Biology Chp 1 Notes (The Science of Life)
... a. Cell Division: the formation of two new cells from one existing cell 1. all living things grow this way b. Development: the process by which an organism becomes a mature adult 1. achieved by cell division and differentiation 2. an adult organism is composed of many different cells 6. Reproductio ...
... a. Cell Division: the formation of two new cells from one existing cell 1. all living things grow this way b. Development: the process by which an organism becomes a mature adult 1. achieved by cell division and differentiation 2. an adult organism is composed of many different cells 6. Reproductio ...
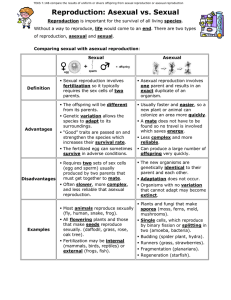
MYP Biology Year 11 Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Name:
... .A sea anemone can split down the middle and ...
... .A sea anemone can split down the middle and ...
Animal Body Systems
... activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. ...
... activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. ...
Animal Body Systems
... activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. ...
... activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. ...
Biology Study Guide 2nd Semester Exam
... 18. In angiosperms, reproduction takes place in _______________. 19. In an angiosperm, pollen grains are produced in the _______________. (Chapter 24) 20. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have ______________________________. 21. What is the difference between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryot ...
... 18. In angiosperms, reproduction takes place in _______________. 19. In an angiosperm, pollen grains are produced in the _______________. (Chapter 24) 20. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have ______________________________. 21. What is the difference between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryot ...
Lecture 19
... – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
... – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
Animal Reproduction - Bio-Guru
... Due to the special environment where an egg can develop, it only takes place in moist environments. ...
... Due to the special environment where an egg can develop, it only takes place in moist environments. ...
big
... – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
... – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... Most animals reproduce sexually (fly, human, snake, frog). All flowering plants and those that make seeds reproduce sexually. (daffodil, grass, rose, oak tree). Fertilization may be internal (mammals, birds, reptiles) or external (frogs, fish). ...
... Most animals reproduce sexually (fly, human, snake, frog). All flowering plants and those that make seeds reproduce sexually. (daffodil, grass, rose, oak tree). Fertilization may be internal (mammals, birds, reptiles) or external (frogs, fish). ...
Animal Body Systems
... activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. ...
... activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. ...
organisms - Lyndhurst Schools
... Smallest unit capable of all life functions Unicellular Organisms Entire organism is made up of one single cell Example:Bacteria and protists ...
... Smallest unit capable of all life functions Unicellular Organisms Entire organism is made up of one single cell Example:Bacteria and protists ...
Biology 2nd QTR EQT Review To which group does an organism
... d. keeping warm with thick fur Which characteristic is used to place the shark and the moray 15. Study the two animals eel into two different taxonomic classes? below. ...
... d. keeping warm with thick fur Which characteristic is used to place the shark and the moray 15. Study the two animals eel into two different taxonomic classes? below. ...
Reproduction
... Reproduction – the process of living things producing the same type of living thing. Examples – horses produce horses, humans produce humans, and tomato plants produce tomatoes. * Like produces like. There are two types of reproduction: asexual and sexual ...
... Reproduction – the process of living things producing the same type of living thing. Examples – horses produce horses, humans produce humans, and tomato plants produce tomatoes. * Like produces like. There are two types of reproduction: asexual and sexual ...
Types of Animals
... 6. Excretion - the removal of wastes from the body a. Diffusion can release wastes in simple aquatic animals b. Excretory system in terrestrial animals removes waste without loss of water 7. Reproduction - process by which organisms make more of their own kind a. Asexual reproduction - reproduction ...
... 6. Excretion - the removal of wastes from the body a. Diffusion can release wastes in simple aquatic animals b. Excretory system in terrestrial animals removes waste without loss of water 7. Reproduction - process by which organisms make more of their own kind a. Asexual reproduction - reproduction ...
Exercise 43
... If not done, would have 2xs the number each time it divided Homologous Chromosomes: chromosomes found on both egg and sperm that carry genes for the same traits Zygote: the fertilized egg formed with the egg and sperm fuse Divides to produce the number of cells needed to make up a human 2n (Diploid) ...
... If not done, would have 2xs the number each time it divided Homologous Chromosomes: chromosomes found on both egg and sperm that carry genes for the same traits Zygote: the fertilized egg formed with the egg and sperm fuse Divides to produce the number of cells needed to make up a human 2n (Diploid) ...
Final Review - Iowa State University
... and separates the mother cell into 2 daughter cells 45) Draw a Punnett squire for a heterozygote male crossed with a heterozygote female ...
... and separates the mother cell into 2 daughter cells 45) Draw a Punnett squire for a heterozygote male crossed with a heterozygote female ...
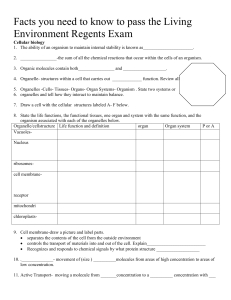
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 44.Gene splicingexample: moving a human insulin-producing gene into a bacterial cell, the bacterium, and all of its offspring- will produce human insulin. This provides a way to produce large quantities of a hormone at low cost. 45._________ is a group of closely related organisms that share certain ...
... 44.Gene splicingexample: moving a human insulin-producing gene into a bacterial cell, the bacterium, and all of its offspring- will produce human insulin. This provides a way to produce large quantities of a hormone at low cost. 45._________ is a group of closely related organisms that share certain ...
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
... 6. Compare the DNA of an offspring to the DNA of its parents. ...
... 6. Compare the DNA of an offspring to the DNA of its parents. ...
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Key Concept Builder LESSON 1 Key Concept
... 6. Compare the DNA of an offspring to the DNA of its parents. ...
... 6. Compare the DNA of an offspring to the DNA of its parents. ...
Introduction to Animals Worksheet
... Introduction to Animals Worksheet Circle the correct response. 1. Animals are [ heterotrophs / autotrophs ] 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chrom ...
... Introduction to Animals Worksheet Circle the correct response. 1. Animals are [ heterotrophs / autotrophs ] 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chrom ...
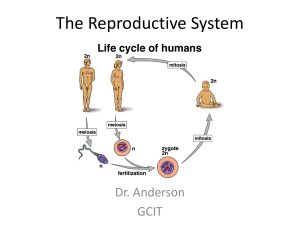
The Reproductive System
... • The brush-like fimbriae bear cilia which sweep the egg into the fallopian tube (most times) ...
... • The brush-like fimbriae bear cilia which sweep the egg into the fallopian tube (most times) ...
meiosis
... In humans, females have two X chromosomes. So, each egg contains one X chromosome. Males have both an X and a Y chromosome. So each sperm cell contains either an X or a Y chromosome. Sex-linked disorders occur in males more often than in females. Colorblindness and hemophilia are examples ...
... In humans, females have two X chromosomes. So, each egg contains one X chromosome. Males have both an X and a Y chromosome. So each sperm cell contains either an X or a Y chromosome. Sex-linked disorders occur in males more often than in females. Colorblindness and hemophilia are examples ...
1-3 Studying Life: Read pages 16-22 carefully
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.