SexDetermination_posted
... determined by the incubation temperature during a critical period of embryo development. This is known as ____________________________. ...
... determined by the incubation temperature during a critical period of embryo development. This is known as ____________________________. ...
Reproduction - Edquest Science
... parent, not by the union of two cells. One parent may produce many spores, each of which will grow into a new individual, identical to its parent. (fungi, green algae, moulds, ferns) • Vegetative Reproduction - is the reproduction of a plant not involving a seed, including; cuttings, runners, sucker ...
... parent, not by the union of two cells. One parent may produce many spores, each of which will grow into a new individual, identical to its parent. (fungi, green algae, moulds, ferns) • Vegetative Reproduction - is the reproduction of a plant not involving a seed, including; cuttings, runners, sucker ...
Sc9 - a 2.2(teacher notes)
... Male gametes = sperm cells. Female gametes = egg cell. During mating, the SPERM CELL and EGG CELL unite. This creates one entity, the ZYGOTE. The zygote is the first complete cell of the individual. Each and every cell will be then be duplicated by splitting in half: the size of each cell stays the ...
... Male gametes = sperm cells. Female gametes = egg cell. During mating, the SPERM CELL and EGG CELL unite. This creates one entity, the ZYGOTE. The zygote is the first complete cell of the individual. Each and every cell will be then be duplicated by splitting in half: the size of each cell stays the ...
Part B: Sexual Reproduction
... made up of the anther and filament. Male sex cells are produced by the anther and packaged within the pollen grains. The female parts of the flower are called the pistil. The stigma, style and ovary make up the pistil. Female sex cells are produced by the ovary and packaged within the ovules. Pollin ...
... made up of the anther and filament. Male sex cells are produced by the anther and packaged within the pollen grains. The female parts of the flower are called the pistil. The stigma, style and ovary make up the pistil. Female sex cells are produced by the ovary and packaged within the ovules. Pollin ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Focus Question
... b. Choose ONE organism or group of organisms that reproduce asexually. Describe the mode of asexual reproduction in that organism and explain the advantages to the organism of asexual reproduction. c. Choose ONE organism or group of organisms that reproduce sexually. Describe the mode of sexual repr ...
... b. Choose ONE organism or group of organisms that reproduce asexually. Describe the mode of asexual reproduction in that organism and explain the advantages to the organism of asexual reproduction. c. Choose ONE organism or group of organisms that reproduce sexually. Describe the mode of sexual repr ...
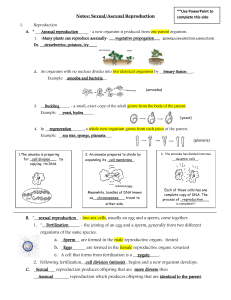
B. *__sexual reproduction_ - two sex cells, usually an egg and a
... 3. The amoeba has divided into two __daughter cells__. ...
... 3. The amoeba has divided into two __daughter cells__. ...
A-3 Notes
... Note that in each of the above kinds of organisms, they will routinely reproduce sexually in addition to asexually. Why would they do this? ...
... Note that in each of the above kinds of organisms, they will routinely reproduce sexually in addition to asexually. Why would they do this? ...
Sc9 - a 2.2(student notes)
... the parent organism produces a bud (a smaller version of itself), which eventually detaches itself from the parent and ______________________________________________ to the parent. Coral also reproduces in this way, but do not detach themselves ...
... the parent organism produces a bud (a smaller version of itself), which eventually detaches itself from the parent and ______________________________________________ to the parent. Coral also reproduces in this way, but do not detach themselves ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... produced by the division of cells on the parent, not by the union of two cells. One parent may produce many spores, each of which will grow into a new individual, identical to its parents. (fungi, green algae, molds, ferns) • Vegetative Production – is the reproduction of a plant not involving a see ...
... produced by the division of cells on the parent, not by the union of two cells. One parent may produce many spores, each of which will grow into a new individual, identical to its parents. (fungi, green algae, molds, ferns) • Vegetative Production – is the reproduction of a plant not involving a see ...
Reproduction - VCE
... There are three main categories for honey bees. 1. The queen lays eggs. She mates once and retains the sperm for the rest of her life. 2. Fertilized eggs become sterile female workers. 3. Unfertilized eggs develop into male drones via parthenogenesis. ...
... There are three main categories for honey bees. 1. The queen lays eggs. She mates once and retains the sperm for the rest of her life. 2. Fertilized eggs become sterile female workers. 3. Unfertilized eggs develop into male drones via parthenogenesis. ...
No Slide Title
... • The examples we have seen so far were genes on autosomes, so it didn’t matter which parent was mother or father • Many organisms are “monoecious” - an individual can produce both male and female gametes • Others (including humans, birds, fruit-flies) are “dioecious” so individuals are either male ...
... • The examples we have seen so far were genes on autosomes, so it didn’t matter which parent was mother or father • Many organisms are “monoecious” - an individual can produce both male and female gametes • Others (including humans, birds, fruit-flies) are “dioecious” so individuals are either male ...
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction. • We will also talk about the reproductive systems of males and females and fertilization and development of humans. • Then we will talk about heredity and how our genes are expressed to make us who we are. ...
... gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction. • We will also talk about the reproductive systems of males and females and fertilization and development of humans. • Then we will talk about heredity and how our genes are expressed to make us who we are. ...
8.2. Reproduction is a characteristic of living systems and it is
... organism contains the number of chromosomes that are typical for that species. For example, cells in human beings contain 23 pairs of chromosomes; 46 in all. 4. Organisms grow by increasing the number of body cells. During mitosis, a body cell first duplicates the chromosomes and then divides into t ...
... organism contains the number of chromosomes that are typical for that species. For example, cells in human beings contain 23 pairs of chromosomes; 46 in all. 4. Organisms grow by increasing the number of body cells. During mitosis, a body cell first duplicates the chromosomes and then divides into t ...
19_Sex - life.illinois.edu
... Two features that distinguish sexual from asexual reproduction: meiosis and syngamy ...
... Two features that distinguish sexual from asexual reproduction: meiosis and syngamy ...
Sexual Reproduction
... • Usually involves two individuals • In humans and mammals, it involves a male and female. Also occurs in other species, like plants and coral, that are not necessarily male or female • Sexual reproduction in plants or animals is the union of two sex cells, also called gametes to produce a new indiv ...
... • Usually involves two individuals • In humans and mammals, it involves a male and female. Also occurs in other species, like plants and coral, that are not necessarily male or female • Sexual reproduction in plants or animals is the union of two sex cells, also called gametes to produce a new indiv ...
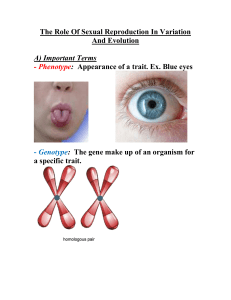
The Role Of Sexual Reproduction In Variation And Evolution
... that when two meiotic cells are joined, the # of chromosomes is a full and complete (diploid). Produces four daughter haploid cells (23 chromosomes). Example: producing haploid eggs and haploid sperm cells. IT OCCURS ONLY IN THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. ...
... that when two meiotic cells are joined, the # of chromosomes is a full and complete (diploid). Produces four daughter haploid cells (23 chromosomes). Example: producing haploid eggs and haploid sperm cells. IT OCCURS ONLY IN THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... Sponges reproduce by both asexual and sexual means. Most poriferans that reproduce by sexual means are hermaphroditic and produce eggs and sperm at different times. ...
... Sponges reproduce by both asexual and sexual means. Most poriferans that reproduce by sexual means are hermaphroditic and produce eggs and sperm at different times. ...
Reproduction
... Sexual- involves the fusion of two special cells called gametes, sperm and eggs, one from each type of gender. Asexual- reproducing without the interaction of two sexes or genders. ...
... Sexual- involves the fusion of two special cells called gametes, sperm and eggs, one from each type of gender. Asexual- reproducing without the interaction of two sexes or genders. ...
Worksheet for grade 12 biology REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
... 6. Juvenile Phase: It is the period of growth before maturity when sex organs are not functional. 7. Meiocytes: These are specialized cells of diploid organisms which undergo meiosis. 8. Pericarp: It is the protective covering of fruit, may be divided into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Parthenogen ...
... 6. Juvenile Phase: It is the period of growth before maturity when sex organs are not functional. 7. Meiocytes: These are specialized cells of diploid organisms which undergo meiosis. 8. Pericarp: It is the protective covering of fruit, may be divided into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Parthenogen ...
What is meiosis? - Perry Local Schools
... Sex Chromosomes directly control the development of sexual characteristics. Females have 2 X chromosomes and males have an X and Y chromosome. The 23rd chromosome in humans. X chromosome contains more genes than the Y because it is larger. Not all these genes relate to sexual characterist ...
... Sex Chromosomes directly control the development of sexual characteristics. Females have 2 X chromosomes and males have an X and Y chromosome. The 23rd chromosome in humans. X chromosome contains more genes than the Y because it is larger. Not all these genes relate to sexual characterist ...
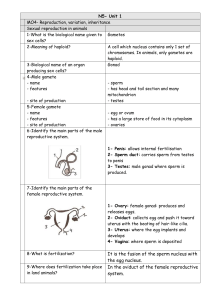
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
... MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual reproduction in animals 1-What is the biological name given to Gametes sex cells? 2-Meaning of haploid? A cell which nucleus contains only 1 set of chromosomes. In animals, only gametes are haploid. 3-Biological name of an organ Gonad producing sex ce ...
... MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual reproduction in animals 1-What is the biological name given to Gametes sex cells? 2-Meaning of haploid? A cell which nucleus contains only 1 set of chromosomes. In animals, only gametes are haploid. 3-Biological name of an organ Gonad producing sex ce ...
sexual reproduction
... - a ZYGOTE is first formed when the male a and female sex cells unite - the zygote then divides in two and the divisions repeated during a process called CLEAVAGE -the continued cell divisions result in an EMBRYO being formed -the new organism will show characteristics of both parents ...
... - a ZYGOTE is first formed when the male a and female sex cells unite - the zygote then divides in two and the divisions repeated during a process called CLEAVAGE -the continued cell divisions result in an EMBRYO being formed -the new organism will show characteristics of both parents ...
Methods of Sexual Reproduction
... Examples organisms: some aquatic animals such as sharks and most land animals. Humans reproduce this way!! ...
... Examples organisms: some aquatic animals such as sharks and most land animals. Humans reproduce this way!! ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.