomic radii from top to bottom. How does the nature of orbital influence the value of ionization energies of elements? Ans.The outermost electrons to be removed ...
... Why atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group? Ans.The increasing number of shells and increasing. shielding effect increase the atomic radii from top to bottom. How does the nature of orbital influence the value of ionization energies of elements? Ans.The outermost electrons to be removed ...
CP - Fundamentals
... We just learned that simple quantitative relationships based upon the idea of the law of simple proportions could be combined with other concepts from Dalton’s Atomic Theory to create a host of problems based upon the quantitative relationships between atoms in molecules. We learned to use unit fact ...
... We just learned that simple quantitative relationships based upon the idea of the law of simple proportions could be combined with other concepts from Dalton’s Atomic Theory to create a host of problems based upon the quantitative relationships between atoms in molecules. We learned to use unit fact ...
Net Ionic Prep Session NMSI INSTRUCTOR
... 3. Halides: All are soluble except silver, mercury or lead. 4. Strong acids: hydrochloric, hydrobromic, hydroiodic, nitric, perchloric, sulfuric— WRITE THESE DISSOCIATED except concentrated sulfuric, it really is 97% H2SO4 and 3% water in the jug, so water is way outnumbered and the molecules don’t ...
... 3. Halides: All are soluble except silver, mercury or lead. 4. Strong acids: hydrochloric, hydrobromic, hydroiodic, nitric, perchloric, sulfuric— WRITE THESE DISSOCIATED except concentrated sulfuric, it really is 97% H2SO4 and 3% water in the jug, so water is way outnumbered and the molecules don’t ...
Unit 3 Homework Booklet
... How many grams of magnesium oxide would be produced by reacting completely 4.0 g of magnesium with oxygen? ...
... How many grams of magnesium oxide would be produced by reacting completely 4.0 g of magnesium with oxygen? ...
5. Formulae, equations and amounts of substance
... •Results should be clearly recorded in a table •Result should be recorded in full (i.e. both initial and final readings) •Record titre volumes to 2dp (0.05 cm3) ...
... •Results should be clearly recorded in a table •Result should be recorded in full (i.e. both initial and final readings) •Record titre volumes to 2dp (0.05 cm3) ...
workbook Chem (WP)
... 5. Write the formula and name the common molecular compounds given in class. Acids and Bases 1. List the characteristics of an acid. 2. List the characteristics of a base. 3. Write the formula for the following: a) hydrochloric acid b) phosphoric acid c) carbonous acid d) hydrofluoric acid e) nitric ...
... 5. Write the formula and name the common molecular compounds given in class. Acids and Bases 1. List the characteristics of an acid. 2. List the characteristics of a base. 3. Write the formula for the following: a) hydrochloric acid b) phosphoric acid c) carbonous acid d) hydrofluoric acid e) nitric ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
materials required/recommended for this paper
... Answer the questions according to the following instructions. Section One: Answer all questions on the separate Multiple-choice Answer Sheet provided. For each questions shade the box to indicate your answer. Use only a blue or black pen to shade the boxes. If you make a mistake, place a cross throu ...
... Answer the questions according to the following instructions. Section One: Answer all questions on the separate Multiple-choice Answer Sheet provided. For each questions shade the box to indicate your answer. Use only a blue or black pen to shade the boxes. If you make a mistake, place a cross throu ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... The amino acids in Table 27.1 that have more than one stereogenic center are isoleucine and threonine. The stereogenic centers are marked with an asterisk in the structural formulas shown. ...
... The amino acids in Table 27.1 that have more than one stereogenic center are isoleucine and threonine. The stereogenic centers are marked with an asterisk in the structural formulas shown. ...
DRAFT AP® CHEMISTRY 2005 SCORING GUIDELINES
... give the credit. Also, would accept ‘re-ignite’ for oxygen. I have a problem with the hydrogen gas because you have to assume that hydrogen gas escapes and oxygen gas comes in to get a pop. If students have seen the demonstration where you take a balloon filled with hydrogen and take a candle to it, ...
... give the credit. Also, would accept ‘re-ignite’ for oxygen. I have a problem with the hydrogen gas because you have to assume that hydrogen gas escapes and oxygen gas comes in to get a pop. If students have seen the demonstration where you take a balloon filled with hydrogen and take a candle to it, ...
Density, Viscosity, Solubility, and Diffusivity of N2O in Aqueous
... carrying out experiments on the absorption of N2O and CO2 in water in the temperature range 292-310 K, using different liquid stirrer speeds. The values of diffusion coefficient of N2O and CO2 in water obtained from the literature9 were used to determine the calibration factor, f. The f factor of th ...
... carrying out experiments on the absorption of N2O and CO2 in water in the temperature range 292-310 K, using different liquid stirrer speeds. The values of diffusion coefficient of N2O and CO2 in water obtained from the literature9 were used to determine the calibration factor, f. The f factor of th ...
Kinetics and Mechanism of Uncatalyzed and Ag (I) Catalyzed
... sulphuric acid medium and sulphato complexes, such as CeSO42+, Ce(SO4)2 and Ce(SO4)32- have been established and quantified [26]. However, cerium (IV) in perchloric acid medium does not indicate complex formation, although Ce4+, Ce(OH)3+, (Ce-O-Ce)6+ and (HOCe-O-CeOH)4+ species of cerium (IV) are we ...
... sulphuric acid medium and sulphato complexes, such as CeSO42+, Ce(SO4)2 and Ce(SO4)32- have been established and quantified [26]. However, cerium (IV) in perchloric acid medium does not indicate complex formation, although Ce4+, Ce(OH)3+, (Ce-O-Ce)6+ and (HOCe-O-CeOH)4+ species of cerium (IV) are we ...
5. Formulae, equations and amounts of substance
... •Results should be clearly recorded in a table •Result should be recorded in full (i.e. both initial and final readings) •Record titre volumes to 2dp (0.05 cm3) ...
... •Results should be clearly recorded in a table •Result should be recorded in full (i.e. both initial and final readings) •Record titre volumes to 2dp (0.05 cm3) ...
Sugar Amino Acids - The Krasavin research group
... Furanoid α-SAAs have been reported mainly by Fleet and colleagues starting from the mid-1990s. The common features of these molecules, possessing the furanoid scaffold, is to have the carboxylic and amino functional groups installed at C1 in place of the hemiacetalic moiety (Figure 7.2). Dondoni and ...
... Furanoid α-SAAs have been reported mainly by Fleet and colleagues starting from the mid-1990s. The common features of these molecules, possessing the furanoid scaffold, is to have the carboxylic and amino functional groups installed at C1 in place of the hemiacetalic moiety (Figure 7.2). Dondoni and ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.