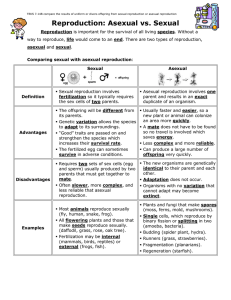
Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction
... Organisms have to grow and develop until they are old enough to produce sex cells Search and find a mate Searching can expose individuals to predators, diseases, or harsh environmental conditions Fertilization cannot take place during pregnancy, which can last as long as 2 years for some mammals ...
... Organisms have to grow and develop until they are old enough to produce sex cells Search and find a mate Searching can expose individuals to predators, diseases, or harsh environmental conditions Fertilization cannot take place during pregnancy, which can last as long as 2 years for some mammals ...
Notes Sexual - Weiss World of Science
... In internal fertilization, sperm and egg join _________ parents, embryo is nourished inside _________ Advantages: Embryo ___________ from predators Offspring more likely to survive, as many species will _________ them while they mature Disadvantages: Much more __________ required to find mate ______ ...
... In internal fertilization, sperm and egg join _________ parents, embryo is nourished inside _________ Advantages: Embryo ___________ from predators Offspring more likely to survive, as many species will _________ them while they mature Disadvantages: Much more __________ required to find mate ______ ...
If Humans Did Asexual Reproduction #1 Binary Fission
... Some send out: ________________________ A stem that grows _____________________________ along soil surface A runner can grow _______________________________ and become independent Ex. ____________________________________________ Some send out: ________________________ Form from base of t ...
... Some send out: ________________________ A stem that grows _____________________________ along soil surface A runner can grow _______________________________ and become independent Ex. ____________________________________________ Some send out: ________________________ Form from base of t ...
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... Types of organisms that reproduce asexually include: 1. Prokaryotic organisms, like bacteria. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission, where they grow and divide in half ( Figure 1.1). First, their chromosome replicates and the cell enlarges. The cell then divides into two cells as new membranes f ...
... Types of organisms that reproduce asexually include: 1. Prokaryotic organisms, like bacteria. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission, where they grow and divide in half ( Figure 1.1). First, their chromosome replicates and the cell enlarges. The cell then divides into two cells as new membranes f ...
Bell Work: 4/8/13
... A)delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells B)carrying carbon dioxide away from cells C)removing solid waste from the body D)pumping blood throughout the body ...
... A)delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells B)carrying carbon dioxide away from cells C)removing solid waste from the body D)pumping blood throughout the body ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 44.Gene splicingexample: moving a human insulin-producing gene into a bacterial cell, the bacterium, and all of its offspring- will produce human insulin. This provides a way to produce large quantities of a hormone at low cost. 45._________ is a group of closely related organisms that share certain ...
... 44.Gene splicingexample: moving a human insulin-producing gene into a bacterial cell, the bacterium, and all of its offspring- will produce human insulin. This provides a way to produce large quantities of a hormone at low cost. 45._________ is a group of closely related organisms that share certain ...
Reproduction
... Fertilization in Animals Two major patterns of fertilization: • External fertilization – Eggs are shed by the female and fertilized by the male in the environment ...
... Fertilization in Animals Two major patterns of fertilization: • External fertilization – Eggs are shed by the female and fertilized by the male in the environment ...
Science 9 Topic 3 Passing It On
... – Asexual reproduction can occur in plants by activating merstematic cells in different plant structures. – You can then take cuttings from the plants and plant it. – Offspring are clones (exact copies) of parents. ...
... – Asexual reproduction can occur in plants by activating merstematic cells in different plant structures. – You can then take cuttings from the plants and plant it. – Offspring are clones (exact copies) of parents. ...
Mitosis/ Meiosis – Asexual/ Sexual Reproduction
... Metaphase – chromosomes meet in the middle of cell Anaphase – sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of cell Telophase – two nuclear membranes form around each group of chromosomes, cytokinesis begins 6. Interphase 7. Interphase 8. diploid 9. diploid 10. two 11. identical to the parent ...
... Metaphase – chromosomes meet in the middle of cell Anaphase – sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of cell Telophase – two nuclear membranes form around each group of chromosomes, cytokinesis begins 6. Interphase 7. Interphase 8. diploid 9. diploid 10. two 11. identical to the parent ...
POLYGENIC INHERITANCE The term “polygenic inheritance” is
... In animal lifecycles, asexual reproduction sometimes alternates with sexual reproduction. ...
... In animal lifecycles, asexual reproduction sometimes alternates with sexual reproduction. ...
Study Guide 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of
... Disadvantage: Slow Reproduction and 2 parents are needed (male and female) ...
... Disadvantage: Slow Reproduction and 2 parents are needed (male and female) ...
Animal Body Systems
... Reproductive Strategies Asexual Reproduction-reproduction that does not ...
... Reproductive Strategies Asexual Reproduction-reproduction that does not ...
Reproduction of Organisms
... homologous chromosomes pairs of chromosomes—one inherited from each parent—that have genes for the same traits arranged in the same order meiosis process in which one diploid cell divides to make haploid sex cells sexual reproduction production of offspring f ...
... homologous chromosomes pairs of chromosomes—one inherited from each parent—that have genes for the same traits arranged in the same order meiosis process in which one diploid cell divides to make haploid sex cells sexual reproduction production of offspring f ...
Asexual Reproduction Content Practice B LESSON 2
... statement is false, change the underlined word(s) to make it true. Write your changes on the lines provided. ...
... statement is false, change the underlined word(s) to make it true. Write your changes on the lines provided. ...
2 N - Malibu High School
... Formation of new individual by a combination of two haploid sex cells (gametes). Fertilization- combination of genetic information from two separate cells that have one half the original genetic information Gametes for fertilization usually come from separate parents Female- produces an egg Male ...
... Formation of new individual by a combination of two haploid sex cells (gametes). Fertilization- combination of genetic information from two separate cells that have one half the original genetic information Gametes for fertilization usually come from separate parents Female- produces an egg Male ...
Animal Reproduction
... reproductive systems. The uterus is partly or completely divided into two chambers in most vertebrates. Humans & other mammals with few young, birds & snakes have a single structure. ...
... reproductive systems. The uterus is partly or completely divided into two chambers in most vertebrates. Humans & other mammals with few young, birds & snakes have a single structure. ...
ASEXUALREPRODUCTIONSMR
... Some organisms reproduce asexually During asexual reproduction all genetic information comes from a single a single parent Organisms that result from asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent ...
... Some organisms reproduce asexually During asexual reproduction all genetic information comes from a single a single parent Organisms that result from asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent ...
Chapter 23
... • Represented by: n • The gametes contain half the number of chromosomes • Remember, gametes are sex cells that combine to form new offspring. Therefore gametes are haploid and once they fuse (combine), they form a zygote that is diploid ...
... • Represented by: n • The gametes contain half the number of chromosomes • Remember, gametes are sex cells that combine to form new offspring. Therefore gametes are haploid and once they fuse (combine), they form a zygote that is diploid ...
REPRODUCTION Part 1
... embryo is an early stage in the development of an organism. In this process, the same DNA is copied in each cell. ...
... embryo is an early stage in the development of an organism. In this process, the same DNA is copied in each cell. ...
Reproduction: Asexual vs
... Most animals reproduce sexually (fly, human, snake, frog). All flowering plants and those that make seeds reproduce sexually. (daffodil, grass, rose, oak tree). Fertilization may be internal (mammals, birds, reptiles) or external (frogs, fish). ...
... Most animals reproduce sexually (fly, human, snake, frog). All flowering plants and those that make seeds reproduce sexually. (daffodil, grass, rose, oak tree). Fertilization may be internal (mammals, birds, reptiles) or external (frogs, fish). ...
Basics of biology part 2 - Jocha
... c) What animal will lose more heat to the environment, a small one or a big one? d) What animal will have a harder time floating in the water, a small one or a big one? Modes of reproduction in living things 8. What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? 9. Which one allows for g ...
... c) What animal will lose more heat to the environment, a small one or a big one? d) What animal will have a harder time floating in the water, a small one or a big one? Modes of reproduction in living things 8. What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? 9. Which one allows for g ...
SEVENTH GRADE LIFE SCIENCES THEME: LIFE AROUND US
... 3. Cell Division and Genetics – The student will explore how traits are passed from one generation to another. a. Analyze cell division in asexual reproduction (e.g. mitosis, diploid cells). b. Analyze cell division in sexual reproduction (e.g. meiosis, haploid cells).Explain the significance of chr ...
... 3. Cell Division and Genetics – The student will explore how traits are passed from one generation to another. a. Analyze cell division in asexual reproduction (e.g. mitosis, diploid cells). b. Analyze cell division in sexual reproduction (e.g. meiosis, haploid cells).Explain the significance of chr ...
Protists
... 2. Division 1 = pairs split 3. Pairs line up and split – 4 result – 4 gametes (eggs or sperm) ...
... 2. Division 1 = pairs split 3. Pairs line up and split – 4 result – 4 gametes (eggs or sperm) ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.