Unit D: Quantitative Relationships in Chemical Change
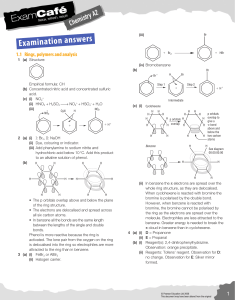
... and a precipitate forms. What amount of precipitate will form if the student has reacted 0.314 mol of silver nitrate? ...
... and a precipitate forms. What amount of precipitate will form if the student has reacted 0.314 mol of silver nitrate? ...
L22 - Supplementary Student Notes Package
... c) What mass of sulfur must have reacted in order to produce 75 g of the compound? ...
... c) What mass of sulfur must have reacted in order to produce 75 g of the compound? ...
Radiation Chemistry of Overirradiated Aqueous Solutions of
... (Reeves 1979), the radiogenic heat o f which could be sufficient to maintain liquid water cores in larger comets for several million years (Irvine et al. 1980; Wallis 1980). This article concerns the effects of irradiation at absorbed doses larger, by up to about one order of magnitude, than those p ...
... (Reeves 1979), the radiogenic heat o f which could be sufficient to maintain liquid water cores in larger comets for several million years (Irvine et al. 1980; Wallis 1980). This article concerns the effects of irradiation at absorbed doses larger, by up to about one order of magnitude, than those p ...
Ch 4 Student.pptx
... • Balanced chemical equations provide the exact relationships between the amount of reactants and products. • 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) • For example 2 molecules of octane (gasoline) react with 25 molecules of oxygen to produce 16 molecules of carbon dioxide gas and 18 mol ...
... • Balanced chemical equations provide the exact relationships between the amount of reactants and products. • 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) • For example 2 molecules of octane (gasoline) react with 25 molecules of oxygen to produce 16 molecules of carbon dioxide gas and 18 mol ...
Experimental skills and abilities
... 1 Some dyes have a greater solubility than others in the different solvents. The dyes which have moved the greatest distance have the greatest solubility in the solvents. Their Rf values are also greater. 2 The dye which was least soluble is the one which does not travel as far up the chromatogram ...
... 1 Some dyes have a greater solubility than others in the different solvents. The dyes which have moved the greatest distance have the greatest solubility in the solvents. Their Rf values are also greater. 2 The dye which was least soluble is the one which does not travel as far up the chromatogram ...
UILChemistryProblemsPart2
... No matter what the starting concentrations, at equilibrium the mass action expression is always equal to a certain number, the equilibrium constant (Kc) for that reaction at a specified temp. (known as equilibrium law for that reaction.) The reaction quotient (Q) is also equal to the value of the ma ...
... No matter what the starting concentrations, at equilibrium the mass action expression is always equal to a certain number, the equilibrium constant (Kc) for that reaction at a specified temp. (known as equilibrium law for that reaction.) The reaction quotient (Q) is also equal to the value of the ma ...
4.1 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Singlet Oxygen Production by Soybean Lipoxygenase Isozymes”
... Baker Superoxol) was assayed using the method of Cotton and Dunford (22). All other inorganic chemicals as well as the acetone and ethanol were reagent grade. Water was glass-distilled. Experimental Conditions-Most experiments were done in buffers made with deuterium oxide which enhanced the emissio ...
... Baker Superoxol) was assayed using the method of Cotton and Dunford (22). All other inorganic chemicals as well as the acetone and ethanol were reagent grade. Water was glass-distilled. Experimental Conditions-Most experiments were done in buffers made with deuterium oxide which enhanced the emissio ...
AP Chemistry - West Bloomfield School District
... In a certain experiment, 6.00 g of aluminum is burned in 24.0 g of bromine. What is the maximum amount of aluminum bromide that can be produced? 67. Acid-base neutralization reactions are very common in industrial processes. This is the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide: H2SO4 (aq) + 2 ...
... In a certain experiment, 6.00 g of aluminum is burned in 24.0 g of bromine. What is the maximum amount of aluminum bromide that can be produced? 67. Acid-base neutralization reactions are very common in industrial processes. This is the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide: H2SO4 (aq) + 2 ...
Lab Manual Quantitative Analytical Method
... 4. Burette for the NaOH Clean, rinse well (with deionized water), and dry three 125-mL or 250-mL conical flasks. Measure between 0.20 – 0.25 g of potassium hydrogen phthalate into each. conical flask. Record Clean, rinse well (with deionized water), and dry three 125-mL or 250-mL Conical flasks. Mea ...
... 4. Burette for the NaOH Clean, rinse well (with deionized water), and dry three 125-mL or 250-mL conical flasks. Measure between 0.20 – 0.25 g of potassium hydrogen phthalate into each. conical flask. Record Clean, rinse well (with deionized water), and dry three 125-mL or 250-mL Conical flasks. Mea ...
AP Chemistry Review Preparing for the AP
... Focus on your weakest areas; it is doubtful you can do/know everything. The AP Chemistry Exam is designed so that it is impossible to know absolutely everything on it (in case you haven’t noticed). Review your incorrect MC from the Practice Exam and understand the concepts. Know the 6 strong acids H ...
... Focus on your weakest areas; it is doubtful you can do/know everything. The AP Chemistry Exam is designed so that it is impossible to know absolutely everything on it (in case you haven’t noticed). Review your incorrect MC from the Practice Exam and understand the concepts. Know the 6 strong acids H ...
Identification of Aspartic and Isoaspartic Acid Residues in Amyloid β
... Asp isomerization;32,33 however, this can only be applied to detection of modification sites in the protein, but not to identify modifications already existing in biological samples prior the analysis. In addition, Alfaro et al. recently introduced a new method for the affinity enrichment of isoaspa ...
... Asp isomerization;32,33 however, this can only be applied to detection of modification sites in the protein, but not to identify modifications already existing in biological samples prior the analysis. In addition, Alfaro et al. recently introduced a new method for the affinity enrichment of isoaspa ...
the chemistry of life: organic and biological chemistry
... atoms per carbon atom, they are called saturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes, also known as olefins, are hydrocarbons that contain at least one C=C double bond, as in ethylene (C 2H 4 ). Alkynes contain at least one C==C triple bond, as in acetylene (C 2H 2). In aromatic hydrocarbons the carbon atoms are ...
... atoms per carbon atom, they are called saturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes, also known as olefins, are hydrocarbons that contain at least one C=C double bond, as in ethylene (C 2H 4 ). Alkynes contain at least one C==C triple bond, as in acetylene (C 2H 2). In aromatic hydrocarbons the carbon atoms are ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylation of r
... an asymmetric catalyst, see: Kruger, J.; Carreira, E. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 837. Chiral Cu(I)-based bisimine and bisoxazoline complexes are effective catalysts for asymmetric cyclopropanation and aziridination reactions, see, for cyclopropanation: (a) Doyle, M. P. Recl. TraV. Chim. Pays-Ba ...
... an asymmetric catalyst, see: Kruger, J.; Carreira, E. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 837. Chiral Cu(I)-based bisimine and bisoxazoline complexes are effective catalysts for asymmetric cyclopropanation and aziridination reactions, see, for cyclopropanation: (a) Doyle, M. P. Recl. TraV. Chim. Pays-Ba ...
National 5 - Deans Community High School
... Copy the graph showing reaction A and add the corresponding curves which could have been obtained for experiments B, C and D. (Label each curve clearly.) 18. The collision theory states that for two molecules to react, they must first collide with one another. Use the collision theory to explain the ...
... Copy the graph showing reaction A and add the corresponding curves which could have been obtained for experiments B, C and D. (Label each curve clearly.) 18. The collision theory states that for two molecules to react, they must first collide with one another. Use the collision theory to explain the ...
Lab 1
... All Calculators have different key setups ….so you will have to figure out where you SCIENTIFIC NOTATION button is on your calculator. Locate ONE of the following scientific notation buttons on your calculator (it may not even be listed here): ...
... All Calculators have different key setups ….so you will have to figure out where you SCIENTIFIC NOTATION button is on your calculator. Locate ONE of the following scientific notation buttons on your calculator (it may not even be listed here): ...
Synthesis of esterified solid fat from fractionated
... esters (FAME), F-07, was acquired from Larodan Fine Chemicals AB (Malmö, Sweden). All the other chemicals and solvents came from VWR (Stockholm, Sweden), unless otherwise stated. Fractionation of RSO RSO and acetone were mixed together at a ratio of 1:5 (v/v) in a conical flask. The conical flask wa ...
... esters (FAME), F-07, was acquired from Larodan Fine Chemicals AB (Malmö, Sweden). All the other chemicals and solvents came from VWR (Stockholm, Sweden), unless otherwise stated. Fractionation of RSO RSO and acetone were mixed together at a ratio of 1:5 (v/v) in a conical flask. The conical flask wa ...
Experiment 1 - Melting Points - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... to overcome the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, and Hbonding) that confine them to the solid state. The determination of melting points is particularly important to organic chemists, since they often work with solid molecular compounds that have low melting points (below ...
... to overcome the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, and Hbonding) that confine them to the solid state. The determination of melting points is particularly important to organic chemists, since they often work with solid molecular compounds that have low melting points (below ...
Praktikum in Allgemeiner Chemie für Biologen und Pharmazeuten
... equipped with a fireproof glass plate while test tubes can be exposed directly to the flame. In order to avoid sudden eruptions of liquid during the heating of solutions in large vessels boiling aids must be added. Test tubes are held in a wooden clamp and the flame is applied just below the liquid ...
... equipped with a fireproof glass plate while test tubes can be exposed directly to the flame. In order to avoid sudden eruptions of liquid during the heating of solutions in large vessels boiling aids must be added. Test tubes are held in a wooden clamp and the flame is applied just below the liquid ...
synthesis-structure relationship in the aqueous ethylene glycol
... shows a remarkable stability, due to the very strong hydrogen bonds between adjacent layers, therefore it is practically insoluble in water and in common organic solvents. In pure state, its composition does not alter with time and it can only be destructurated in a strongly acidic medium or by trea ...
... shows a remarkable stability, due to the very strong hydrogen bonds between adjacent layers, therefore it is practically insoluble in water and in common organic solvents. In pure state, its composition does not alter with time and it can only be destructurated in a strongly acidic medium or by trea ...
Lab 1
... Some metals such as sodium or calcium may have a white coating of oxide formed by reacting with oxygen in the air. If these are cut, you can see the fresh shiny metal underneath. In contrast, nonmetals are not good conductors of heat and electricity, are brittle (not ductile), and appear dull, not s ...
... Some metals such as sodium or calcium may have a white coating of oxide formed by reacting with oxygen in the air. If these are cut, you can see the fresh shiny metal underneath. In contrast, nonmetals are not good conductors of heat and electricity, are brittle (not ductile), and appear dull, not s ...
Synthesis of monoselenanedisulfanediphosphonate by the reaction
... (10 mmol) of ascorbic acid in 75 ml of water; then a solution of potassium dihydrogenmonothiophosphate, KH2PO3S, prepared by dissolution of 3.04 g (20 mmol) of KH2PO3S in 75 ml of water was added into it. The solution (2) was slowly added to the solution (1), and a clear yellowish-green solution of ...
... (10 mmol) of ascorbic acid in 75 ml of water; then a solution of potassium dihydrogenmonothiophosphate, KH2PO3S, prepared by dissolution of 3.04 g (20 mmol) of KH2PO3S in 75 ml of water was added into it. The solution (2) was slowly added to the solution (1), and a clear yellowish-green solution of ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.