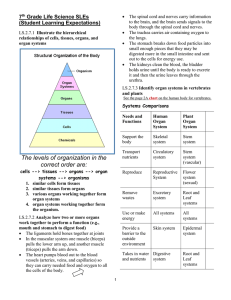
Cells and Reproduction 1
... When a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a suitable flower it begins to grow a pollen tube. Once this pollen tube reaches the ovary the male sex cell is released from the pollen grain and travels down the tube towards an ovule. Fertilisation takes place when the male sex cell reaches the female se ...
... When a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a suitable flower it begins to grow a pollen tube. Once this pollen tube reaches the ovary the male sex cell is released from the pollen grain and travels down the tube towards an ovule. Fertilisation takes place when the male sex cell reaches the female se ...
Sexual Reproduction
... Essential Question: What is sexual reproduction? What is internal and external fertilization? Sexual Reproduction- involves two partners and results in offspring that have some genetic material (DNA) from each parent. The result is an organism that may be similar to one or both parents, but is not ...
... Essential Question: What is sexual reproduction? What is internal and external fertilization? Sexual Reproduction- involves two partners and results in offspring that have some genetic material (DNA) from each parent. The result is an organism that may be similar to one or both parents, but is not ...
- Academy Test Bank
... 28. The process by which the fetus gestates in an environment external to the mother is called: A. exogestational birth B. assisted gestation C. ectopic birth D. ectogenesis 29. Some key concerns regarding in vitro fertilization procedures include all of the following EXCEPT: A. there is a greater r ...
... 28. The process by which the fetus gestates in an environment external to the mother is called: A. exogestational birth B. assisted gestation C. ectopic birth D. ectogenesis 29. Some key concerns regarding in vitro fertilization procedures include all of the following EXCEPT: A. there is a greater r ...
Regents Review
... molecules are decaying plants and animals accumulate. • Water cycle- water continually moves from earths surface to the atmosphere and back. • Flow of energy in an ecosystem is presented by food chains, food webs and energy pyramids • Carrying capacity- number of individuals of a species the environ ...
... molecules are decaying plants and animals accumulate. • Water cycle- water continually moves from earths surface to the atmosphere and back. • Flow of energy in an ecosystem is presented by food chains, food webs and energy pyramids • Carrying capacity- number of individuals of a species the environ ...
Study questions - test 2 Excretory systems ch.42 Digestion ch.43
... dimorphism. (precisely) 42)how does sexual dimorphism relate to the idea that “sperm are cheap”? 43)what are some of the problems with sexual reproduction? 44)what is sequential hermaphroditism? examples? 45) what are some of the differences in internal and external fertilization? 46)know a little b ...
... dimorphism. (precisely) 42)how does sexual dimorphism relate to the idea that “sperm are cheap”? 43)what are some of the problems with sexual reproduction? 44)what is sequential hermaphroditism? examples? 45) what are some of the differences in internal and external fertilization? 46)know a little b ...
Human Reproduction
... with a female sex cell, called an egg, during a process called fertilization (fur-tuh-lih-ZAY-shun). These sex cells contained half of the normal amount of information in a human body cell, so that when they combined, the full amount of information was present in the offspring. The new cell formed b ...
... with a female sex cell, called an egg, during a process called fertilization (fur-tuh-lih-ZAY-shun). These sex cells contained half of the normal amount of information in a human body cell, so that when they combined, the full amount of information was present in the offspring. The new cell formed b ...
Meiosis I
... •A.K.A. Gametes •Examples: human egg and sperm cells •Function is to fertilize •Used to carry out sexual reproduction 23 chromosomes each •Have _____ MEIOSIS Created by the process of __________ ...
... •A.K.A. Gametes •Examples: human egg and sperm cells •Function is to fertilize •Used to carry out sexual reproduction 23 chromosomes each •Have _____ MEIOSIS Created by the process of __________ ...
grade 7 natural science term one: life and living contents topic 1
... allow them to move quickly and close to the ground while others, like snakes, have no limbs and slither in an S-shape. Reptiles are covered in scales and reproduce by laying ...
... allow them to move quickly and close to the ground while others, like snakes, have no limbs and slither in an S-shape. Reptiles are covered in scales and reproduce by laying ...
The Human Body: The Reproductive System
... Meiosis is cell division that occurs in reproductive cells; gametes. ...
... Meiosis is cell division that occurs in reproductive cells; gametes. ...
The Reproductive System
... Meiosis is cell division that occurs in reproductive cells; gametes. ...
... Meiosis is cell division that occurs in reproductive cells; gametes. ...
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
... Meiosis is a complex process by which gametes form; involves duplication and division of reproductive cells and their chromosomes. The number of chromosomes in cells divide into two’s, and each set of cell will receive 1 from each sets of chromosomes makes up 23 sets. This type of cell divis ...
... Meiosis is a complex process by which gametes form; involves duplication and division of reproductive cells and their chromosomes. The number of chromosomes in cells divide into two’s, and each set of cell will receive 1 from each sets of chromosomes makes up 23 sets. This type of cell divis ...
Topic 17: Reproduction
... enzymes from its head to digest a way into the egg The sperm leaves the tail outside then the nucleus of the sperm and that of ovum fuse together to form the zygote Once a sperm has succeeded in penetrating the egg , a fertilization membrane is formed quickly to prevent any other sperm enter the ovu ...
... enzymes from its head to digest a way into the egg The sperm leaves the tail outside then the nucleus of the sperm and that of ovum fuse together to form the zygote Once a sperm has succeeded in penetrating the egg , a fertilization membrane is formed quickly to prevent any other sperm enter the ovu ...
ANSWERS on Inheritance File
... 1. breed / “Peaches and Cream” / eq; 2. named good feature of other variety / larger seeds / more seeds / more yellow / more white / sweeter / eq; 3. collect seeds / seeds produced / eq; 4. grow seeds / eq; 5. test new sweet corn / eq; 6. continue process / repeat / further selective breeding / eq ; ...
... 1. breed / “Peaches and Cream” / eq; 2. named good feature of other variety / larger seeds / more seeds / more yellow / more white / sweeter / eq; 3. collect seeds / seeds produced / eq; 4. grow seeds / eq; 5. test new sweet corn / eq; 6. continue process / repeat / further selective breeding / eq ; ...
Document
... pollen in place style: tube between the stigma and ovary through which the pollen tube must grow to deliver the sperm to the egg (ovule) ovary: organ where the ovules (eggs) are produced; will become the fruit of the plant ovule (egg): the female reproductive cell; will become the seed ...
... pollen in place style: tube between the stigma and ovary through which the pollen tube must grow to deliver the sperm to the egg (ovule) ovary: organ where the ovules (eggs) are produced; will become the fruit of the plant ovule (egg): the female reproductive cell; will become the seed ...
AP Exam Additional Content Information
... - Seminal Vesicles – dump fluid into vas deferens to send with sperm, which helps sperm in many ways (adds energy, power, help with swimming) Female Anatomy: - Ovary: site of egg production; eggs move from here through the fallopian tube (oviduct) to the uterus, which is where a fertilized egg attac ...
... - Seminal Vesicles – dump fluid into vas deferens to send with sperm, which helps sperm in many ways (adds energy, power, help with swimming) Female Anatomy: - Ovary: site of egg production; eggs move from here through the fallopian tube (oviduct) to the uterus, which is where a fertilized egg attac ...
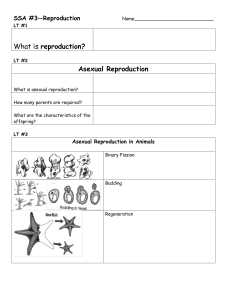
What is reproduction? Asexual Reproduction
... Grasshopper body cells have 24 chromosomes. 39. How many chromosomes in a grasshopper’s sex cell?______________ 40. How many chromosomes in a grasshopper’s fertilized egg? __________ 41. In a grasshopper leg cell? ____________ Decide if the statement is a asexual or sexual reproduction based on the ...
... Grasshopper body cells have 24 chromosomes. 39. How many chromosomes in a grasshopper’s sex cell?______________ 40. How many chromosomes in a grasshopper’s fertilized egg? __________ 41. In a grasshopper leg cell? ____________ Decide if the statement is a asexual or sexual reproduction based on the ...
Chapter 31
... • budding occurs where part of the parent’s body becomes separated from the rest and differentiates into a new individual. ...
... • budding occurs where part of the parent’s body becomes separated from the rest and differentiates into a new individual. ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitA2 - JA Williams High School
... A2.1 distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction, and identify and interpret examples of asexual and sexual reproduction in different species, by: ● describing mechanisms of asexual reproduction including binary fission, budding and the production of spores ● describing mechanisms of se ...
... A2.1 distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction, and identify and interpret examples of asexual and sexual reproduction in different species, by: ● describing mechanisms of asexual reproduction including binary fission, budding and the production of spores ● describing mechanisms of se ...
Reproduction: Asexual vs. Sexual
... energy. The fertilized egg Less complex and more reliable. (zygote) can sometimes survive in adverse conditions (drought). ...
... energy. The fertilized egg Less complex and more reliable. (zygote) can sometimes survive in adverse conditions (drought). ...
Human Reproduction
... contained half of the normal amount of information in a human body cell, so that when they combined, the full amount of information was present in the offspring. The new cell formed by fertilization, called a zygote (ZYEgoat), contained all of the information needed to grow into you—a complex organi ...
... contained half of the normal amount of information in a human body cell, so that when they combined, the full amount of information was present in the offspring. The new cell formed by fertilization, called a zygote (ZYEgoat), contained all of the information needed to grow into you—a complex organi ...
Bigsby - Bio S - 5 - Reproduction and Development
... The morula contains small cells tightly packed together. These cells continue to divide, but at this point, different genes get switched on and off. This leads to secretion of fluids and formation of a hollow space in the midst of the cell mass. Eventually, a hollow ball of around five hundred to t ...
... The morula contains small cells tightly packed together. These cells continue to divide, but at this point, different genes get switched on and off. This leads to secretion of fluids and formation of a hollow space in the midst of the cell mass. Eventually, a hollow ball of around five hundred to t ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.