Dr. Spencer`s PPT
... and points out similarities and differences between reactions more easily. (i.e., EVERY neutralization reaction appears the same); 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) ...
... and points out similarities and differences between reactions more easily. (i.e., EVERY neutralization reaction appears the same); 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) ...
2005/6 - SAASTA
... aqueous systems, the hydrogen ion activity is dictated by the dissociation constant of water (Kw = 1.011 × 10−14 M2 at 25 °C) and interactions with other ions in solution. Due to this dissociation constant, a neutral solution (hydrogen ion activity equals hydroxide ion activity) has a pH of approxim ...
... aqueous systems, the hydrogen ion activity is dictated by the dissociation constant of water (Kw = 1.011 × 10−14 M2 at 25 °C) and interactions with other ions in solution. Due to this dissociation constant, a neutral solution (hydrogen ion activity equals hydroxide ion activity) has a pH of approxim ...
Alberta Chemistry 20-30 Sample CAB Questions - McGraw
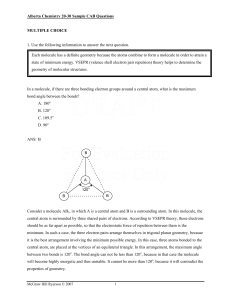
... central atom is surrounded by three shared pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, these electrons should be as far apart as possible, so that the electrostatic force of repulsion between them is the minimum. In such a case, the three electron pairs arrange themselves in trigonal planar geome ...
... central atom is surrounded by three shared pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, these electrons should be as far apart as possible, so that the electrostatic force of repulsion between them is the minimum. In such a case, the three electron pairs arrange themselves in trigonal planar geome ...
CHM 1033 Chemistry for Health Sciences
... 7. Identify one alkaline metal, one halogen and one noble gas. 8. What’s the tendency of each of these elements when becoming ions (loosing or gaining electrons?) 9. Indicate in each element whether they tend to form a positive or negative charged ion 10. What’s the relationship between the Energy L ...
... 7. Identify one alkaline metal, one halogen and one noble gas. 8. What’s the tendency of each of these elements when becoming ions (loosing or gaining electrons?) 9. Indicate in each element whether they tend to form a positive or negative charged ion 10. What’s the relationship between the Energy L ...
Chapter 4
... Here, the Na+ and NO3- ions are called "spectator ions" because they appear unchanged on both sides of the equation. The spectator ions do not participate in the chemically important part of the reaction -- the precipitation of BaCO3 The essential chemical process can be written without the spectato ...
... Here, the Na+ and NO3- ions are called "spectator ions" because they appear unchanged on both sides of the equation. The spectator ions do not participate in the chemically important part of the reaction -- the precipitation of BaCO3 The essential chemical process can be written without the spectato ...
8 SHS Ch 8 Lecture shs_ch_8_lecture_2012
... CH4 (l) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + H2 O(l) Count the number of each element on both sides ...
... CH4 (l) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + H2 O(l) Count the number of each element on both sides ...
Topic 14 - Fertilisers
... This reaction can be used to prove that a compound is an ammonium compound ...
... This reaction can be used to prove that a compound is an ammonium compound ...
Document
... A cationic chiral cyclophane was synthesized and studied as a host for chiral and racemic π-donor molecules. The cyclophane host has a rigid binding cavity flanked by (S)-(valine-leucine-alanine) and N,N′-dibenzyl-4,4′-bipyridinium subunits, which allow for hydrogen-bonding and π-stacking interactio ...
... A cationic chiral cyclophane was synthesized and studied as a host for chiral and racemic π-donor molecules. The cyclophane host has a rigid binding cavity flanked by (S)-(valine-leucine-alanine) and N,N′-dibenzyl-4,4′-bipyridinium subunits, which allow for hydrogen-bonding and π-stacking interactio ...
avogadro exam 1994 - University of Waterloo
... 14. What volume of argon gas at 100 kPa and 25°C must be added to a 1.00-Litre glass flask containing nitrogen gas at 70 kPa and 25°C to give a mixture of gases having a total pressure of 210 kPa at 25°C? ...
... 14. What volume of argon gas at 100 kPa and 25°C must be added to a 1.00-Litre glass flask containing nitrogen gas at 70 kPa and 25°C to give a mixture of gases having a total pressure of 210 kPa at 25°C? ...
Chapter 19.1 Balancing Redox Equations
... According to the collision theory of kinetics, which statement best describes the rate of a chemical reaction? a) All collisions result in a chemical reaction. b) The greater the difference in energy between the reactants and the transition state, the faster is the reaction. c) All collisions betwee ...
... According to the collision theory of kinetics, which statement best describes the rate of a chemical reaction? a) All collisions result in a chemical reaction. b) The greater the difference in energy between the reactants and the transition state, the faster is the reaction. c) All collisions betwee ...
CH 151 Companion
... approximate amount you need from the bottle into a small container and take this to your bench. d. Always use a metal spatula or scoopula to transfer solid chemicals. Do not use your finger to transfer chemicals. This will directly expose you to the potential hazards of the chemical and might contam ...
... approximate amount you need from the bottle into a small container and take this to your bench. d. Always use a metal spatula or scoopula to transfer solid chemicals. Do not use your finger to transfer chemicals. This will directly expose you to the potential hazards of the chemical and might contam ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... an unknown substance and the solute of the standard solution. The completion of the reaction is indicated by the end point of the reaction, which is observed by the colour change either due to the indicator or due to the solute itself. Whether the reactions during the analysis are either between an ...
... an unknown substance and the solute of the standard solution. The completion of the reaction is indicated by the end point of the reaction, which is observed by the colour change either due to the indicator or due to the solute itself. Whether the reactions during the analysis are either between an ...
Chemistry in Society Homework Booklet
... How many grams of magnesium oxide would be produced by reacting completely 4.0 g of magnesium with oxygen? ...
... How many grams of magnesium oxide would be produced by reacting completely 4.0 g of magnesium with oxygen? ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
Answers to Selected Questions and Problems
... (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i) subatomic particle; (j) alkali metal; (k) periodic table Dalton used the laws of conservation of mass (Lavoisier) and definite proportions (Proust ...
... (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i) subatomic particle; (j) alkali metal; (k) periodic table Dalton used the laws of conservation of mass (Lavoisier) and definite proportions (Proust ...
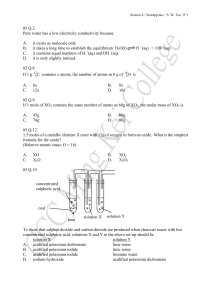
85 Q.2 Pure water has a low electricity conductivity because A. it
... Which of the following gases can be dried by anhydrous calcium chloride? (1) oxygen (2) chlorine (3) ammonia A. (1) only B. (1) and (2) only C. (1) and (3) only D. (1), (2) and (3) 85 Q.52 Which of the following tests can be used to distinguish between sodium nitrate and sodium chloride? (1) heating ...
... Which of the following gases can be dried by anhydrous calcium chloride? (1) oxygen (2) chlorine (3) ammonia A. (1) only B. (1) and (2) only C. (1) and (3) only D. (1), (2) and (3) 85 Q.52 Which of the following tests can be used to distinguish between sodium nitrate and sodium chloride? (1) heating ...
Table of contents
... electricity since d electrons are loose. Low ionization energies; have various oxidation states since they can lose d and s electrons. Can form complex ions with water called hydration complexes or with nonmetals. They can also absorb frequencies of light. The frequencies not absorbed, their subtrac ...
... electricity since d electrons are loose. Low ionization energies; have various oxidation states since they can lose d and s electrons. Can form complex ions with water called hydration complexes or with nonmetals. They can also absorb frequencies of light. The frequencies not absorbed, their subtrac ...
SODIUM HYDROGEN CARBONATE
... produce sodium bicarbonate is worth more than the sodium bicarbonate. Were it not for the recycling of ammonia, the Solvay process would be economically impractical. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used in medicine (frequently as an antacid), as a leavening agent in baking (it is “baking soda”), and in ...
... produce sodium bicarbonate is worth more than the sodium bicarbonate. Were it not for the recycling of ammonia, the Solvay process would be economically impractical. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used in medicine (frequently as an antacid), as a leavening agent in baking (it is “baking soda”), and in ...
Chemistry - CBSE Academic
... A. List of apparatus for identification for assessment in practicals (All experiments) Beaker, Tripod stand, Wire gauze, glass rod, funnel, filter paper, Bunsen burner, test tube, test tube ...
... A. List of apparatus for identification for assessment in practicals (All experiments) Beaker, Tripod stand, Wire gauze, glass rod, funnel, filter paper, Bunsen burner, test tube, test tube ...
unit 4: chemical reaction rates
... Scientists discovered that by simply determining the mass of the substance, it was possible to count particles or atoms. A mole (mol) is the amount of a pure substance that contains the same amount of chemical units as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon, namely 12. In order to avoid confu ...
... Scientists discovered that by simply determining the mass of the substance, it was possible to count particles or atoms. A mole (mol) is the amount of a pure substance that contains the same amount of chemical units as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon, namely 12. In order to avoid confu ...
chemistry-c7-what-you-should
... I can recall that the feedstocks of nitrogen and hydrogen for the Haber process are made from air, natural gas and steam I in the context of the Haber process: a. I understand that the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is a reversible reaction b. I understand how the yield of am ...
... I can recall that the feedstocks of nitrogen and hydrogen for the Haber process are made from air, natural gas and steam I in the context of the Haber process: a. I understand that the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is a reversible reaction b. I understand how the yield of am ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.