600 C.E.–1450
... 4. Personal ambitions – gain wealth and land 5. Racial and religious prejudice a. Period of stability after 1000 CE led to increased trade/higher agricultural output 1. Population boom tripled number b. Pope encouraged military expeditions to reclaim Holy Land 1. 1059-1212 – take control from Muslim ...
... 4. Personal ambitions – gain wealth and land 5. Racial and religious prejudice a. Period of stability after 1000 CE led to increased trade/higher agricultural output 1. Population boom tripled number b. Pope encouraged military expeditions to reclaim Holy Land 1. 1059-1212 – take control from Muslim ...
The Barbarian Invasions
... The fall of the Roman Empire is traditionally believed to have started in the 5th century. The beginning of the fall was started by the tribes of Huns united under Attila the Hun. They migrated from the plains of Asia in the east pushing the Germanic tribe, the Visigoths, into violating Roman territ ...
... The fall of the Roman Empire is traditionally believed to have started in the 5th century. The beginning of the fall was started by the tribes of Huns united under Attila the Hun. They migrated from the plains of Asia in the east pushing the Germanic tribe, the Visigoths, into violating Roman territ ...
The Post Classical Era 500 * 1000 AD
... –Created large empire made of self-sufficient manors –Counts kept order in his kingdom –Made Aachen a new center for learning • Division of Frankish Kingdom –Kingdom divided into three parts after Charlemagne’s death –Division weakened Empire’s unity and caused the collapse of the Frankish Kingdom ...
... –Created large empire made of self-sufficient manors –Counts kept order in his kingdom –Made Aachen a new center for learning • Division of Frankish Kingdom –Kingdom divided into three parts after Charlemagne’s death –Division weakened Empire’s unity and caused the collapse of the Frankish Kingdom ...
1 - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 4. Personal ambitions – gain wealth and land 5. Racial and religious prejudice a. Period of stability after 1000 CE led to increased trade/higher agricultural output 1. Population boom tripled number b. Pope encouraged military expeditions to reclaim Holy Land 1. 1059-1212 – take control from Muslim ...
... 4. Personal ambitions – gain wealth and land 5. Racial and religious prejudice a. Period of stability after 1000 CE led to increased trade/higher agricultural output 1. Population boom tripled number b. Pope encouraged military expeditions to reclaim Holy Land 1. 1059-1212 – take control from Muslim ...
Exploration
... Columbian Exchange • European conquest of the new world brought changes on both sides • Movement of goods and ideas from each side is called the Columbian Exchange. • Watch the video and complete the Chart. ...
... Columbian Exchange • European conquest of the new world brought changes on both sides • Movement of goods and ideas from each side is called the Columbian Exchange. • Watch the video and complete the Chart. ...
Chapter 8 The Middle Ages in Europe
... • Byzantine Empire merged with Constantinople, lasting 1K years—Emperor Justinian used Roman laws to create new legal code • After fall of Roman Empire, Europe fell into period of chaos know as the Dark Ages—invaders kept cities in chaos—cities became ruined and weak—the learning of the ancient worl ...
... • Byzantine Empire merged with Constantinople, lasting 1K years—Emperor Justinian used Roman laws to create new legal code • After fall of Roman Empire, Europe fell into period of chaos know as the Dark Ages—invaders kept cities in chaos—cities became ruined and weak—the learning of the ancient worl ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... 42. Describe trade and trading cities of the West African kingdoms. 43. What religions influenced Japan? 44. Identify the Japanese archipelago? 45. Describe the geography, religions, economies, and representative cities of the Mayan, Aztec, and Incan ...
... 42. Describe trade and trading cities of the West African kingdoms. 43. What religions influenced Japan? 44. Identify the Japanese archipelago? 45. Describe the geography, religions, economies, and representative cities of the Mayan, Aztec, and Incan ...
TCI Chap 2-Guided Reading Answer Key
... 1. What led to the success of the Franks after the fall of the Roman Empire? The Franks were successful because they had developed a new style of warfare- knights were heavily armed and fought on horseback. 2. How did Clovis bring unity to the empire? Clovis was baptized a Christian and Christianity ...
... 1. What led to the success of the Franks after the fall of the Roman Empire? The Franks were successful because they had developed a new style of warfare- knights were heavily armed and fought on horseback. 2. How did Clovis bring unity to the empire? Clovis was baptized a Christian and Christianity ...
Chapter 9 PP: Feudal Europe - Auburndale High School AP World
... – Seljuk Turks defeated Byzantines making pilgrimages difficult ...
... – Seljuk Turks defeated Byzantines making pilgrimages difficult ...
Period 3: Regional and Transregional Interactions, c. 600 C.E. to c
... Griots: Professional oral historians who served as keepers of traditions and advisors to kings. Timbuktu: Niger River port city of Mali; had a famous Muslim university. Songhay: Successor state to Mali; dominated middle reaches of the Niger valley; capital at Gao. Ibn Batuta: Muslim traveler who des ...
... Griots: Professional oral historians who served as keepers of traditions and advisors to kings. Timbuktu: Niger River port city of Mali; had a famous Muslim university. Songhay: Successor state to Mali; dominated middle reaches of the Niger valley; capital at Gao. Ibn Batuta: Muslim traveler who des ...
chapter 11 updated notes
... Territories began breaking off and becoming independent so caliphs attempted to curtail this problem But they could not and now other families were plotting to replace the Abbaids In 945 the armies of one of the regional dynasties, the Buyids of Persia attacked and captured Baghdad. The caliphs were ...
... Territories began breaking off and becoming independent so caliphs attempted to curtail this problem But they could not and now other families were plotting to replace the Abbaids In 945 the armies of one of the regional dynasties, the Buyids of Persia attacked and captured Baghdad. The caliphs were ...
The Middle Ages - Ms-Ball-NEHS
... • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
... • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
Unit II: 600-1450 - Spokane Public Schools
... Roman Catholic Church only became a powerful institution due to the lack of a centralized authority that could protect the people. The Truce of God in 1083 (Doc. 5) does display the influence of the Church but does more to show the horrors that occurred on a daily basis. Murder, arson, robbery, assa ...
... Roman Catholic Church only became a powerful institution due to the lack of a centralized authority that could protect the people. The Truce of God in 1083 (Doc. 5) does display the influence of the Church but does more to show the horrors that occurred on a daily basis. Murder, arson, robbery, assa ...
Capital = Constantinople • Continued as the New ROME • Kings saw
... Question. What is a dynasty? C. Umayyad Dynasty – ruling family that created an Islamic Empire 1. Spread Islam 2. Caused a schism (split) in Islam. 3. Religious Sect: separate part of one religion 4. Two Sects in Islam a) Sunni- those who believe any devout (religious) Muslim could be caliph b) Shii ...
... Question. What is a dynasty? C. Umayyad Dynasty – ruling family that created an Islamic Empire 1. Spread Islam 2. Caused a schism (split) in Islam. 3. Religious Sect: separate part of one religion 4. Two Sects in Islam a) Sunni- those who believe any devout (religious) Muslim could be caliph b) Shii ...
Middle Ages, Medieval Times, Dark Ages: What`s the Difference
... following the fall of the Roman Empire called the Dark ages? ...
... following the fall of the Roman Empire called the Dark ages? ...
1 The Barbarian Invasions Remember, in 375 A.D., the Roman
... eastern areas. He and his followers preferred a more Greek way of life and a more Greek view of Christianity, so he renamed the eastern empire: the Byzantine Empire. Eastern Orthodox Christians did not answer to the Pope in the western area. (map 6). After the Great Schism, nearly all ties between t ...
... eastern areas. He and his followers preferred a more Greek way of life and a more Greek view of Christianity, so he renamed the eastern empire: the Byzantine Empire. Eastern Orthodox Christians did not answer to the Pope in the western area. (map 6). After the Great Schism, nearly all ties between t ...
franks__feudalism_best
... Clovis’s conquests • by 511 AD—united all of the Franks into one kingdom • two forces were now allied 1. Military (Franks) 2. Spiritual (Church) ...
... Clovis’s conquests • by 511 AD—united all of the Franks into one kingdom • two forces were now allied 1. Military (Franks) 2. Spiritual (Church) ...
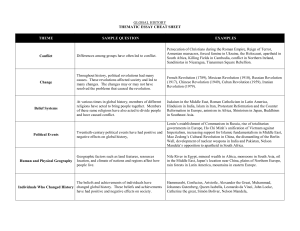
Thematic Essay Cheat Sheet
... Turning points are major events in history that have led to lasting change. ...
... Turning points are major events in history that have led to lasting change. ...
Humanity 238 - WordPress.com
... Germanic kingdoms. He conquered new lands to both the south and the east. Through these conquests, Charlemagne spread Christianity. He reunited western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire. By 800, Charlemagne’s empire was larger than the Byzantine Empire. He had become the most powerful ...
... Germanic kingdoms. He conquered new lands to both the south and the east. Through these conquests, Charlemagne spread Christianity. He reunited western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire. By 800, Charlemagne’s empire was larger than the Byzantine Empire. He had become the most powerful ...
Answers and Explanations
... ) Answers and Explanations 1. B-Feudalism in Western Europe was based on a reciprocal, or mutual relationship of responsibility between lord and vassal, whereas Japanese feudalism exacted obedience from the samurai regardless of the responsibility of the daimyo. European chivalry was binding to the ...
... ) Answers and Explanations 1. B-Feudalism in Western Europe was based on a reciprocal, or mutual relationship of responsibility between lord and vassal, whereas Japanese feudalism exacted obedience from the samurai regardless of the responsibility of the daimyo. European chivalry was binding to the ...
the mongol empire in world history
... The book’s objective is to facilitate a more nuanced student understanding of this great empire. This volume addresses expected elements in empire-building while including information on the complexities of these elements. For example, as expected, the role of political intrigue and competition for ...
... The book’s objective is to facilitate a more nuanced student understanding of this great empire. This volume addresses expected elements in empire-building while including information on the complexities of these elements. For example, as expected, the role of political intrigue and competition for ...
WHAP - Maritime Revolution
... Negotiated by pope Splits Atlantic Ocean with imaginary line Americas = Spain Africa & S Asia = Portugal ...
... Negotiated by pope Splits Atlantic Ocean with imaginary line Americas = Spain Africa & S Asia = Portugal ...
The Middle Ages - Class Notes For Mr. Pantano
... land we now call France. Known as “Charlemagne” (means Charles the Great) His mission was to create a Christian empire. ...
... land we now call France. Known as “Charlemagne” (means Charles the Great) His mission was to create a Christian empire. ...
Post-classical history

Post-classical history (also called the Postclassical Era) is the period of time that immediately followed ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200-600 and AD 1200–1500. The major classical civilizations the era follows are Han China (ending in 220), the Western Roman Empire (in 476), the Gupta Empire (in the 550s), and the Sasanian Empire (in 651). The post-classical era itself was followed by the early modern era, and forms the middle period in a three-period division of world history: ancient, post-classical, and modern. The era is thought to be characterized by invasions from Central Asia, the development of the great world religions (Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism), and of networks of trade and military contact between civilizations.The name of this era of history derives from classical antiquity (or the Greco-Roman era) of Europe. In European history, ""post-classical"" is synonymous with the medieval time or Middle Ages, the period of history from around the 5th century to the 15th century. In Europe, the fall of the Western Roman Empire saw the depopulation, deurbanization, and limited learning of the ""Dark Ages"" (except in Eastern Mediterranean Europe, where the Eastern Roman Empire flourished until 1204), but gradually revived somewhat under the institutions of feudalism and a powerful Catholic Church. Art and architecture were characterized by Christian themes. Several attempts by the Crusades to recapture the Holy Land for Christianity were unsuccessful.In Asia, the depredations of the Dark Ages were avoided, at least in the west, where the Spread of Islam created a new empire and civilization with trade between the Asian, African, and European continents, and advances in science. East Asia experienced the full establishment of power of Imperial China (after the interregnum chaos of the Six Dynasties), which established several prosperous dynasties influencing Korea, Vietnam, and Japan. Religions such as Buddhism and Neo-Confucianism spread. Gunpowder was originally developed in China during the post-classical era. The invention of gunpowder led to the invention of fireworks, then to its use in warfare. Also, the invention spread around the world. The Mongol Empire greatly affected much of Europe and Asia, the latter of which was conquered in many areas. The Mongols were able to create safe trade and stability between the two regions, but inadvertently encouraged the spread of the Black Plague.The timelines of the major civilizations of the Americas—Maya (AD 250 to 900), the Aztec (14th to 16th centuries), and the Inca (1438 to 1533)—do not correspond closely to the Classical Age of the Old World.Outstanding cultural achievement in the post-classical era include books like the Code of Justinian,The Story of the Western Wing, and The Tale of Genji; the mathematics of Fibonacci, Oresme, and Al-Khwārizmī; the philosophy of Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas, Petrarch, Zhu Xi, and Kabir; the painting of Giotto, Behzād, and Dong Yuan; the astronomy of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi and Su Song; the poetry of Rumi, Dante, Chaucer, and the Li Bai; the travels of Marco Polo and Ibn Battuta; the historiography of Leonardo Bruni and Ibn Khaldun; and the architecture of places like Chartres, the Mezquita, Angkor Wat, and Machu Picchu.