CHAPTER 16 TEST REVIEW 1. The achievements of the early
... CHAPTER 16 TEST REVIEW 1. The achievements of the early Middle Ages included; a restoration of political order through a feudal system, economic recovery, the creation of an institutional framework for the Christian church based in Rome 2. Roman imperial power ended in 476 C.E. with the invasion of ...
... CHAPTER 16 TEST REVIEW 1. The achievements of the early Middle Ages included; a restoration of political order through a feudal system, economic recovery, the creation of an institutional framework for the Christian church based in Rome 2. Roman imperial power ended in 476 C.E. with the invasion of ...
Early Middle Ages
... Pope Gregory the Great Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages Charles Martel – “The ...
... Pope Gregory the Great Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages Charles Martel – “The ...
WORLD HISTORY (Pt1) SOL Review Packet
... were the most important rivers in the Indian sub-continent. 3. The early Indians, or Aryans, developed a system that shaped and dictated social classes. 4. The “golden age” of classical India was under the empire. 5. Buddha means the “_______________________________________________________ “. 6. Bud ...
... were the most important rivers in the Indian sub-continent. 3. The early Indians, or Aryans, developed a system that shaped and dictated social classes. 4. The “golden age” of classical India was under the empire. 5. Buddha means the “_______________________________________________________ “. 6. Bud ...
unit2test
... e) Fear of the spread of the plague to China 18. Which of the following languages came into existence after 1000 as the direct result of expanding global trade patterns? a) Arabic b) Chinese c) Latin d) Sanskrit e) Swahili 19. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the Mongol Empire? ...
... e) Fear of the spread of the plague to China 18. Which of the following languages came into existence after 1000 as the direct result of expanding global trade patterns? a) Arabic b) Chinese c) Latin d) Sanskrit e) Swahili 19. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the Mongol Empire? ...
13.1 Rise of the Franks-teacher version
... Middle Ages-medieval period, time period between the classical period and the modern era. 400-1500 ...
... Middle Ages-medieval period, time period between the classical period and the modern era. 400-1500 ...
Europe during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance
... First crusade was a success for the Christian knights by 1099 in one of the bloodiest examples in military history, butchering every Muslim and Jew within the city walls. Lack of unity amongst the Turks, Arabs, and Muslims contributed to their defeat. ...
... First crusade was a success for the Christian knights by 1099 in one of the bloodiest examples in military history, butchering every Muslim and Jew within the city walls. Lack of unity amongst the Turks, Arabs, and Muslims contributed to their defeat. ...
Europe during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance
... First crusade was a success for the Christian knights by 1099 in one of the bloodiest examples in military history, butchering every Muslim and Jew within the city walls. Lack of unity amongst the Turks, Arabs, and Muslims contributed to their defeat. ...
... First crusade was a success for the Christian knights by 1099 in one of the bloodiest examples in military history, butchering every Muslim and Jew within the city walls. Lack of unity amongst the Turks, Arabs, and Muslims contributed to their defeat. ...
MIDDLE AGES
... Over a century before the final end of the Western Roman Empire barbarian tribes were already both attacking and, as Roman soldiers, defending the Roman Empire. Many Germanic tribal chiefs rose to high ranks in the Roman Army – eg. Vandal general Stilicho defeated a Visigoth army under Alerich advan ...
... Over a century before the final end of the Western Roman Empire barbarian tribes were already both attacking and, as Roman soldiers, defending the Roman Empire. Many Germanic tribal chiefs rose to high ranks in the Roman Army – eg. Vandal general Stilicho defeated a Visigoth army under Alerich advan ...
Unit 1
... Old Kingdom (2700–2200B.C.) – Egypt ruled by god-like pharaohs with absolute power! • Great Pyramids of Giza buried Pharaohs, showed absolute power of royal families (started by Pharaoh Khufu) mummification – preserving the body through drying methods and removing internal organs ...
... Old Kingdom (2700–2200B.C.) – Egypt ruled by god-like pharaohs with absolute power! • Great Pyramids of Giza buried Pharaohs, showed absolute power of royal families (started by Pharaoh Khufu) mummification – preserving the body through drying methods and removing internal organs ...
WHI.8 Byzantine Empire and Russia packet
... Research and fill in the chart below to show the differences and ...
... Research and fill in the chart below to show the differences and ...
Slide 1
... Early Middle Ages: 500 – 1000 High Middle Ages: 1000 – 1250 Late Middle Ages: 1250 - 1500 •Western Europe not as commercially or culturally developed as the great world civilizations ...
... Early Middle Ages: 500 – 1000 High Middle Ages: 1000 – 1250 Late Middle Ages: 1250 - 1500 •Western Europe not as commercially or culturally developed as the great world civilizations ...
Chapter 7.1 ppt
... • Expand their empire from Palestine to N. Africa to Spain • Charles Martel defeats Muslims at Battle of Tours in 732 (see map p. 215) ...
... • Expand their empire from Palestine to N. Africa to Spain • Charles Martel defeats Muslims at Battle of Tours in 732 (see map p. 215) ...
Unit 2 How did the Fall of Rome lead to the Rise of the Byzantines in
... help in defeating the Seljuk Turks. Pope Urban II called upon the Kings of Europe for an armed “pilgrimage” to recover Jerusalem from the Muslims. Among his goals was the strengthening of the Pope’s power by bringing the Greek Orthodox Church under papal authority. (Crusaders would get a “Sin Wash”) ...
... help in defeating the Seljuk Turks. Pope Urban II called upon the Kings of Europe for an armed “pilgrimage” to recover Jerusalem from the Muslims. Among his goals was the strengthening of the Pope’s power by bringing the Greek Orthodox Church under papal authority. (Crusaders would get a “Sin Wash”) ...
Viking Invasions and the Rise of Feudalism
... The Church takes Control Takes power from the weak governments in Europe The Church was also a unifying bond between the different social classes in Europe The Church used fear (Threat of Excommunication) to force people to follow ...
... The Church takes Control Takes power from the weak governments in Europe The Church was also a unifying bond between the different social classes in Europe The Church used fear (Threat of Excommunication) to force people to follow ...
Political
... continuation of the Roman Empire. At this empire’s greatest size, it included parts of southern and eastern Europe, northern Africa, and the Middle East. The Byzantine people spoke Greek. Greek culture continued to influence this region. It was Constantine, the Roman Emperor, who moved the capital t ...
... continuation of the Roman Empire. At this empire’s greatest size, it included parts of southern and eastern Europe, northern Africa, and the Middle East. The Byzantine people spoke Greek. Greek culture continued to influence this region. It was Constantine, the Roman Emperor, who moved the capital t ...
Middle Ages - Cloudfront.net
... A Test for the Church •Church inspiration brought a renewal of faith and zeal. •Calls came from around Europe for the Church’s influence and strength. •The most important was a Crusade, or holy war. Pope Urban II received a letter asking for help in reclaiming the Holy Land of Jerusalem from the Mu ...
... A Test for the Church •Church inspiration brought a renewal of faith and zeal. •Calls came from around Europe for the Church’s influence and strength. •The most important was a Crusade, or holy war. Pope Urban II received a letter asking for help in reclaiming the Holy Land of Jerusalem from the Mu ...
World History Final Review --- George The following questions are
... World History Final Review --- George The following questions are in the writing section of the final: these will need to be answered in 1-2 paragraphs each (4-6 sentences per paragraph) The questions are in the order and they come from Chapter 13-24 1. What were the key webs or networks of influenc ...
... World History Final Review --- George The following questions are in the writing section of the final: these will need to be answered in 1-2 paragraphs each (4-6 sentences per paragraph) The questions are in the order and they come from Chapter 13-24 1. What were the key webs or networks of influenc ...
Introduction to Medieval European History
... • *Hollister, Medieval Europe • *Strayer, Joseph. On the Medieval Origins of the Modern State • Magna Carta in England, 1215 --Parliament --- constitutional monarchy • The rise of University: Paris, Oxford, Cambridge, etc. • [Baldwin, John W. The Scholastic Culture of the Middle Ages, 10001300] ...
... • *Hollister, Medieval Europe • *Strayer, Joseph. On the Medieval Origins of the Modern State • Magna Carta in England, 1215 --Parliament --- constitutional monarchy • The rise of University: Paris, Oxford, Cambridge, etc. • [Baldwin, John W. The Scholastic Culture of the Middle Ages, 10001300] ...
Introduction to Medieval European History
... • Hollister, Medieval Europe • Strayer, Joseph. On the Medieval Origins of the Modern State • (Magna Carta in England, 1215 --Parliament --- constitutional monarchy) • (The rise of University: Paris, Oxford, Cambridge, etc.) • [Baldwin, John W. The Scholastic Culture of the Middle Ages, 10001300] ...
... • Hollister, Medieval Europe • Strayer, Joseph. On the Medieval Origins of the Modern State • (Magna Carta in England, 1215 --Parliament --- constitutional monarchy) • (The rise of University: Paris, Oxford, Cambridge, etc.) • [Baldwin, John W. The Scholastic Culture of the Middle Ages, 10001300] ...
The Middle Ages
... • Emperor Justinian (A.D. 527 – 565) developed set of laws called Justinian Code • Justinian Code later became basis for most European law • Justinian Code also basis for Quebec’s legal system ...
... • Emperor Justinian (A.D. 527 – 565) developed set of laws called Justinian Code • Justinian Code later became basis for most European law • Justinian Code also basis for Quebec’s legal system ...
File
... secured the relationship between Frankish kings and the papacy • Charlemagne became the first ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, a dynasty that would last for more than 700 years • Charlemagne- imposed order on empire through the Church and state • Ordered the standardization of Latin, textbooks, manua ...
... secured the relationship between Frankish kings and the papacy • Charlemagne became the first ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, a dynasty that would last for more than 700 years • Charlemagne- imposed order on empire through the Church and state • Ordered the standardization of Latin, textbooks, manua ...
Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms
... office) beyond its spiritual role Made the Church a secular power Pope’s palace became center of Roman government Used church revenue to raise armies, repair roads, and help the poor Negotiated treaties with invaders Region from Italy to England and Spain to Germany fell under his responsibility ...
... office) beyond its spiritual role Made the Church a secular power Pope’s palace became center of Roman government Used church revenue to raise armies, repair roads, and help the poor Negotiated treaties with invaders Region from Italy to England and Spain to Germany fell under his responsibility ...
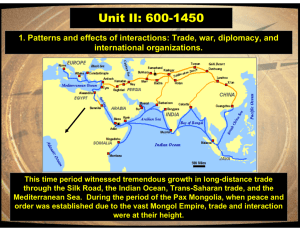
Unit II: 600-1450 international organizations.
... 2. The dynamics of change and continuity across world history Major changes: Classical empires fall leaving behind new political units of organization such as feudalism, religious empires, and other decentralized states. Nomadic migrations of Turks and Mongols caused major changes throughout the wor ...
... 2. The dynamics of change and continuity across world history Major changes: Classical empires fall leaving behind new political units of organization such as feudalism, religious empires, and other decentralized states. Nomadic migrations of Turks and Mongols caused major changes throughout the wor ...
Dancing in the Dark Ages (Middle Age Europe)
... Lets Be Frank, (The Franks are the Strongest Barbarians) • The Franks were farmers than lived in small communities in Northern Europe • In 486 King Clovis of the Franks conquered Gaul • Clovis preserved many Roman customs, one was the Latin language. • Clovis Converted to Christianity and the Frank ...
... Lets Be Frank, (The Franks are the Strongest Barbarians) • The Franks were farmers than lived in small communities in Northern Europe • In 486 King Clovis of the Franks conquered Gaul • Clovis preserved many Roman customs, one was the Latin language. • Clovis Converted to Christianity and the Frank ...
The Spread of Christianity, AD 400-750
... 1. The colony of Byzantium, which was to become the site of Constantinople, was established by the Greek city of Megara in the seventh century B.C. It was located on a triangular peninsula on the European side of the Sea of Marmara at the western end of the seventeen mile Bosphorus Strait. Adjacent ...
... 1. The colony of Byzantium, which was to become the site of Constantinople, was established by the Greek city of Megara in the seventh century B.C. It was located on a triangular peninsula on the European side of the Sea of Marmara at the western end of the seventeen mile Bosphorus Strait. Adjacent ...
Post-classical history

Post-classical history (also called the Postclassical Era) is the period of time that immediately followed ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200-600 and AD 1200–1500. The major classical civilizations the era follows are Han China (ending in 220), the Western Roman Empire (in 476), the Gupta Empire (in the 550s), and the Sasanian Empire (in 651). The post-classical era itself was followed by the early modern era, and forms the middle period in a three-period division of world history: ancient, post-classical, and modern. The era is thought to be characterized by invasions from Central Asia, the development of the great world religions (Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism), and of networks of trade and military contact between civilizations.The name of this era of history derives from classical antiquity (or the Greco-Roman era) of Europe. In European history, ""post-classical"" is synonymous with the medieval time or Middle Ages, the period of history from around the 5th century to the 15th century. In Europe, the fall of the Western Roman Empire saw the depopulation, deurbanization, and limited learning of the ""Dark Ages"" (except in Eastern Mediterranean Europe, where the Eastern Roman Empire flourished until 1204), but gradually revived somewhat under the institutions of feudalism and a powerful Catholic Church. Art and architecture were characterized by Christian themes. Several attempts by the Crusades to recapture the Holy Land for Christianity were unsuccessful.In Asia, the depredations of the Dark Ages were avoided, at least in the west, where the Spread of Islam created a new empire and civilization with trade between the Asian, African, and European continents, and advances in science. East Asia experienced the full establishment of power of Imperial China (after the interregnum chaos of the Six Dynasties), which established several prosperous dynasties influencing Korea, Vietnam, and Japan. Religions such as Buddhism and Neo-Confucianism spread. Gunpowder was originally developed in China during the post-classical era. The invention of gunpowder led to the invention of fireworks, then to its use in warfare. Also, the invention spread around the world. The Mongol Empire greatly affected much of Europe and Asia, the latter of which was conquered in many areas. The Mongols were able to create safe trade and stability between the two regions, but inadvertently encouraged the spread of the Black Plague.The timelines of the major civilizations of the Americas—Maya (AD 250 to 900), the Aztec (14th to 16th centuries), and the Inca (1438 to 1533)—do not correspond closely to the Classical Age of the Old World.Outstanding cultural achievement in the post-classical era include books like the Code of Justinian,The Story of the Western Wing, and The Tale of Genji; the mathematics of Fibonacci, Oresme, and Al-Khwārizmī; the philosophy of Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas, Petrarch, Zhu Xi, and Kabir; the painting of Giotto, Behzād, and Dong Yuan; the astronomy of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi and Su Song; the poetry of Rumi, Dante, Chaucer, and the Li Bai; the travels of Marco Polo and Ibn Battuta; the historiography of Leonardo Bruni and Ibn Khaldun; and the architecture of places like Chartres, the Mezquita, Angkor Wat, and Machu Picchu.